Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 6 (1); March 25, 2016 [Booklet]
Research Paper
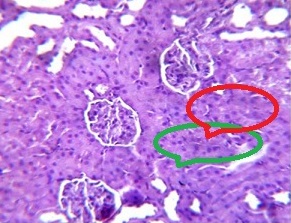
Effects of Drugs on Serum Biochemical Profile and Renal Failure in Humans and Experimental Rats: A Preliminary Report.
Al shafei NK and Nour A.
World's Vet. J. 6(1): 01-09, 2016; pii:S232245681600001-6
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/wvj.20160260
ABSTRACT
Antibiotics and cancer treatment drugs have been associated with renal failure. In developing countries, antibiotics are often obtained without prescription and this misuse increases the risk of renal failure, especially for patients which have been taking gentamicin for a long-term. For example, taking the aminoglycoside antibiotic, particularly in diabetics, without close medical supervision has been suggested to the cause kidney damage and renal failure in many patients. The objectives of this preliminary study were to investigate the association of antibiotics and renal failure in Hemodialysis (HD) patients in Egypt; and to document the changes in biochemical profiles and histopathology of the kidneys when nephrotoxicity is induced by the antibiotic gentamicin (GM) and the cancer therapeutic agent Cisplatin (Cis). Serum biochemical profiles of HD patients and rats with induced renal failure were compared. Fifty HD patients and six normal people were employed in the study. Sixty experimental rats were divided into three groups: Control, gentamicin-induced renal failure group, and cisplatin-induced renal failure group. The survey of HD patients revealed that 6% of the renal failure is antibiotics related. GM and Cis caused kidney damage and renal failure in rats. The levels of blood serum urea, creatinine, and potassium significantly increased in drug-induced renal failure rats. Serum sodium decreased in GM rats with renal failure and in HD patients compared to the control groups. The histopathological changes in renal tissues in Cis and GM induced renal failure appeared in early stage of renal dysfunction. More studies are needed to determine the correlations between biochemical markers and histopathological changes that may be used as an early warning system for assessing earlier drugs-induced stress to the kidneys before renal failure progresses.
Key words: Gentamicin, Csplatin, Drug-Induced renal failure, Hemodialysis, Serum biochemical profile
Evaluation of Using Honey, Cool Water and Levamisole against Heat Stress on Different Traits of Rabbits under Egyptian Summer Conditions.
El Saidy NR, Allam FE, Balabel TM, El-Midany SA.
World's Vet. J. 6(1): 10-18, 2016; pii:S232245681600002-6
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/wvj.20160261
ABSTRACT
This study was conducted in order to estimate the impact of using honey in drinking water, drinking cool water and Levamisole injection as alleviated tools of heat stress on White New Zealand rabbits under Egyptian summer conditions. 40 sexually mature White New Zealand rabbits contained 36 does with an average age of 15-20 (18±2) weeks and nearly similar body weight of 2 kg and 4 fertile bucks with an average age of 24 weeks and average weight of 2.5 kg were used in this experiment. They were allocated into four groups each containing 9 does and 1 buck. Group I was kept as a control without any treatment, group II received honey 20 ml/l on drinking water, group III drank cold water with a temperature ranged from 16-20 0C and group IV received a single dose of subcutaneous Levamisole injection (2 mg/kg BW). Results showed that most of performance, reproductive and physiological parameters of examined rabbits were significantly decreased by heat stress under Egyptian summer conditions. However, treated groups showed improved traits on most examined parameters comparing with control group. Among the treated groups, the one treated with honey expressed significant increase (P<0.05) in body weight, body weight gain, feed intake, feed conversion ratio, water consumption, conception rate, litter size and weight, milk yield, economic efficiency, rectal temperature, hematological parameters and some serum biochemical parameters. On the other hand, the group which received cool water showed the best records for decreased levels of serum urea, creatine and respiratory rate. In conclusion, it is clear that heat stress has negative effects on reproductive and physiological traits of growing rabbits with drawing attention toward the importance of using alleviating methods for mitigating the negative effects of heat stress especially by using honey and drinking cool water.
Key words: Heat stress, Honey, Cool water, Levamisole, Rabbit traits
Research Paper
Dog Bites and Rabies: A Decade Perspective in Nigeria (2005-2014)
Tekki SI, Odita CI, Idachaba ES, Akanbi BO, Moses DG, Barde JI, James AS, Rimfa AG, Kumbish PR, Agama C, Zhakom PN, Okewole PA
World's Vet. J. 6(1): 19-24, 2016; pii:S232245681600003-6
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/wvj.20160262
ABSTRACT
Rabies is a fatal zoonotic encephalitis caused by the rabies virus commonly transmitted to human and other mammals by dog bites. A 10 year review of dog bite cases in humans from 2005 to 2014 was undertaken from archives of the rabies laboratory, National Veterinary Research Institute (NVRI) Vom, Nigeria to assess the magnitude of dog bites and associated risks of human exposure to rabies among bite victims. Of the 1, 840 cases reported, the highest and the lowest rates of bite occurred on 2009 and 2007 respectively. Children constituted 31.5% of the victims, 36.0% were adults, while 32.5% had no age indications. Male victims formed 46.7% of the cases, 38.4% involved females while the genders of the remaining 14.9% were not given. Similarly, prevalence of rabies cases were highest and lowest in 2009 and 2007 respectively while the overall prevalence of rabies-positive dog bite cases during the decade were high (61.1%). However, rabies public campaigns by indigenous veterinary professional groups during the initial editions of the world rabies day improved the level of awareness, which possibly led to the rise in reported cases of dog bites in 2009, while the considerable drop in the cases and probably in rabies in subsequent years, could have been due to vaccination of a considerate number of the dog population. Appreciable reduction in dog bite cases and in rabies nationwide in Nigeria, are only achievable when stakeholders determine to tackle dog bites by supporting responsible ownership and annual mass vaccination of dogs and cats against rabies as well as quarantining or controlling their movements. In rural Africa, where the risk of dog bites and rabies is greatest, it is important to raise public awareness on the roles of accurate laboratory diagnosis and surveillance in the national rabies control and monitoring program.
Key words: Dog bite cases, Humans, Rabies, Nigeria
A Review Article of Artificial Insemination in Poultry.
Getachew T.
World's Vet. J. 6(1): 25-33, 2016; pii:S232245681600004-6
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/wvj.20160263
ABSTRACT
The objective of this review is to discuss the history, importance of Artificial Insemination (AI), semen collection and deposition techniques, physiology of cockerel reproduction, characteristics and chemical components of chicken semen, semen storage, and evaluation of semen, semen extenders and behavior of sperm in the oviduct. The first AI in poultry was reported in 1936. All of the avian male reproductive system is inside the bird unlike the males of mammalian species. Avian semen contains energy source to help the viability of semen for AI. For the purpose of in vitro storage semen extenders with appropriate osmolarity and source of energy can be used. Abdominal massage method is the most common technique to collect semen. The technique involves restraining the male and gently stroking the back of the bird from behind the wings towards the tail with firm rapid strokes and gentle squeeze to extract the semen. There are two methods of semen deposition in poultry. These methods are the Intra-peritoneal insemination and vaginal insemination. Vaginal insemination is the commonly used method. It involves everting (turning inside out) the cloaca to expose the reproductive tract of the female.
Key words: Artificial insemination, Extenders, Ova, Semen
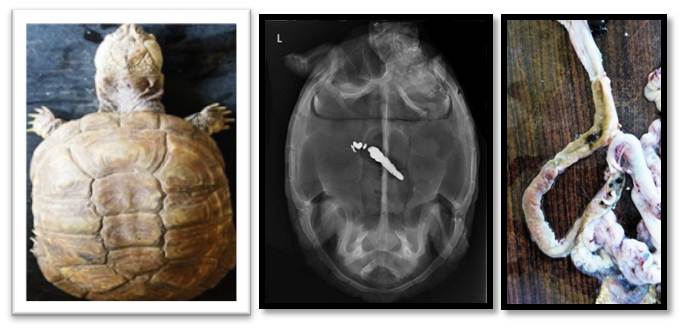
Intestinal Ulceration in West African Mud Turtle (Pelusios Castaneus).
Folayemi O-A, Zainab Omolara A, Adenike O-A, Inalegwu Godwin O, Samuel Gbadebo O.
World's Vet. J. 6(1): 34-37, 2016; pii:S232245681600005-6
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5455/wvj.20160264
ABSTRACT
An adult female West African mud turtle (Pelusios castaneus) that had been acquired as part of study on the digestive anatomy on the P. castaneus presented mild signs of anorexia that had persisted for a week. On radiographic examination of the digestive tract using Barium sulphate contrast agent, a normal study was observed but an area of contrast coating remained at the region of the duodenum following excretion of the contrast agent. The digestive tract was isolated and gross examination of the coated area revealed areas of ecchymotic hemorrhage and ulcers in this turtle. With not much scientific research available on this wildlife species, this case of a gastrointestinal tract abnormality is probably the first report of a digestive tract pathology seen in this tropical fresh water turtle.
Key words: Pelusios castaneus, Duodenum, Ecchymotic hemorrhage, Ulcer
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.