Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 2 (4); December 25, 2012
Research Paper
The Role of Rural Women in improving households Nutritional Status and Food Security through Traditional Production System in Sudan
Malik HEE, Elamin KM and Elagib HAA.
World Vet. J. 2(4): 43-48, 2012; pii:S232245681200011-2
ABSTRACT
This study was conducted to investigate the role of rural women in improving household nutritional status and food security, through raising of family poultry; case study of Eastern Nile- Sudan. The main concept of this study is that family poultry form the basis for increasing food production and income in rural communities. The questionnaire was considered to be the main measuring instrument for data collection, two hundred and fifty two households were selected through systematic sampling and interviewed (From six villages in the area under study). Face to face method was, used, where an immediate feed- back was received. The obtained data were subjected to analysis, through the statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS). The study revealed that although family poultry is carried out with the minimal agricultural, veterinary, extension, training and marketing support. But, still it positively contributes in the improvement of the household nutritional status, income and food security. The study concluded that, improvement in housing, feeding, and diseases control, coupled by institutional support in the dissemination of information, capacity building training programs in poultry husbandry practices, veterinary, extension, and financial services, will ultimately enhance better production. In addition formation of women group can facilitate access to inputs and marketing services.
Key words: Rural women, Household, Nutritional status, Traditional production system.
Research Paper
Some Productive and Reproductive Traits of Kenana × Friesian Cattle in Sudan
Elamin KM, Elebead RA, Mohammed SA and Musa AM.
World Vet. J. 2(4): 49-53, 2012; pii:S232245681200012-2
ABSTRACT
The present study was conducted to investigate the performance of 50% Friesian ×50% Kenana crossbred dairy cattle. 194 records of F1 crossbred (progeny of Kenana ×Friesian) and 48 records of F1×F1 crossbred were analyzed. Traits studied were milk yield (Kg), calving interval (days), conception rate and gestation period (days). Obtained results showed that overall least square means of traits studied were 2444±164 kg, 514±0.53 days, 1.4±0.02 and 281±1.02 days respectively. Results showed that the mode of inducing the exotic blood (kenana× Freisian or F1 ×F1), lactation number and age at first calving significantly (P≤0.05) affected milk yield, F1 cows, and cows in late lactations and young cows at first calving being superior. On the other hand, Blood groups and lactation number adversely affected calving intervals (P≤0.05). Also results showed that blood group differences, lactation number and age at first calving significantly (P≤0.05) affected the number of services per calving. Finally, blood groups, lactation numbers and age at first calving had no significant (P≤0.05) effects on gestation length. It is concluded that, performance of F1×F1 crossbred Kenana Cattle was lower than that of F1 Kenana cattle in studied traits.
Key words: Calving interval, Conception rate, Gestation, Lactation, Nile
Research Paper
Heart Girth Reflect Live Body Weight in Sudanese Shogur Sheep under Field Conditions
Musa AM, Idam NZ and Elamin KM.
World Vet. J. 2(4): 54-56, 2012; pii:S232245681200013-2
ABSTRACT
The reflections of heart girth measurement to live body weight of Sudanese Shogur sheep under field conditions have been studied. Ninety males(90) of each three age groups were randomly selected( With a total population number of 270) in herds from different native areas where the animals were reared and evaluated using live body weight(kg) and heart girth measurement(cm). Means of live body weight and heart girth for the three age groups were calculated (P≤0.05). There were positive correlation coefficients (0.54, 0.66 and 0.81) between live body weight and heart girth. A predictive indices of (W= -4.62 + 0.45(HG), W= -23.78 + 0.73(HG) and W= -55.14 + 1.17(HG)) where more than (55%, 66% and 65%) of the population falls in respectively for the three studied age groups. It was therefore conclude that heart girth measurement is a useful tool in reflecting live body weight of Sudanese Shogur sheep under field conditions.
Research Paper
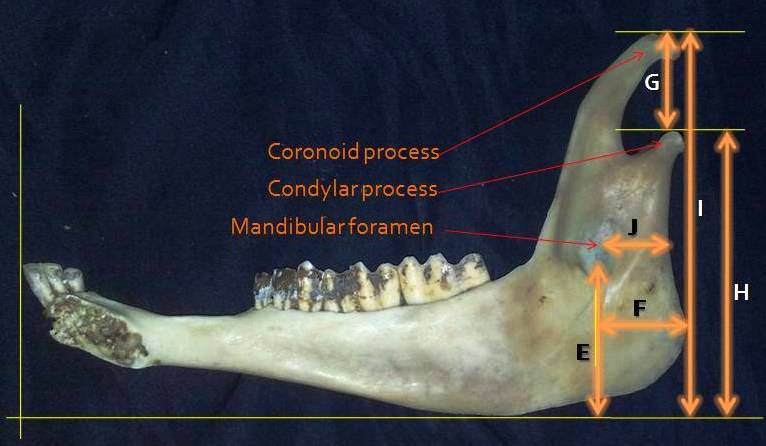
The Lower Jawbone of Mehraban Sheep: A descriptive morphometric approach
Karimi I, Hadipour Mm, Nikbakht P and Motamedi Sh.
World Vet. J. 2(4): 57-60, 2012; pii:S232245681200014-2
ABSTRACT
This study aimed to measure some clinically important landmarks useful for regional anesthesia in the mandibular regions of Mehraban sheep. The distance between the lateral ends of the alveolus of the incisor tooth to the mental foramen was 2.07±0.45 cm. The length and maximum height of the mandibles were 15.76±2.25 cm and 9.57±2.71 cm, respectively. The distance from caudal border of mandible to beneath of mandibular foramen was 1.74±0.33 cm, while the distance from the mandibular foramen to the base of the mandible and caudal border of mandible to the level of mandibular foramen were 4.14±0.47 cm and 1.35±0.29 cm, respectively and the length of diastema was measured 3.98±0.48 cm.
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.