Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 10 (1); March 25, 2020 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 10 (1); March 25, 2020 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
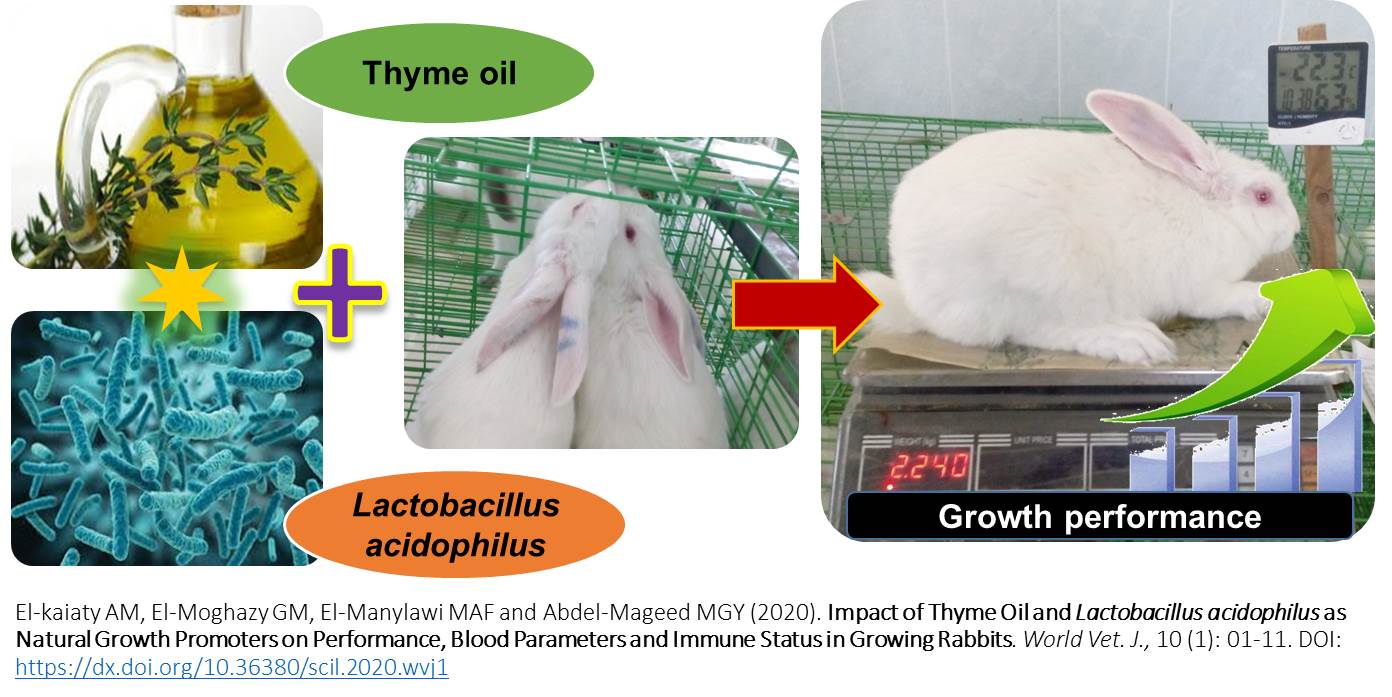
Impact of Thyme Oil and Lactobacillus acidophilus as Natural Growth Promoters on Performance, Blood Parameters and Immune Status in Growing Rabbits
El-kaiaty AM, El-Moghazy GM, El-Manylawi MAF and Abdel-Mageed MGY.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 01-11, 2020; pii:S232245682000001-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj1
ABSTRACT
Present study was conducted to evaluate the effect of thyme oil and lactobacillus acidophilus (supplement) as growth promoters in rabbit. 72 weaned V-Line male rabbits were randomly allocated into 4 equal groups. The first group (G1) was without any additives and consider as control group. The second group (G2) treated with the addition of lactobacillus acidophilus in drinking water in a concentration of 108 cfu/ml. The third group (G3) treated with the addition of thyme oil in drinking water in a concentration of 1 ml/ liter. The fourth group (G4) treated with the addition of both lactobacillus acidophilus and thyme oil in drinking water in a concentration of 108 cfu/ml plus 1ml/L, respectively. The obtained results showed that, all treatments had significant improvement effects on the measured parameters (performance characteristics, cecum characteristics, RBCs, WBCs, kidney function, trigly-cerides, total cholesterol, sheep RBC’s titer, liver antioxidant markers and hormones markers) when compared to the control group. The live body weight of G3 and G4 groups were higher (2116 and 2058 g) than those found in G2 and G1 groups (1958 and 1850 g) respectively. In addition, the body weight gain of G3 and G4 groups were higher (1364 and 1307 g) than those found in G2 and G1 groups (1207 and 1100 g). Moreover, the daily weight gain of G3 and G4 groups were higher (32.49 and 31.13 g/d) than those found in G2 and G1 groups (28.74 and 26.19 g/d). In addition, feed conversion ratio of G3 and G4 groups were higher (3.41 and 3.61) than those found in G2 and G1 groups (3.66 and 4.67). While G4, G2 and G3 groups had a significant enrichment effect on the intestinal beneficial bacteria. In conclusion, in present experiment inclusion thyme oil and/or lactobacillus acidophilus in the drinking water that stimulated body weight gain and increased feed conversion rate, and can be used as growth promoters in rabbit nutrition successfully without notable side effects on growing rabbits. Furthermore, it showed a significant positive effect on the physiology for treatment groups G3, G4 and G2 respectively compared to the control group.
Key words: Immunity, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Performance, Probiotic, Rabbit, Thyme oil
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Molecular and Phylogenic Analysis of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Nineveh province, Iraq
Jassiem Hussain Kh, AL-Farwachi MI and Dhahir Hassan S.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 12-17, 2020; pii:S232245682000002-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj2
ABSTRACT
Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV) is one of the worldwide distributed infectious agents responsible for diversified clinical disease in cattle populations which causes considerable economic loss due to its negative effects on health and production. In this study, 450 nasal swab samples were collected from cows with different ages and breeds in different areas across Nineveh province, Iraq. Molecular diagnosis using nested RT-PCR and phylogenetic analysis of the G gene were performed. The results indicated a 37.31% prevalence rate of BRSV using specific primers in the PCR technique. The local isolate was submitted in GenBank under the accession number MN129181 Mosul isolate. The phylogenetic tree of local isolates of BRSV was made using the neighbor-joining system after comparison with other GenBank data. In conclusion, phylogenetic analysis of BRSV can provide information about the viral strains present in cattle and subsequently may be useful for infection control programs.
Key words: Bovine respiratory syncytial virus, Cattle, PCR, Phylogenic analysis.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
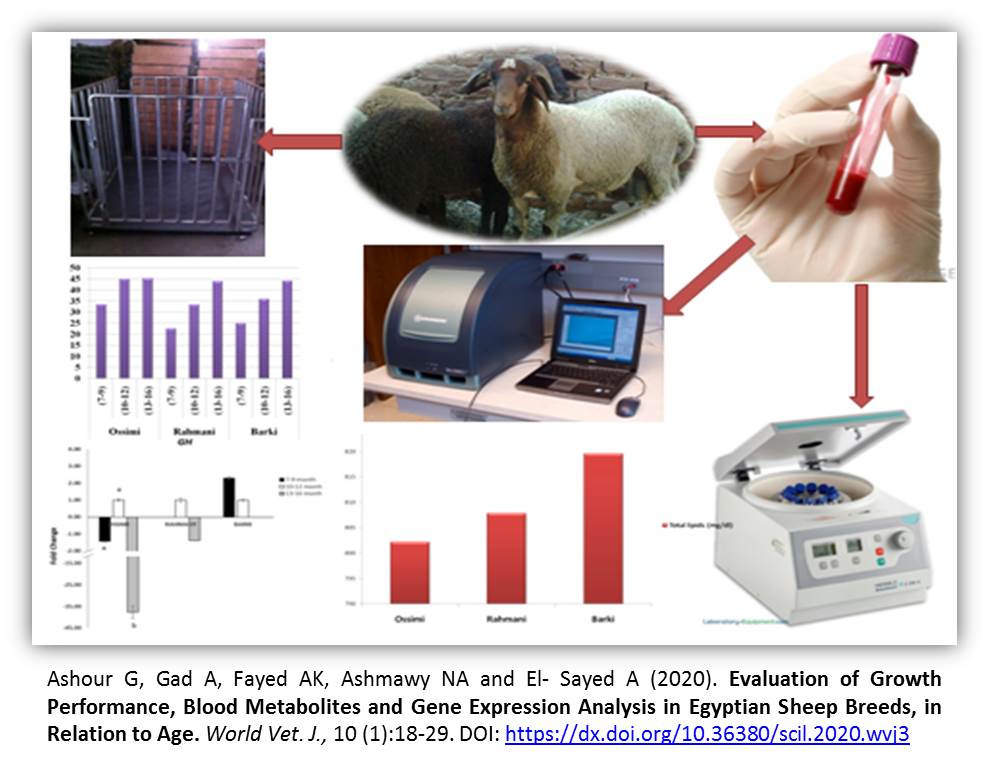
Evaluation of Growth Performance, Blood Metabolites and Gene Expression Analysis in Egyptian Sheep Breeds, in Relation to Age
Ashour G, Gad A, Fayed AK, Ashmawy NA and El- Sayed A.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 18-29, 2020; pii:S232245682000003-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj3
ABSTRACT
The growth performance of lambs attributes the economic viability of animals. Faster growth allows lambs to reach maturity in early age. Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare growth performance, blood metabolites and expression of IGF-1, GH, and Leptin genes in three different Egyptian sheep breeds across age. Thirty Egyptian sheep males from three breeds (Ossimi, Rahmani and Barki) were divided into three ages categorize (7 – 9, 10 – 12, and 13 - 16 months). The results showed that there was a significant increase in sheep’s live body weights toward advanced ages till the second age category for all breeds, the highest values of linear body measurements were observed in Ossimi breed. There was a non-significant inverse effect of advanced age on blood glucose and total lipids levels in all sheep breeds. There wasn’t any significant effect of interaction between age and breed on plasma total protein concentrations. According to age categories, Barki breed showed a significant up-regulation of GH compared to the Ossimi breed in 7-9 months age category. However, Barki breed showed a significant down-regulation of IGF-1compared to the Ossimi breed in 7-9 months. Meanwhile, Leptin expression showed significant differences in Ossimi breed between 10-12 months age category and two other age categories. We concluded that measuring of physical body measurements, blood metabolites and GH, IGF-1 and Leptin genes in early ages is a good and accurate indicator for growth performance in Egyptian sheep breeds.
Key words: Blood metabolites, Egyptian breeds, Gene expression, Growth performance, Linear body measurements
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
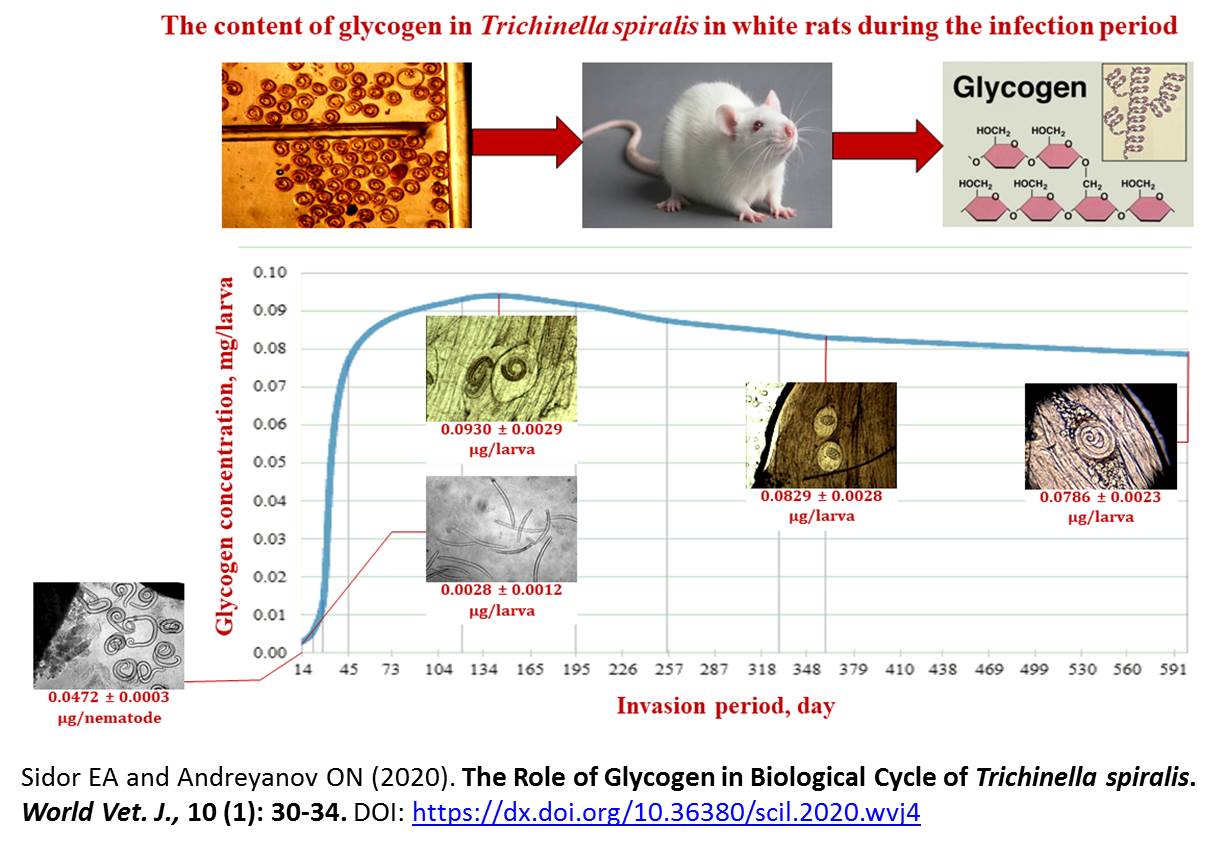
The Role of Glycogen in Biological Cycle of Trichinella spiralis.
Sidor EA and Andreyanov ON.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 30-34, 2020; pii:S232245682000004-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj4
ABSTRACT
The energy sources of Trichinella spiralis change in both the muscular and intestinal stages of its life in the host organism. The purpose of this study was to investigate the quantitative changes in glycogen concentration during the life cycle of T. spiralis in a host organism. Trichinella spiralis was passaged on laboratory rodents under the vivarium conditions. Sixty-nine white rats (350 g each) were infected with T. spiralis at a dose of 5 muscle larvae/gram of body weight. The animals were euthanized at different time periods from the start of the experiment. Trichinella muscle larvae were isolated by artificial fermenting meat mince in gastric juice. To determine the viability of Trichinella larvae, they were heated to 38 ± 2 ° C for 10 minutes their motor activity was investigated. (38 ± 2 °C). To determine the invasive properties of T. spiralis at different stages of its development in rats, the muscular larvae isolated from the rat muscles were used to infect laboratory mice. The invasive capacity of T. spiralis was assessed on day 45 post-infection. For the study of intestinal Trichinella larvae, laboratory rats were not fed a day before infection. Adult nematodes were isolated from the small intestine of laboratory rats at 3, 6 and 24 hours post-infection. The nematodes were counted in the Migacheva-Kotelnikov chamber in each individual sample. The concentration of glycogen in the nematodes was calculated according to the quantitative method for determining glycogen in Trichinella larvae. Low glycogen levels in the muscle larvae were observed on day 14 post-infection. The glycogen concentration in muscular larva was 0.0054 ± 0.0027 μg/ larva on day 21, 0.0136 ± 0.0024 μg/ larva on day 28, and 0.0771 ± 0.0025 μg/ larva on day 45 after the rats were infected. Maximum concentration of glycogen was recorded 4 months post-infection (0.0930 ± 0.0029 μg/larva). Further, the glycogen level began to decrease slowly. In the 20th month post-infection, after infection, the amount of glycogen in a Trichinella larva was 0.0786 ± 0.0023 μg. In the body of intestinal nematodes, 3 hours after infecting the animals, the glycogen concentration was reduced to 0.0472 ± 0.0003 μg in one nematode. The same time period later, it reached to value of 0.0272 ± 0.0002 μg. In intestinal T. spiralis, which remained in the small intestine of rats for 24 hours, the glycogen was not detected. The amount of glycogen at the muscle stage of T. spiralis development was extremely important in the first hours of the helminth’s residing in the host's intestines. Energy requirements during the period when the helminth cannot obtain enough food depend on the glycogen content. When the glycogen concentration in the parasite is insufficient, the Trichinella larvae will lose their invasion capacity.
Key words: Bioassay test; Glycogen; Nematode; Parasitic helminth, Trichinella spiralis
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
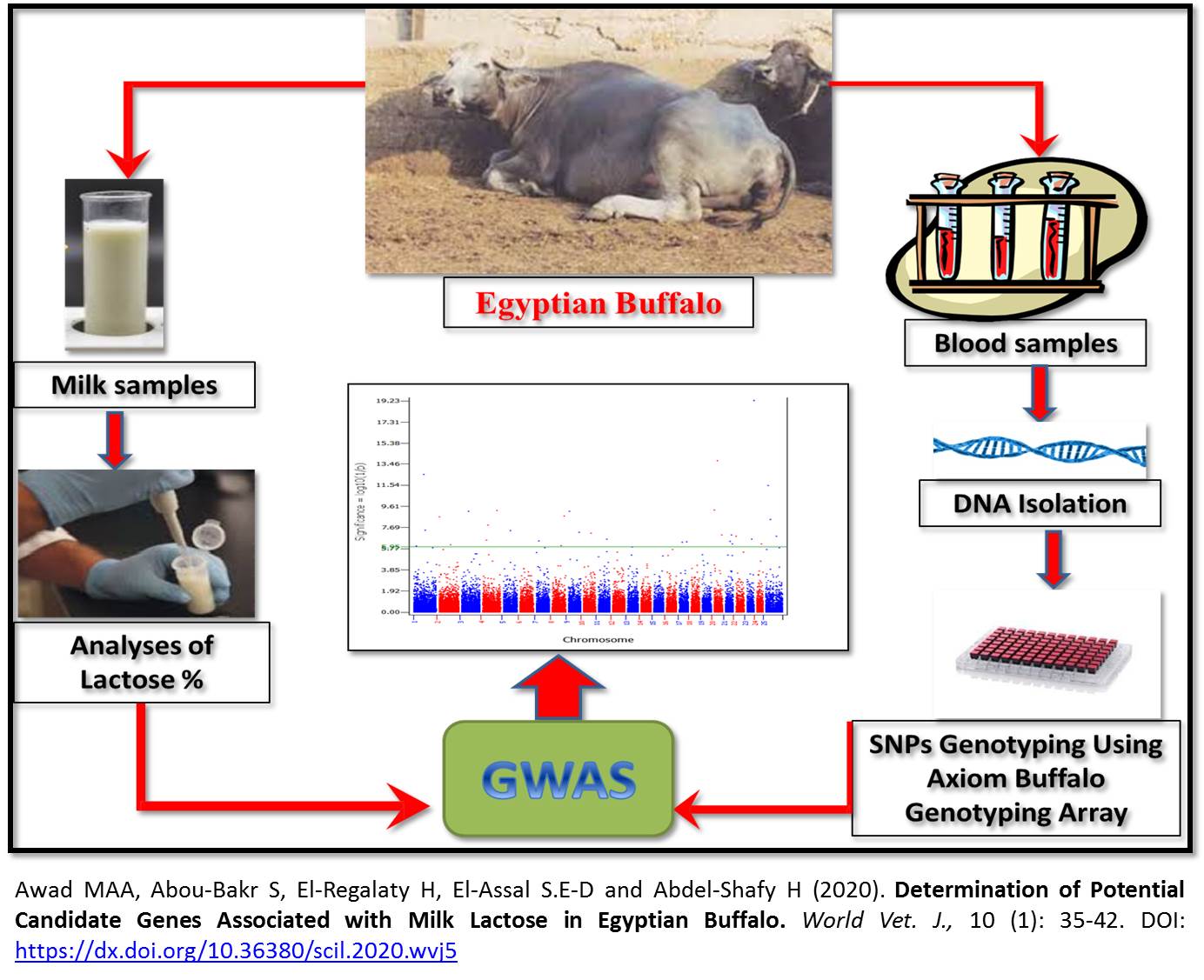
Determination of Potential Candidate Genes Associated with Milk Lactose in Egyptian Buffalo
Awad MAA, Abou-Bakr S, El-Regalaty H, El-Assal S.E-D and Abdel-Shafy H.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 35-42, 2020; pii:S232245682000005-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj5
ABSTRACT
The aim of the present genome-wide association study (GWAS) was to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and candidate genes associated with lactose percentage (LP) and lactose yield (LY) in Egyptian buffalo. The phenotypic dataset included 60,318 monthly measures for LP and LY from 1481 animals. A total number of 114 animals with high and low deviated performance were selected for genotyping with Axiom Buffalo Genotyping 90K Array. Genome-wide analysis was performed using a single marker regression. The GWAS revealed 32 significant and seven suggestive SNPs for LP, however; only two suggestive SNPs were identified for LY. The identified genomic regions are overlapped with previously reported QTL in different cattle breeds. In addition, novel genomic loci were detected. The identified genomic regions harbored many candidate genes with biological roles associated with milk production traits, such as TPD52 and ZBTB10 on chromosome 15; AADAT and GALNTL6 on chromosome 3 and COL8A1 and PLOD2 on chromosome 1. Our findings provide the basis to uncover the key markers and candidate genes affecting lactose traits which facilitate the exploration of the genetic mechanisms that control lactose traits variation in Egyptian buffalo.
Key words: Candidate gene, Egyptian buffalo, Genome, Genomic loci, Lactose
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
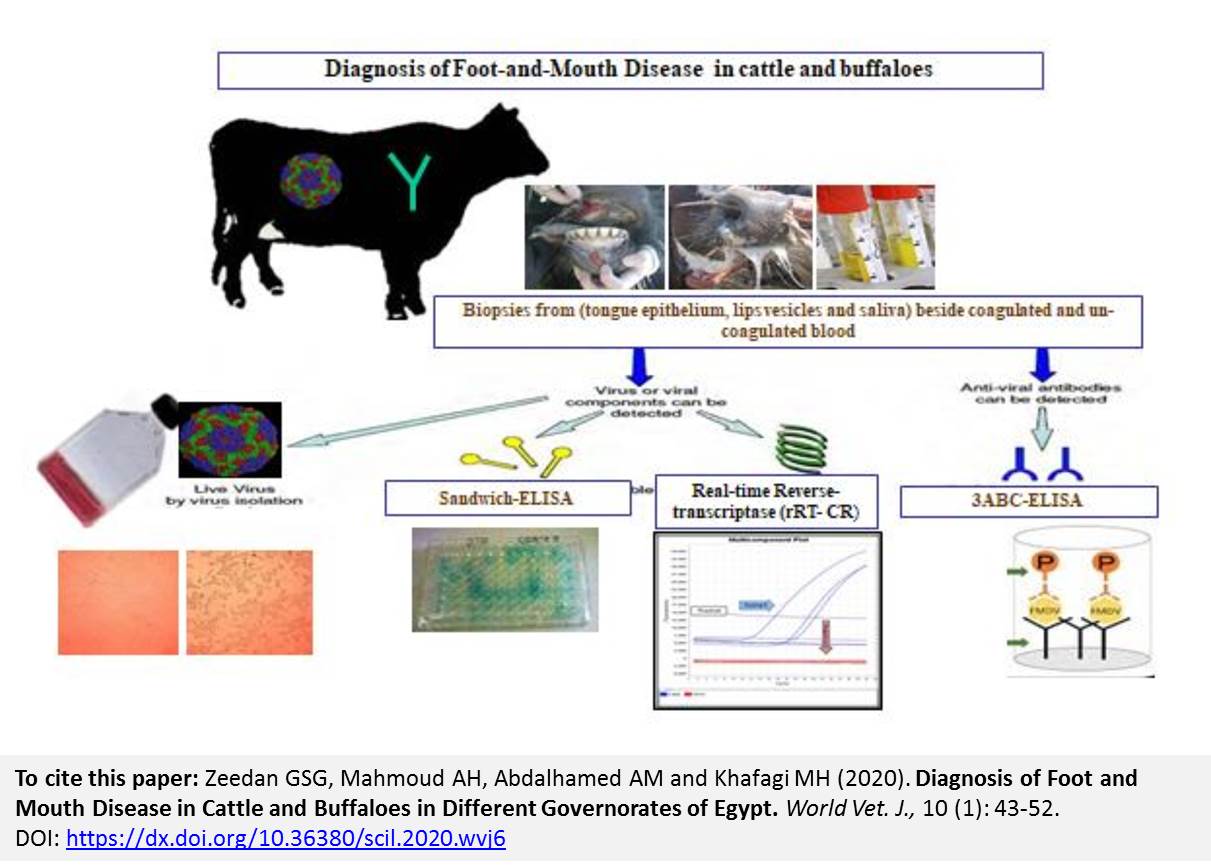
Diagnosis of Foot and Mouth Disease in Cattle and Buffaloes in Different Governorates of Egypt
Zeedan GSG, Mahmoud AH, Abdalhamed AM and Khafagi MH.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 43-52, 2020; pii:S232245682000006-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj6
ABSTRACT
Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) is highly contagious disease affected cloven-hoofed animals which result in substantial economic losses. The present study was aimed to detect FMDV by different serological and molecular methods in cattle and buffaloes for providing an accurate and rapid diagnosis of FMD disease. 86 samples of tongue epithelium biopsies, fluid vesicles samples and saliva, as well as 86 coagulated and uncoagulated blood samples, were collected from 64 and 22 suspected cattle and buffaloes respectively in different governorates in Egypt, during August to December 2017. Serum samples were examined by 3ABC-ELISA for differentiating between infected and non-infected animals. While tissues biopsies and un-coagulated blood samples were examined by Sandwich ELISA, Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) as well as Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (rRT-PCR). FMDV porotypes were identified by rRT-PCR in suspected cattle and buffaloes samples to FMDV serotype A, O and SAT2 and results showed that 54 samples positive for FMDV different serotypes while FMDV serotype differentiation in tissues biopsy of cattle were 18 (28.12%), 12 (18.75%), 3 (4.68 %) and 4 (6.25%). Also, the positive results of tissue samples from buffaloes examined by RT-PCR were 9 (40.09 %), 4 (6.25%), 2 (9.09 %) and 2 (9.09 %) for O, SAT2, serotype A and mixed serotypes respectively by different tests. The rRT-PCR provided an accurate and rapid laboratory diagnosis of FMDV as well as RT-PCR, and 3ABC- ELISA were given nearly the same results. Although the rRT-PCR generated results in less than 6 h and this is an important feature when definitive diagnostic results required in a short timescale during emergencies. Also, this study demonstrated the current situation of circulation FMDV type A, O, and SAT2 serotypes in cattle and buffaloes in Egypt.
Key words: 3ABC-ELISA, Buffaloes, Cattle, Foot and mouth disease, Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
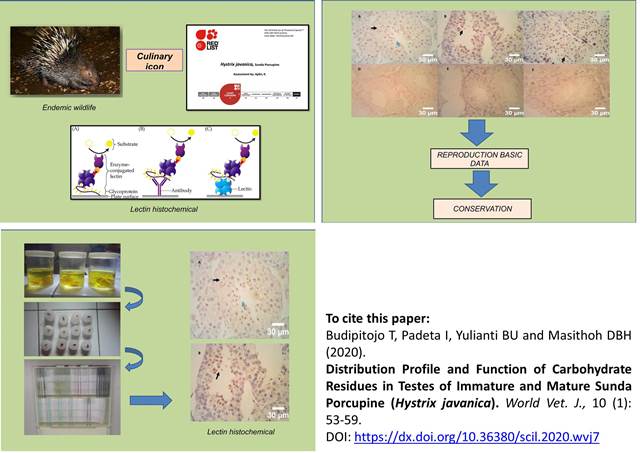
Distribution Profile and Function of Carbohydrate Residues in Testes of Immature and Mature Sunda Porcupine (Hystrix javanica)
Budipitojo T, Padeta I, Yulianti BU and Masithoh DBH.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 53-59, 2020; pii:S232245682000007-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj7
ABSTRACT
The population of Sunda porcupine (Hystrix javanica) declines each year since it is rarely found in nature. The present study aimed to obtain information about the distribution of carbohydrate residues contained in immature and mature of Sunda porcupine’s testes and to discuss its relevant functions. This study used six testes obtained from four immature and two mature Sunda porcupine originated from Ngawi Regency, East Java Province, Indonesia. Testis tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and lectin histochemistry of Lens culinaris agglutinin (LCA), Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L), Pisum sativum agglutinin (PSA), Sophora japonica agglutinin (SJA), and Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). Data were analyzed with descriptive and semi-quantitative method. Lectin histochemical staining with LCA, PHA-L, SJA, PSA, and WGA indicated the presence of alpha-D-mannose and alpha-D-glucose, N-acetylgalactosamine, mannose, and N-acetylglucosamine residues in the immature and mature testes with weak to very strong intensity. In the immature testes of Sunda porcupine, there was positive reactivity with PHA-L for Leydig and Sertoli cells, N-acetylgalactosamine may play an important role in the development and maturation of Leydig and Sertoli cells. Mature testes showed a strong positive reaction to the LCA, SJA, PSA, and WGA which indicated the significant roles of alpha-D-mannose and alpha-D-glucose, N-acetylgalactosamine, mannose, and N-acetylglucosamine residues on the maturation process of early spermatid to the late spermatid. These results can be used as basic data to be implemented in the conservation efforts of Sunda porcupine.
Key words: Carbohydrate residue, Lectin, Spermatogenesis, Sunda porcupine, Testes
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Immunomodulatory Effect of CpG ODN-Adjuvanted Bacterin Against Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis in Broiler Chickens
Abed M, Elhariri M, El-Helw R, Khattab MS, Setta A and Soliman R.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 60-66, 2020; pii:S232245682000008-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj8
ABSTRACT
Bacterial oligodeoxynucleotide containing Cytosine Guanine motifs (CpG-ODN) has been reported to induce immunostimulatory activity against a variety of bacterial, viral, and protozoan infections in a wide range of vertebrate species. The objective of this study was to investigate the dose-dependent immunomodulatory effect of CpG ODN on Salmonella Enteritidis bacterin in broiler chickens. Two hundreds one-day-old broiler chicks, divided into 5 groups, were used in this study. First three groups were immunized with Salmonella Enteritidis bacterin adjuvanted with different doses of CpG ODN (50µg, 100µg and 200µg). The control groups included a group that was immunized with Salmonella Enteritidis bacterin adjuvanted with aluminum hydroxide and a non-immunized group. The intestinal colonization, cellular responses, mucosal and systemic immune responses of immunized chickens was measured at different intervals, until 42 days of age. At two weeks post-immunization, 20 chicks from each group were orally challenged by Salmonella Enteritidis fresh bacterial culture (1.2x108 CFU/ml). The survival rates and the pathological changes of challenged chickens in the different groups were monitored for extra 10 days. Compared to the aluminum hydroxide adjuvanted bacterin, the CpG-ODN adjuvant bacterin induced significant protection and improved survival rate of challenged chickens. Also Salmonella Enteritidis was not recovered from the intestinal tract of vaccinated challenged groups. There was a significant dose-dependent immunostimulatory adjuvant effect of CPG-ODN on the level of secretory IgA and the induced mucosal responses. The 200-CpG ODN group showed the highest IgA response followed by 100-CpG ODN group then the 50-CpG ODN and the aluminum hydroxide groups (P < 0.05). Also, cellular interactions were remarkably reduced in the liver and intestine of CpG ODN-treated chickens. No inflammatory cellular infiltrations were seen in the liver and intestine of 200-CpG ODN treated group. In conclusion, the presented findings have shown the significant immunostimulatory effect of CpG-ODN and its effect on Salmonella Enteritidis bacterin in controlling Salmonella infection in broiler chickens.
Key words: Cellular responses, CpG ODN, Mucosal immunity, Salmonella Enteritidis
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
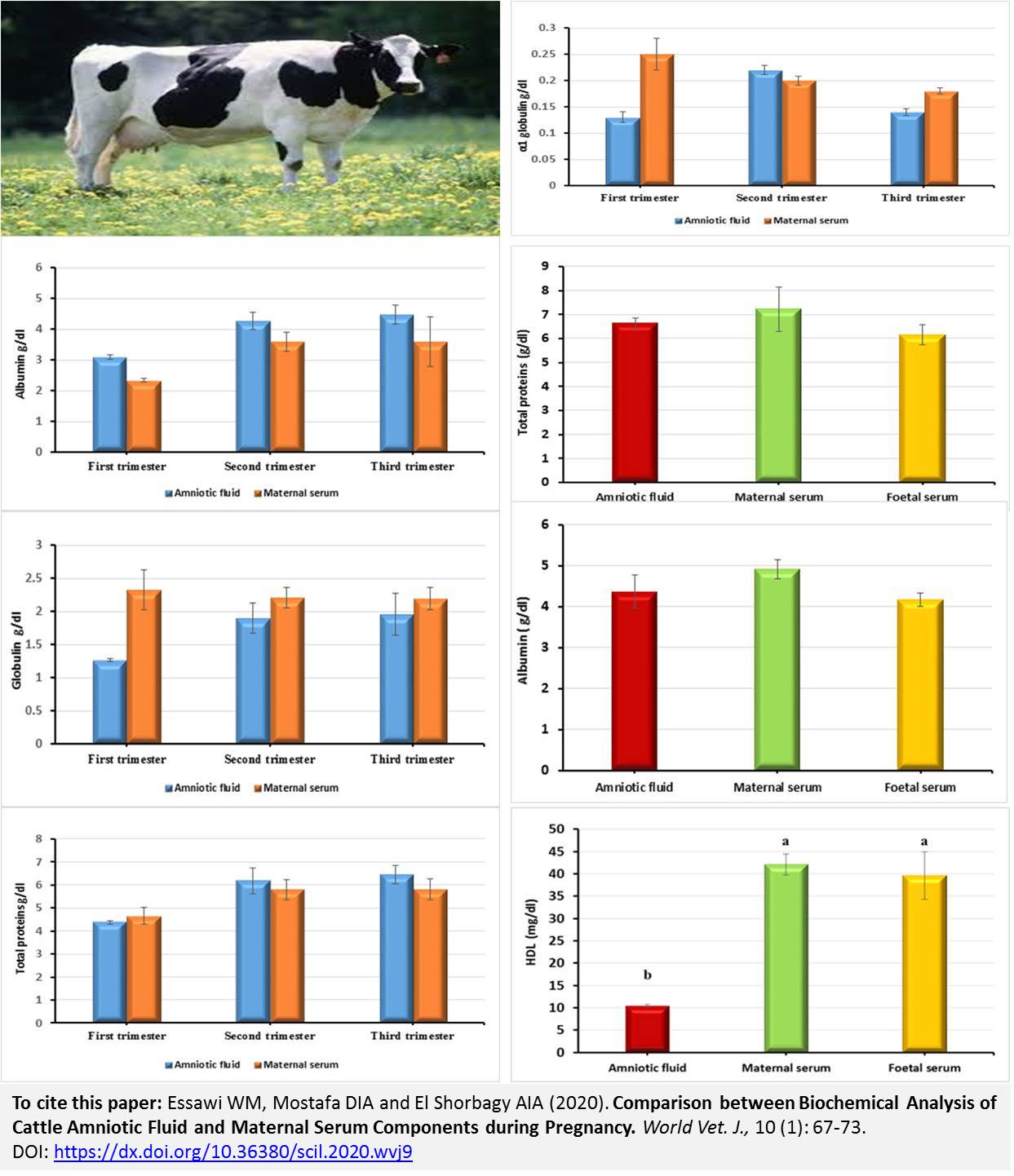
Comparison between Biochemical Analysis of Cattle Amniotic Fluid and Maternal Serum Components during Pregnancy
Essawi WM, Mostafa DIA and El Shorbagy AIA.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 67-73, 2020; pii:S232245682000009-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj9
ABSTRACT
The present study aimed to compare the biochemical components including Total Protein (TP), albumin, globulins, cholesterol, triglycerides, High and Low-Density Lipoproteins (HDL and LDL), creatinine, urea, sodium (Na), potassium (K), chloride (Cl), calcium (Ca) and inorganic phosphorus (P), of Amniotic Fluid (AF) with those of Maternal Serum (MS) during the first, second and third trimesters of pregnancy in cattle and Fetal Serum (FS) at birth. At birth AF, MS and FS were collected. Maternal blood samples and gravid uteri were collected after accidental slaughter. The actual data recorded during three trimesters according to the curved crown-anus length of the fetus. The MS concentrations of globulins, cholesterol, triglycerides, lipoproteins, creatinine, Na, K, Cl, Ca and inorganic-P were significantly higher than the AF during the first trimester. At delivery, the concentrations of cholesterol, triglycerides, and creatinine in the AF were lower than those in the MS or FS. The concentrations of Ca and inorganic-P in the FS were higher than those in the MS or AF. The levels of TP, creatinine, urea in the AF and urea in the MS increased as the gestation stages advanced. The levels of Na and Ca in the AF decreased as the gestation stage advanced while the K concentration increased. In conclusion, our results indicated an active placental transport for Ca and P. The TP, albumin, globulins, cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL and LDL, creatinine, urea, Na, K, Cl, Ca and P in AF and MS during the first, second and third trimesters of pregnancy in cattle might be changed with progressing the gestation.
Key words: Amniotic fluid, Cattle, Fetal serum, Gestation, Maternal blood
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
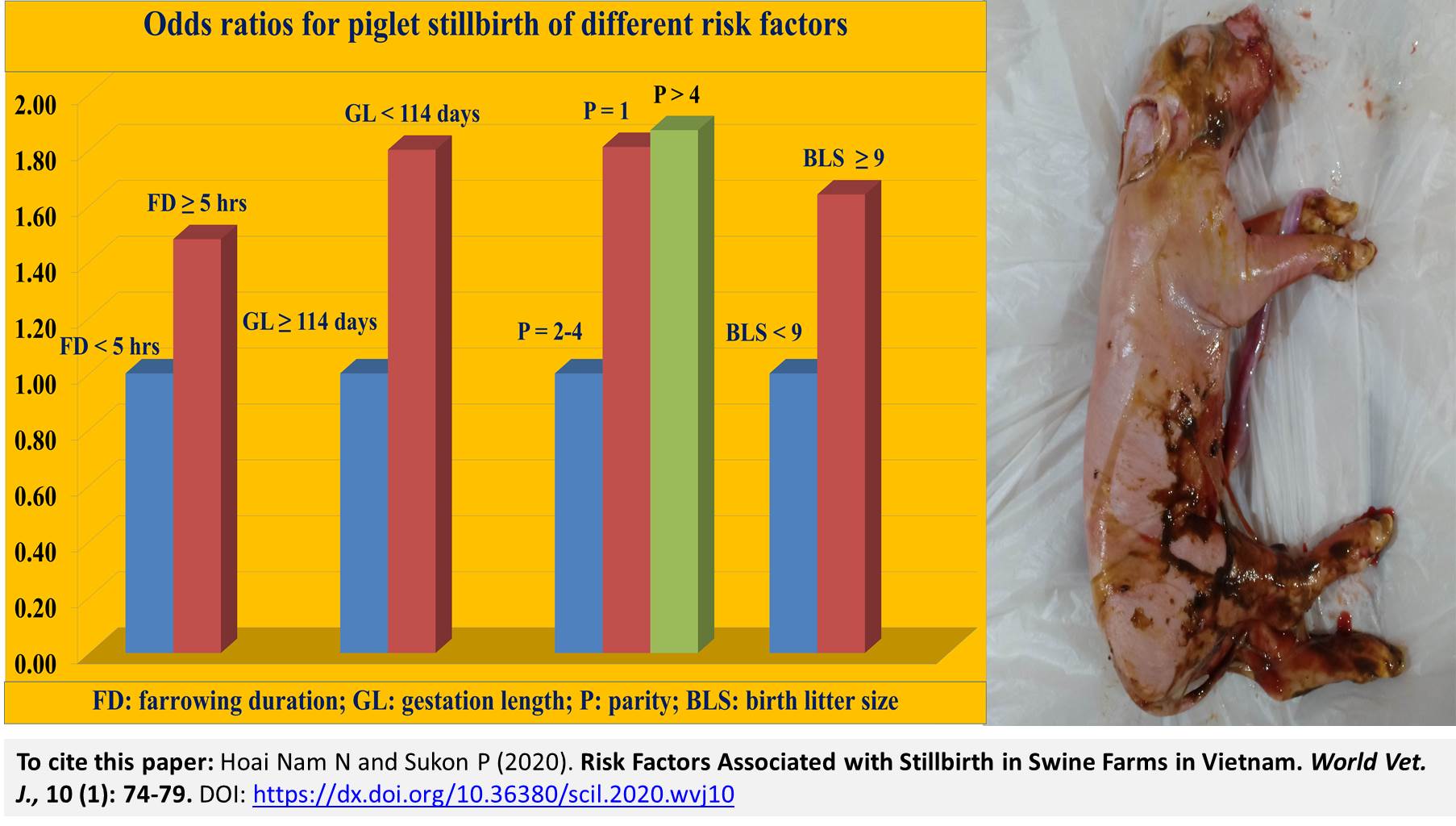
Risk Factors Associated with Stillbirth in Swine Farms in Vietnam
Hoai Nam N and Sukon P.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 74-79, 2020; pii:S232245682000010-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj10
ABSTRACT
Stillbirth in pig has been studied worldwide, but, its situation in Vietnam has never been reported. Therefore, present study aimed to investigate effects of herd, parity, gestation length, birth litter size and farrowing duration on stillbirth at sow level in swine farms in Vietnam. Data was collected from 1174 litters of 1174 Landrace x Yorkshire crossbred sows in 16 farms in the North of Vietnam. Potential risk factors for stillbirth were identified by using logistic regression. The incidence of stillbirth at sow level was 47.9%, and the stillbirth rate was 5.2%. Multivariate logistic regression showed that parity 1 (OR=1.81, 95%CI=1.24-2.63) and >4 (OR=1.87, 95% CI=1.33-2.64), a gestation length <114 days (OR=1.80, 95%CI=1.23-2.65), a birth litter size ≥9 piglets (OR=1.64, 95%CI=1.04-2.61) and a farrowing duration ≥5 hours (OR=1.48, 95%CI=1.05-2.09) were risk factors for stillbirth. This study indicated that stillbirth was common in swine farms in Vietnam. Special attention should be paid to sows at parity 1, > 4, sows with a short gestation, sows with a large birth litter size and sows with a long farrowing duration to reduce stillbirth. Since the use of highly prolific sows is increasing, stillbirth continues to be an issue to be dealt with in swine farms in Vietnam.
Key words: Farrowing; Gestation length; Litter size; Parity; Sow; Stillbirth
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
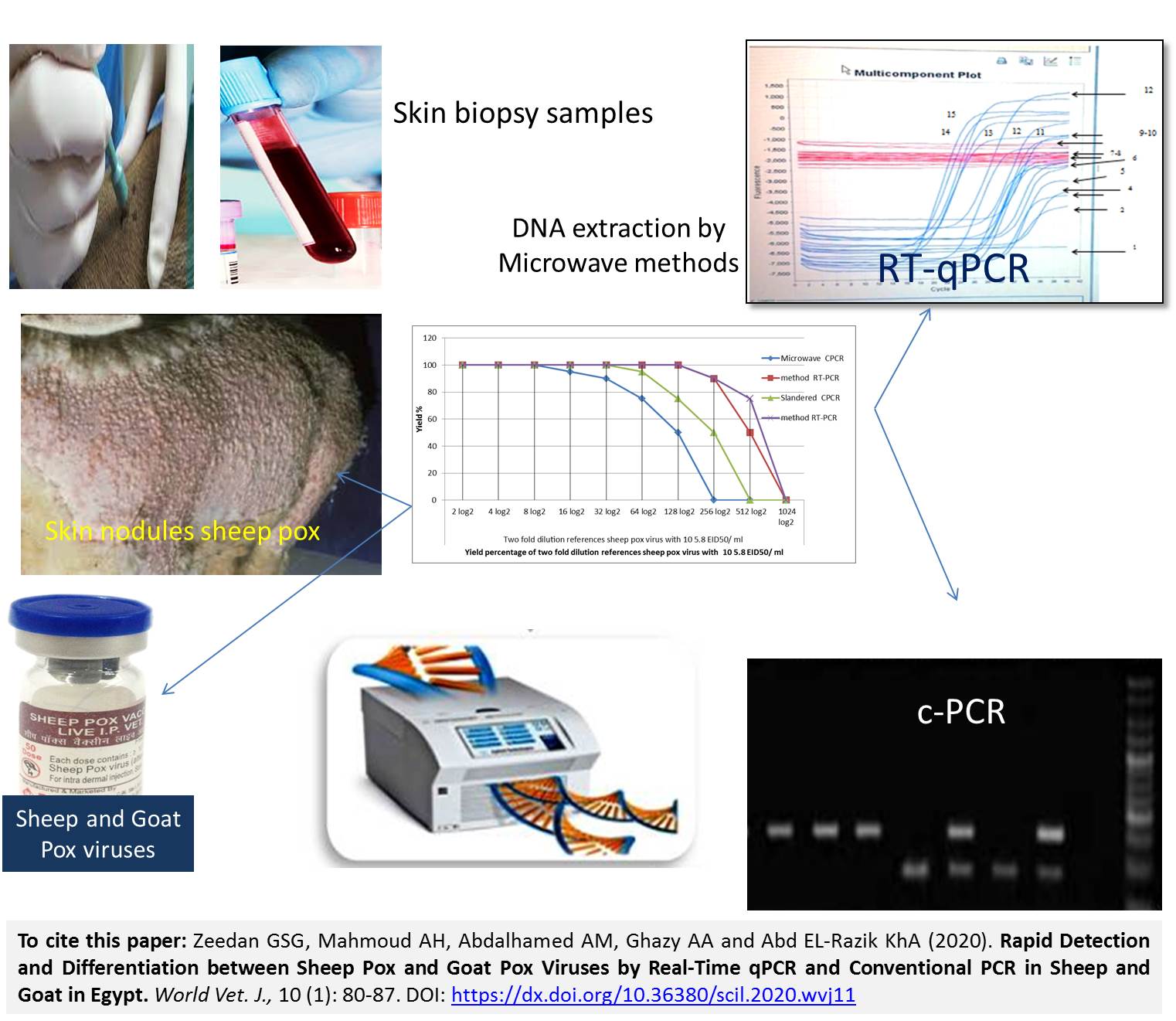
Rapid Detection and Differentiation between Sheep Pox and Goat Pox Viruses by Real-Time qPCR and Conventional PCR in Sheep and Goat in Egypt
Zeedan GSG, Mahmoud AH, Abdalhamed AM, Ghazy AA and Abd EL-Razik KhA.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 80-87, 2020; pii:S232245682000011-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj11
ABSTRACT
Capri Pox Virus (Ca PV) is the causative agent of important diseases in sheep and goat with severe socio-economic impact. Sheep Poxvirus (SPPV), Goat Poxvirus (GTPV) and Lumpy Skin Disease Virus (LSDV) are three members of the Capripox virus genus of Poxviridae family, which infect sheep, goats, and cattle, respectively. A rapid diagnostic assay for Ca PV by using conventional PCR RNA polymerase gene RP030 and real-time qPCR would be useful for disease surveillance, detection and differentiation of Ca PV in clinical and subclinical samples for management and treatments of outbreaks. The present study aimed to detect and identify Ca PV (SPPV and GTPV) in natural, infected scabs biopsy samples, which were collected from sheep and goats in different governorates in 2017 during outbreaks in Egypt using the conventional PCR RNA polymerase gene RP030 gene based and Real-Time qPCR fluorescent based. We collected eighty scabs from clinically affected animals (54 sheep and 26 goat) that were vaccinated in Chorio-Allantoic-Membranes (CAM) from 10-days-old embryonated-chicken eggs. The positive CAM showed pock lesions, which were observed with a thickening of the membrane after 2-3 passages post samples inoculation, and harvested positive CAMs, which were determined by Agar Gel Precipitation Test (AGPT) , Counter Immune Electrophoresis (CIE), and conventional PCR and real time qPCR were examined for the presences of Ca PVs. DNA extraction from clinical samples and positive CAM with pox lesions using DNA slandered references extraction kits compared to novel modification method (Microwave extraction). The PCR based RPO30 gene and the real-time qPCR showed 15 positive with percentage 27.77% in 54 sheep and 3 positive with percentage 12.5% in 26 goats. Although, AGPT and CIE gave lower result than molecular methods, they gave 11 and 13 positive samples from 54 sheep and in goats were 1 and 2 from 26 scab biopsy samples respectively, however they are useful for early confirmation of positive Ca PVs in low-income countries. PCR based RNA polymerase gene RP030 gene and real-time-PCR considered sensitive, rapid, and reliable methods for differentiating SPPV and GTPV from AGPT and CIE in CAM or in clinical samples without further isolation and propagation in embryonated-chicken eggs. The novel microwave method used to isolate high quality of DNA extracted from infected skin biopsy with SPPV and GPPV with no further purification steps required. It was done in 3 minutes only. The results of the current study confirmed that the suitability of the PCR-based RNA polymerase gene RP030 gene is suitable for differentiating between SPPV and GTPV; in one PCR run; without any post-processing steps.
Key words: Capripox virus, DNA extraction, Goat pox, KOH extraction method, Real-Time qPCR, RPO30, Sheep pox
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
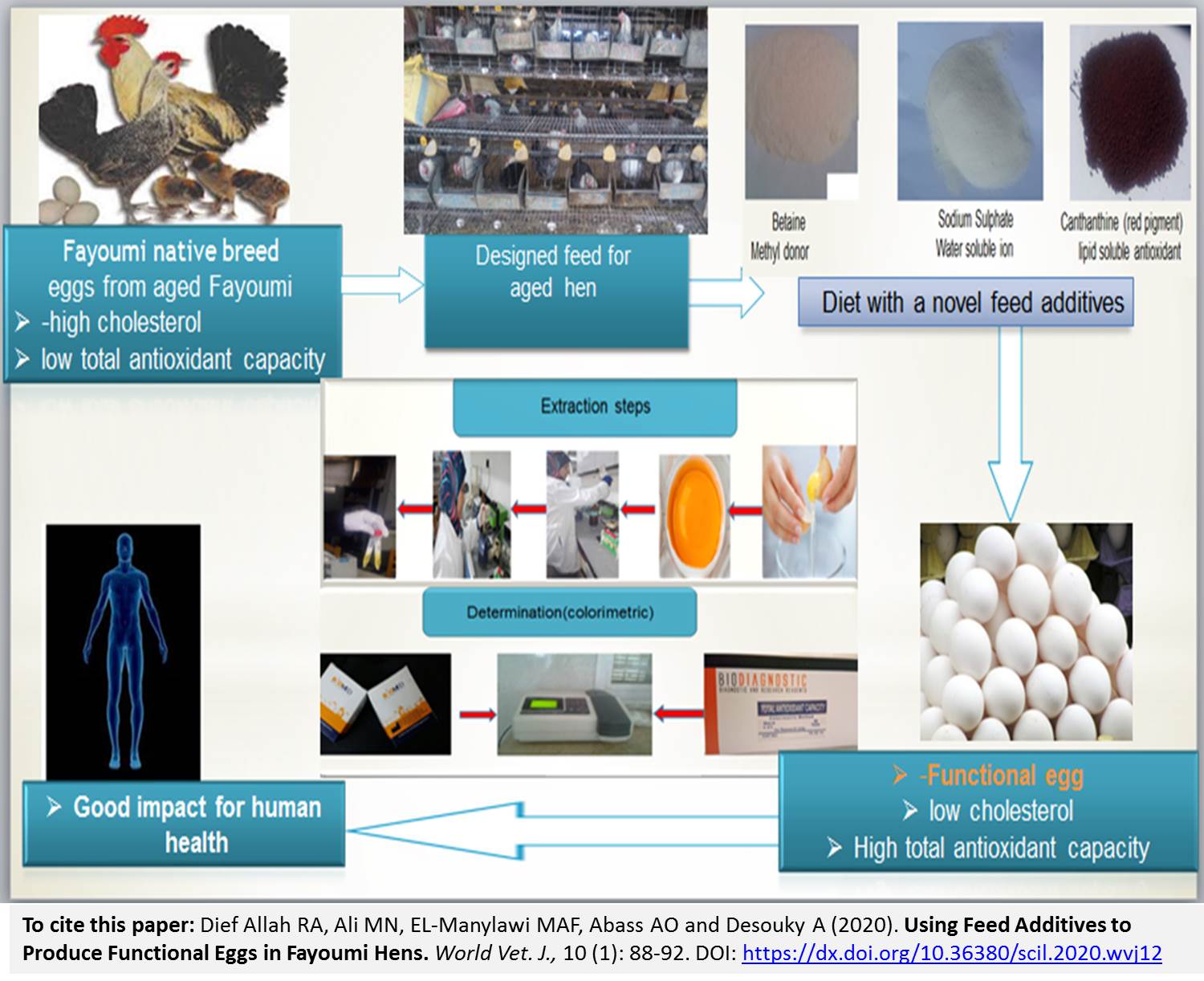
Using Feed Additives to Produce Functional Eggs in Fayoumi Hens
Dief Allah RA, Ali MN, EL-Manylawi MAF, Abass AO and Desouky A.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 88-92, 2020; pii:S232245682000012-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj12
ABSTRACT
Lately human have become more apprehensive for the health and their food relationship. Egg considered cheap source of animal protein. Eggs are rich in various essential nutrients that contribute to the quality of human diet. But its cholesterol can contributes with some human serious disease. The current study examines the hypothesis that assumed addition of antioxidant such as CAX, SS, B or their mixtures to the diet can produce functional egg from Fayoumi hens at late phase of egg production. A number of 168 Fayoumi hens (46weeks of age) were randomly assigned into 8 dietary groups as follows: Basal diet alone or with CAX (6 ppm), SS (0.5 g/kg), B (1 g/kg), CAX+SS, CAX+B, SS+B, and CAX+SS+B separately. Forty eight eggs (6 per each group) were analyzed for estimating cholesterol and total antioxidant capacity. Egg of hens fed a combination of CAX+SS+B which had the best total antioxidant capacity value, while the CAX group recorded the best lowest cholesterol value compared to other groups (P < 0.05). It could be concluded that basal diet supplemented with CAX, SS, B alone or with mixture of them may have lowering effect on yolk total cholesterol. This could lead to produce functional eggs which have positive effects on human health and favorable for those suffering from heart syndromes.
Key words: Cholesterol, Fayoumi, Functional Egg, Total Antioxidant Capacity
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
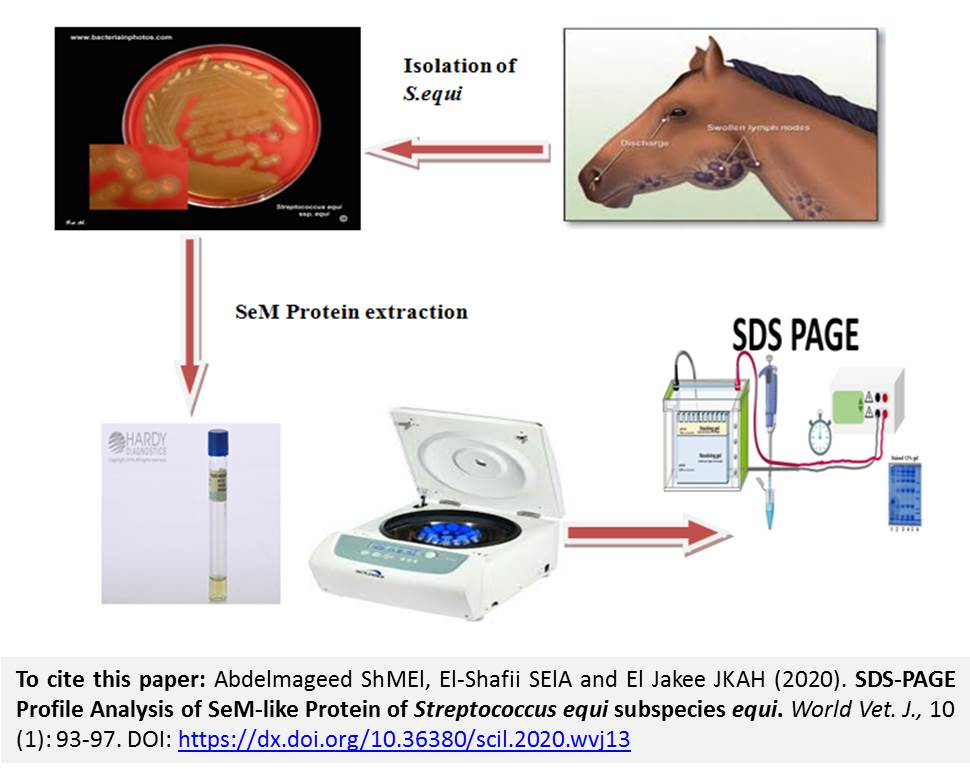
SDS-PAGE Profile Analysis of SeM-like Protein of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi
Abdelmageed ShMEl, El-Shafii SElA and El Jakee JKAH.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 93-97, 2020; pii:S232245682000013-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj13
ABSTRACT
S. equi subspecies equi, causing strangles in equine, is characterized by comprising a major virulence factor called M like protein or SeM protein. This study aimed to extract SeM protein from local S. equi strain in Egypt and to detect its antigenic components. After centrifugation, the native 58 kilo Dalton (kDa) SeM protein was detected both in the supernatant and sediment of the prepared extract. With modification by more centrifugation, the formed supernatants were separated and fractionated using SDS-PAGE with silver nitrate staining, which led to the appearance of a band at Molecular Weight (MW) 70.9 kDa. in SeM1, the presence of 7 bands at MW of 105, 87.8, 70.9, 61.1, 44, 37.9 and 18.4 in SeM2; 5 bands at MW 70.9, 58.9, 37.2, 29.8 and 18.3kDa in SeM3 and 4 bands at MW of 72.0, 58.6, 29.8 and 18.0 kDa in SeM4. This study suggested that a further modification of SeM extraction revealed the presence of heterogeneous complex fragments of SeM.
Key words: SeM protein, SDS-PAGE, Strangles, Streptococcus equi subspecies equi
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
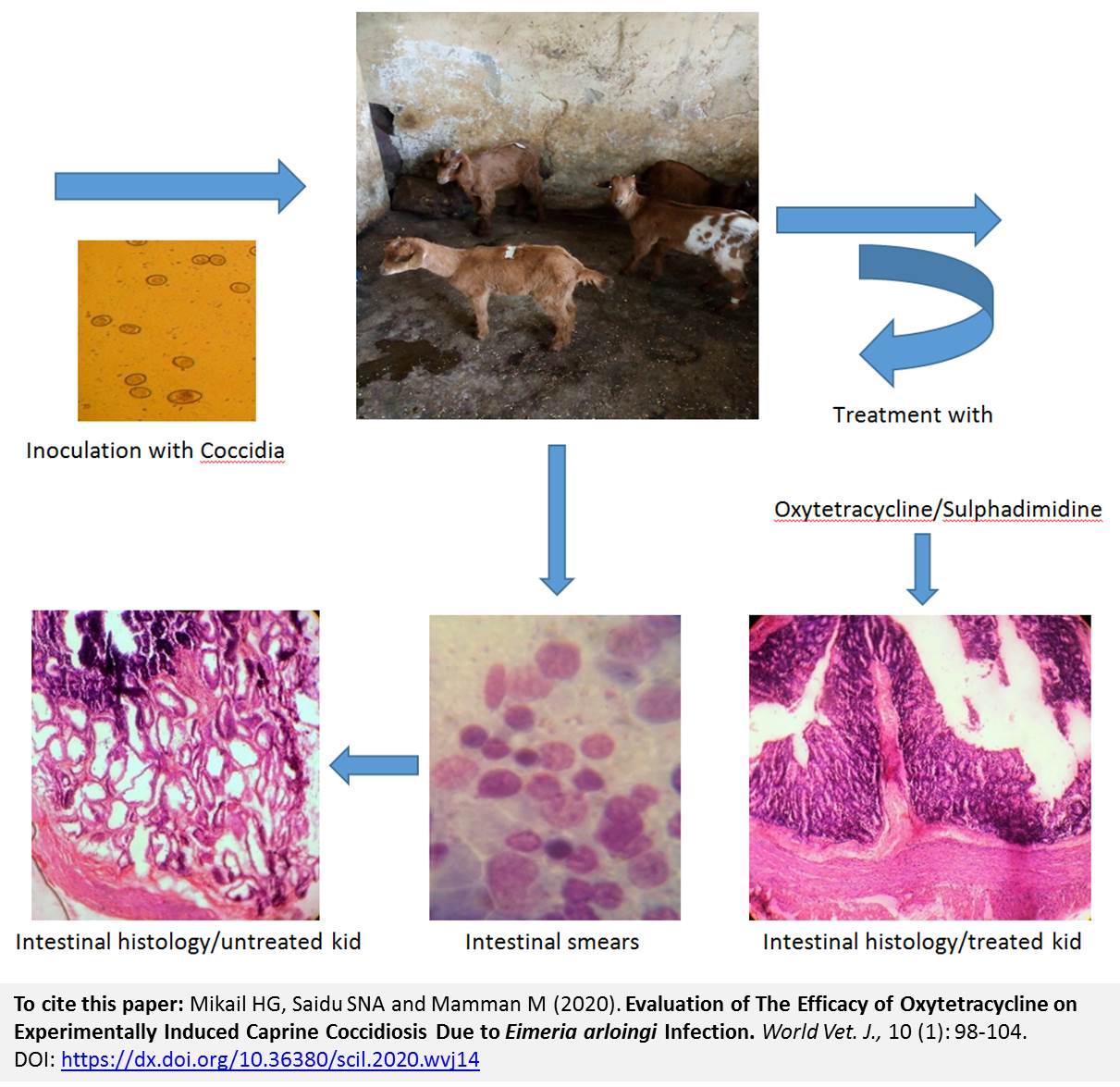
Evaluation of The Efficacy of Oxytetracycline on Experimentally Induced Caprine Coccidiosis Due to Eimeria arloingi Infection
Mikail HG, Saidu SNA and Mamman M.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 98-104, 2020; pii:S232245682000014-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj14
ABSTRACT
Coccidiosis is a protozoan disease caused by members of the genus Eimeria that affect domestic animal species. The current study was aimed at evaluating the effect of oxytetracycline administration on experimental caprine coccidiosis. Sixteen red Sokoto goat kids divided into four groups (A to D) of four goat kids each, were used for the study. Groups A, B and C were infected by oral inoculation with two ml containing 1.5 ×103 sporulated oocysts of Eimeria arlongi per animal, while group D was the neutral control group. Group A was treated with 10 % oxytetracycline intramuscularly daily for five days. Group B was treated with Sulfadimidine 33.3% subcutaneously daily for five days and group C served as an infected untreated group. Fecal oocysts per gram count was conducted during the experiment. The present result showed a significant decrease (P ≤ 0.05) in fecal oocysts load in the treated groups. Neither schizonts nor merozoites were detected in the intestinal smear of kid treated with oxytetracycline but were detected in the intestinal smear of infected untreated goat kid. Cystic degenerative changes were seen in the intestinal glandular cells of the infected untreated goat kid. Conclusively, the current finding suggests that oxytetracycline can effectively be used in treating caprine coccidiosis.
Key words: Coccidiosis, Caprine, Eimeria arlongi, Goat Kids, Oxytetracycline, Treatment
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
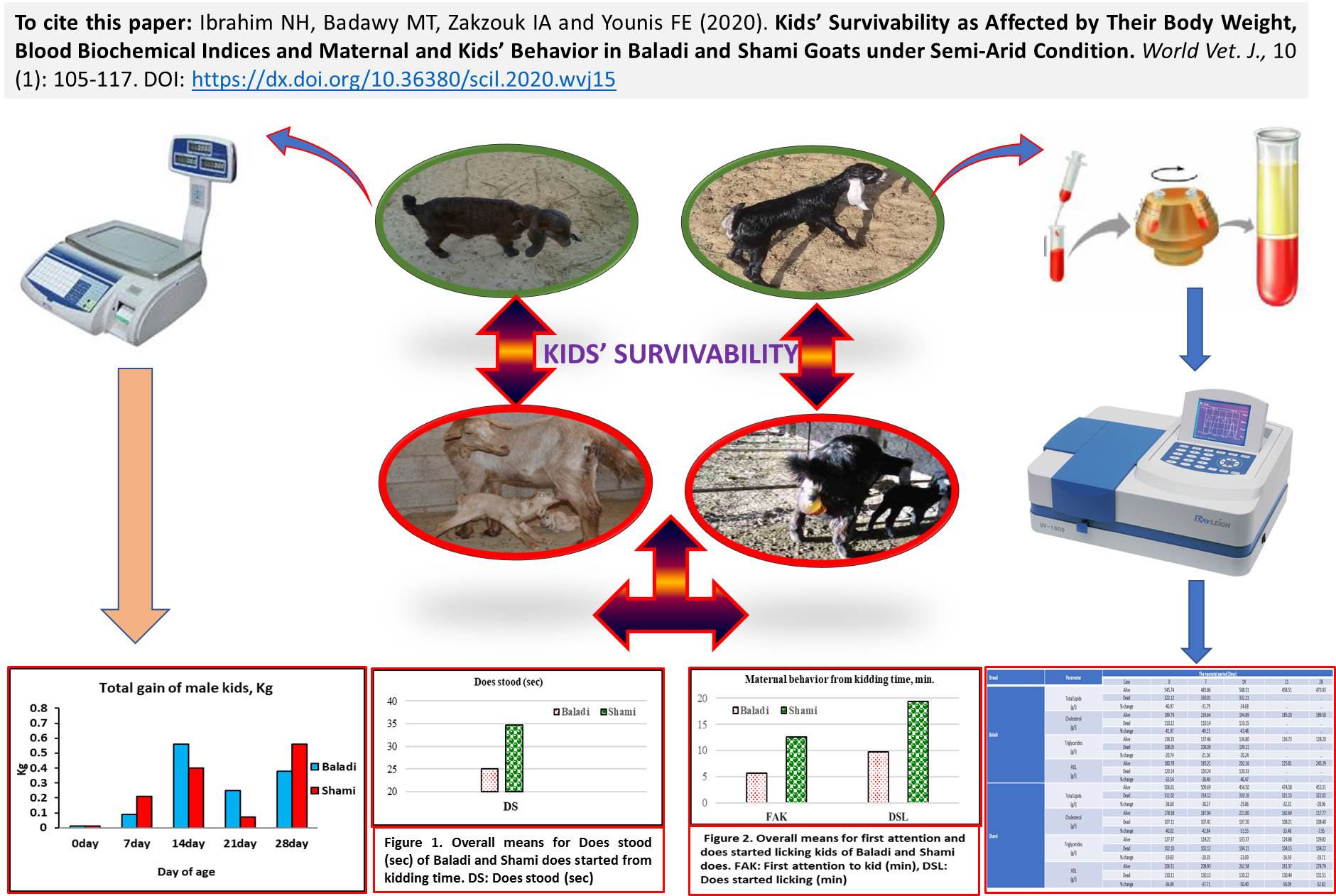
Kids’ Survivability as Affected by Their Body Weight, Blood Biochemical Indices and Maternal and Kids’ Behavior in Baladi and Shami Goats under Semi-Arid Condition
Ibrahim NH, Badawy MT, Zakzouk IA and Younis FE.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 105-117, 2020; pii:S232245682000015-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj15
ABSTRACT
The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of body weight, blood biochemical parameters and post parturient behavioral activities of goats and their kids on kids' mortality rate in Baladi and Shami breeds during neonatal period. Twenty-five adults does of each breed (average age: 18 months old) were selected during breeding season. All female goats were estrus synchronized and naturally mated. After parturition, one hundred and one kids (39 Baladi and 62 Shami) were followed for up to 30 days of their age. The overall mean birth weights of female kids of Baladi and Shami goats were 2.47 and 2.81 Kg, respectively. For male kids, birth weights were 2.43 and 2.47 kg, respectively. There was no significant difference in average daily gain (g/day) between Baladi and Shami kids during the first 30 days of age. Male kids recorded higher mortality rate than female kids. The percent of death for male and female kids were 87.50% and 36.84% in Shami while, were 33.33% and 14.28% in Baladi respectively. However, death stopped in Baladi kids after 14 days, but continued in Shami kids to 28 days post-partum. Present data revealed that goat breed and neonatal period showed a significant effect on urea concentration and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and insignificant effect on creatinine concentration, alanine transferase (ALT), gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT), total lipids, cholesterol and triglycerides in Baladi and Shami Kids. While aspartate transferase (AST), were not affected by goat breed and was significantly affected by both age of birth and interactions. Baladi breed showed significantly better maternal activity than Shami does as they spend lesser time to concern their newly born kids. Baladi kids had more strong behavior towards their dams when compared to Shami ones. It was concluded that body weight, blood biochemical parameters and Maternal and kid's behavior had notable effect on kid’s survivability. Our results might declare superiority of Baladi kids than Shami ones which reflected on the significant reduction of mortality rate in Baladi kids as compared to Shami ones.
Key words: Body weight, Goat, Kids behavior, Maternal behavior, Offspring survival
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
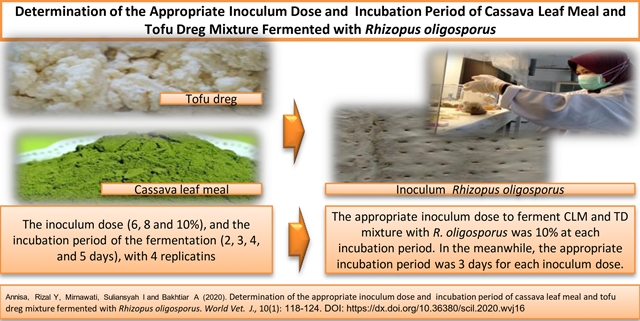
Determination of the appropriate inoculum dose and incubation period of cassava leaf meal and tofu dreg mixture fermented with Rhizopus oligosporus
Annisa, Rizal Y, Mirnawati, Suliansyah I and Bakhtiar A.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 118-124, 2020; pii:S232245682000016-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj16
ABSTRACT
The present study was conducted to determine the appropriate inoculum dose and incubation period for the mixture of Cassava Leaf Meal (CLM) and Tofu Dreg (TD) fermented with Rhizopus oligosporus. This experiment was carried out in a completely randomized design in a 3 x 4 factorial treatments arrangement with 4 replications. The first factor was the inoculum dose (6, 8 and 10%), and the second factor was the incubation period of the fermentation (2, 3, 4, and 5 days). Measured variables were the changes in Dry Matter (DM), Organic Matter (OM), crude fat, Crude Fiber (CF), and Crude Protein (CP). The experimental results showed that there was no interaction between the inoculum dose and an incubation period of the fermentation in the reduction of DM, organic matter, and crude fat as well as the increase in the CP of fermented CLM and TD with Rhizopus oligosporus. However, the interaction was occurred between inoculum dose and incubation period in the reduction in CF. The inoculum dose significantly decreased the DM, OM, crude fat and CF and also increased the CP. The best inoculum dose effect was at 10%. The incubation period had a significant reduction in the DM, OM, crude fat, and CF and also increased the CP. The best incubation period of fermentation was at 3 days. The results indicated that the appropriate inoculum dose to ferment CLM and TD mixture with Rhizopus oligosporus was 10% at each incubation period. In the meanwhile, the appropriate incubation period was 3 days for each inoculum dose.
Key words: Fermentation, Inoculum dose, Incubation time, Rhizopus oligosporus
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
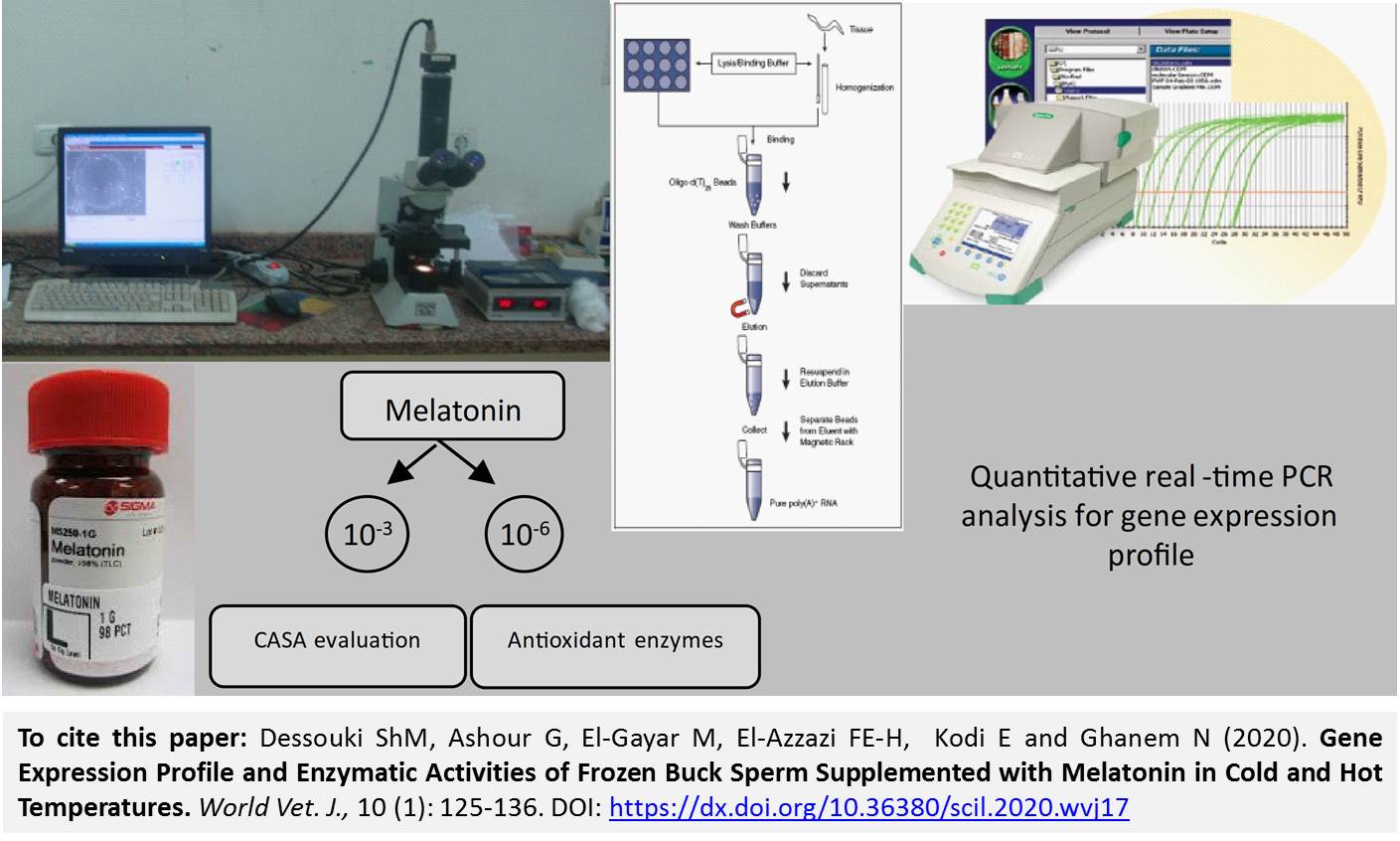
Gene Expression Profile and Enzymatic Activities of Frozen Buck Sperm Supplemented with Melatonin in Cold and Hot Temperatures
Dessouki ShM, Ashour G, El-Gayar M, El-Azzazi FE, Kodi E and Ghanem N.
World Vet. J. 10(1): 125-136, 2020; pii:S232245682000017-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj17
ABSTRACT
This study was carried out to improve the freezability of buck semen using two different types of cryoprotectants supplemented with melatonin as antioxidant in cold and hot temperature of breeding season. Ejaculates from four mature Egyptian baladi bucks were pooled after collection. Semen was extended with Tris-fructose-citric containing egg yolk using glycerol and dimethyl sulfoxide supplemented with two doses of melatonin (10-6M and 10-3M) in addition to control group. Types of motility as well as velocity, enzymatic activity and expression profile of selected genes were measured. The results revealed that the progressive motility percentage was significantly higher in samples supplemented with low dose of melatonin (10-6 M) compared to high dose (10-3M) in glycerol (74.4 versus 64.4) and Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) based extender (35.5 versus 32.9) in cold temperature. The same trend was found in samples cryopreserved with glycerol (75.1 versus 53.5) and DMSO (32.1 versus 22) in hot temperature. The results also demonstrated that CASA parameters (VAP and VCL) were significantly increased in low compared to high melatonin dose in glycerol based extender during cold and hot temperature. The activity of total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was significantly higher in samples supplemented with low (0.49 mM/L) than high melatonin dose (0.16 mM/L) in DMSO extender. CPT2, ATP5F1A and SOD2 genes were up regulated in glycerol based extender groups in cold temperature compared to other groups of this study. On the other hand, NFE2L2 gene was up-regulated in groups cryopreserved with DMSO in hot temperature compared with all other experimental groups. Therefore, it could be concluded that the glycerol based extender in cold season supplemented with low dose of melatonin improved semen quality, antioxidant defense capacity and transcriptional profile, which may maintain the post-thaw fertilizing ability of buck semen.
Key words: Antioxidant enzymes, Bucks, Melatonin, Motility, Transcript abundance
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).