Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 10 (2); June 25, 2020 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 10 (2); June 25, 2020 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
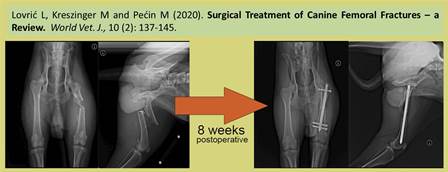
Surgical Treatment of Canine Femoral Fractures – a Review
Lovrić L, Kreszinger M and Pećin M.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 137-145, 2020; pii:S232245682000018-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj18
ABSTRACT
Femoral fractures in dogs and cats account for 20-25% of all fractures for which surgical treatment is a method of choice. Surgical treatment is based upon biological principle of open anatomic reduction and osteosynthesis. Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen (AO) classification of fractures has a widespread use in general. Present study discusses different methods of osteosynthesis and healing process based on special cases managed in a certain small animal clinic in Hollabrunn, Austria, in 2016. The level of femoral fracture and the chosen method of osteosynthesis are shown respectively. According to available literature and author’s personal observations during externship period, the best results have been achieved using minimally invasive surgery. The surgical method choice depends on type, level and complexity of fracture, surgical skills and equipment of the team providing care respectively.
Key words: Dog, Femur, Fracture, Osteosynthesis.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
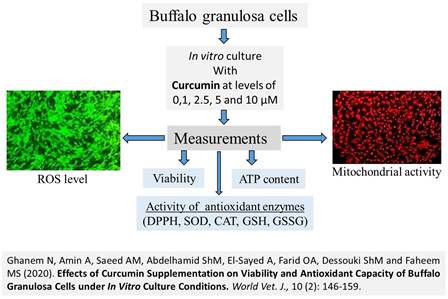
Effects of Curcumin Supplementation on Viability and Antioxidant Capacity of Buffalo Granulosa Cells under In Vitro Culture Conditions
Ghanem N, Amin A, Saeed AM, Abdelhamid ShM, El-Sayed A, Farid OA, Dessouki ShM and Faheem MS.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 146-159, 2020; pii:S232245682000019-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj19
ABSTRACT
The current study was conducted to investigate the possible protective effect of curcumin supplementation on buffalo granulosa cells (GCs) under in vitro culture condition. Buffalo ovaries were collected from local abattoir in physiological saline solution and transported directly to laboratory. Follicular fluid containing GCs and cumulus-oocyte-complexes were aspirated from antral follicles with diameter 2-8 mm. The collected GCs were seeded (Approximately 375,000 viable cells) in an 8-well culture plate containing tissue culture medium-199 (TCM-199) and kept at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2. The curcumin was supplemented to TCM media at levels of 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 μM for 24 and 48 h at 37 °C or kept without treatment as control group. The viability of cells was determined using the trypan blue test. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was assessed by measuring the fluorescent intensity of 6-carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorodihydro fluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA). In addition, mitochondrial activity of GCs was determined. The results of the present study indicated that the viability of GCs under culture conditions was significantly decreased in groups treated with 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 µM curcumin (86.0%, 86.26%, 83.0% and 74.0%, respectively) compared to control group (93.60 %). The two groups of granulosa cells cultured with 2.5 and 5 µM curcumin recorded greater level of mitochondrial activity than the groups cultured with 1 µM and 10 µM curcumin. Moreover, there was a significant increase in ROS level in group cultured with 10 µM curcumin, compared to control and other experimental groups. The enzyme activity of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH) and 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) was increased after treating in vitro cultured granulosa cells with 5 µM of curcumin. However, the enzymatic activity of CAT, SOD, GSH and DPPH was declined significantly 48 h post-curcumin treatment. In conclusion, supplementation of curcumin at low concentration (2.5 µM) for 24 h to in vitro cultured GCs improved intracellular metabolic activity and antioxidant protective system, whereas it could not sustain this action for 48 h. Moreover, supplementation of curcumin at high concentration and for long duration may negatively affect viability of GCs under in vitro culture condition via induction of oxidative stress.
Key words: Antioxidant, Buffalo, Granulosa cells, Oxidative stress, Viability.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
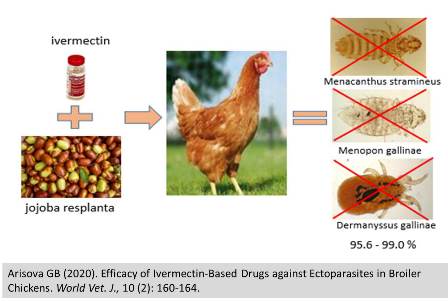
Efficacy of Ivermectin-Based Drugs against Ectoparasites in Broiler Chickens
Arisova GB.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 160-164, 2020; pii:S232245682000020-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj20
ABSTRACT
This research aimed to study the efficacy of two different ivermectin-based drugs against ectoparasites of chickens. In total 1200 Highsex brown chickens aged 1-1.5 years were examined to determine the prevalence of ectoparasites among chickens. The diagnosis of ectoparasites in chickens was established using clinical and entomological methods. For studying drug efficacy, 20 chickens were selected and divided into two groups (experimental and control) of 10 birds each according to the principle of analogs. A prepared ivermectin-based drug consisting of active substance ivermectin and the auxiliary substances including jojoba Resplanta, diethylene glycol monoethyl ether, Tween-80, benzyl alcohol, and purified water, was administered to the experimental group at a dose of 0.4 ml/L of drinking water (400 μg ivermectin per 1 kg of body weight) twice with a 24-hour interval. The treatment was repeated after 14 days. The control group was administered another drug based on ivermectin in the same dose and manner as the drug given in the experimental group. The efficacy of the drugs was determined by counting the number of ectoparasites per chicken before and after treatment. The clinical condition of the birds was monitored from day 1 to day 28 of the experiment. To evaluate the physiological state of chickens, blood and biochemical tests were performed on day 28 of the experiment. The results revealed that the prevalence of infection with Menacanthus stramineus, Menopon gallinae, and Dermanyssus gallinae in chickens was 34.5%, 21.5%, and 12%, respectively. The number of parasites/chicken after treatment between the experimental and the control group was significantly different. The efficacy of the drugs against ectoparasites in the experimental and control group was 95.6-99.0% and 85.1-91.1%, respectively. The blood tests showed that hematological and biochemical parameters were within physiological norms for both groups. Also, a pharmacokinetic study was performed on 18 ISA cross, 40-day-old chickens administered orally with the test drug at the same dose. The results revealed that ivermectin reached maximum concentration at 30-60 minutes after administration to the bird. After 1 hour, the concentration of the active substance of the drug in the blood serum of chickens decreased sharply and reached the limit of quantification by 12-24 hours. In conclusion, this drug can be recommended for use in poultry as an effective and safe drug for the treatment of arachnoentomosis in birds.
Key words: Chickens, Ectoparasites, Ivermectin.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
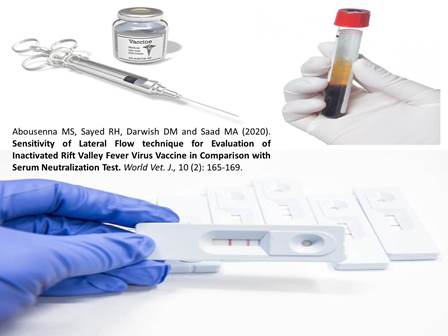
Sensitivity of Lateral Flow technique for Evaluation of Inactivated Rift Valley Fever Virus Vaccine in Comparison with Serum Neutralization Test
Abousenna MS, Sayed RH, Darwish DM and Saad MA.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 165-169, 2020; pii:S232245682000021-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.20209.wvj21
ABSTRACT
Rift Valley Fever (RVF) is a zoonotic mosquito-borne bunyaviral disease associated with high abortion rate, neonatal death, fetal malformations in ruminants, and mild to severe disease in human. The vaccination has significantly reduced the abortion of ewes and mortality of newborn lambs during an outbreak, and induced immunity in cattle. The evaluation of inactivated RVF vaccine required in vivo and in vitro techniques. The present research aimed to evaluate the sensitivity of the Lateral Flow Device (LFD) in comparison with Serum Neutralization Test (SNT) by reference sera to determine the humoral immune response of the sheep vaccinated with an inactivated RVF vaccine. Three batches of inactivated RVF vaccine were inoculated in three sheep groups. Then samples of their sera were collected weekly, and tested by SNT and LFD. It was found that the sensitivity of LFD at a serum dilution of 1:128 was 95%, while SNT carried out at the fourth week after the vaccination showed that antibody titers was 32,64 and 32. On the other hand, LFD had positive results at dilutions of 1:32, 1:128 and 1:64 for the vaccine batches 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These findings suggest the possibility of using LFD for detection of the immune response of vaccinated sheep to the inactivated Rift Valley Fever Virus vaccine, and it could be improved to be more quantitative in future.
Key words: Lateral flow device, Rift valley fever virus, RVFV inactivated vaccine, Vaccine evaluation
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Molecular Evidence of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei in Asian Wild Frogs (Rana rugulosa) from Banyuwangi City, Indonesia
Yudhana A, Praja RN, Yunita MN and Wardhana DK.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 170-174, 2020; pii:S232245682000022-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj22
ABSTRACT
The tapeworm Spirometra erinaceieuropaei is the most frequently species which found in wild frog and causing a serious parasitic zoonosis known as sparganosis. This study aimed to provide molecular evidences of spargana collected from wild frogs which used as food and contribute to provide important implication for prevention and control of sparganosis. A total of 185 Asian wild frog (Rana rugulosa) samples were selected from food markets in Banyuwangi City, Indonesia. Molecular identification based on spargana that were collected and coding gene of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase 1 (cox1) using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) method. Spargana were found in 9.1% (17/185) of the frogs and PCR analysis results identified all specimens belonging to the species S. erinaceieuropaei, therefore indicated that S. erinaceieuropaei is the major causative agent of sparganosis from frogs which sold as food in markets. These findings can be useful to the molecular diagnosis and control of Spirometra infections in humans and animals.
Key words: Asian wild frog, Rana rugulosa, Sparganosis, Spirometra erinaceieuropaei.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
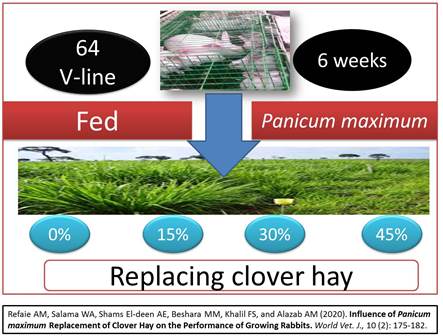
Influence of Panicum maximum Replacement of Clover Hay on the Performance of Growing Rabbits
Refaie AM, Salama WA, Shams El-deen AE, Beshara MM, Khalil FS, and Alazab AM.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 175-182, 2020; pii:S232245682000023-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj23
ABSTRACT
Two experiments were performed to evaluate Panicum maximum (Pm) and its effect on rabbits’ growth performance. In the first experiment, six adult V-line male rabbits were used to determine the digestible energy in Pm by continuously feeding these 120 gram (g) Pm and 120 g clover hay for 3 days, and then the digestible energy was recorded 1959 kcal /kg. In second experiment, a total of 64 rabbits of V-line, 6 weeks old with average weight of 702 g, were divided into 4 groups, each in 4 replicates (4 rabbits/replicate), the first fed basic diet; control (T1), the 3 groups fed on the diet contained Pm to replace clover hay as a percentage of 15%, 30% and 45%, which corresponds to 4.5%, 9% and 13.5% of the total diet; which represent T2, T3, and T4, respectively. Rabbits were fed ad libitum with pellet feed until the end of growth attempt (14 weeks). The results indicated that the proximate analysis of Pm was 11.65% crude protein, 2.67% crude fat, and 30.66% crude fiber. Rabbits in T4 group significantly had the best final weight, daily weight gain, and Feed Conversion Ratio FCR. All groups had high crude protein digestibility except the group fed T3 diet. The total number of cecum bacterial count was improved in all tested groups. In conclusion, feeding growing rabbits with Pm up to 45% instead of clover hay achieved higher growth performance and lower cecum coliform bacteria.
Key words: Cecum bacteria, Growth performance, Panicum maximum, Rabbits.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
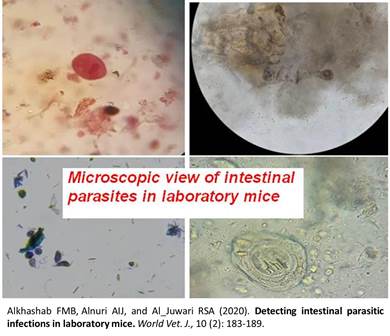
Detecting intestinal parasitic infections in laboratory mice
Alkhashab FMB, Alnuri AIJ, and Al_Juwari RSA.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 183-189, 2020; pii:S232245682000024-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj24
ABSTRACT
A total of 150 Laboratory mice divided into four age groups consisted of 4, 6, 8 and 10 weeks old were used in this study by placing each animal individually in a special cage within the period between October 2019 to the end of February 2020 at the Research and Graduate Studies Laboratory University of Mosul, Iraq. This study aimed to investigate intestinal parasitic infections in laboratory mice, stool samples were collected for 150 laboratory mice and periodically to perform laboratory tests that included direct slide examination and using the concentration method to detect eggs of worms and cysts of protozoa parasites, the culture of parasites also was used by prepared manufactured culture media to develop parasites. The infection was diagnosed in 136 (90.66%) mice while the rest 14 (9.33%) mice did not record any parasitic infection (clean). The higher rate of infection 58% was reported for Trichomonas muris followed by Entamoeba muris and Giardia muris which found in 22%, 15.3% respectively. In the other hand the infection with Hymenolepis diminuta was recorded in 16% from infected cases by identifying the eggs of this worm in stool samples. This study shows the high rate of parasites infection in laboratory mice which might have negative effects on the result of previous scientific researches, in addition to wasting effort, time, and materials.
Key words: Entamoeba muris, Giardia muris, Laboratory mice, Trichomonas muris
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
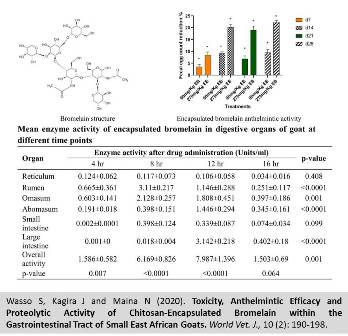
Toxicity, Anthelmintic Efficacy and Proteolytic Activity of Chitosan-Encapsulated Bromelain within the Gastrointestinal Tract of Small East African Goats
Wasso S, Kagira J and Maina N.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 190-198, 2020; pii:S23224568200002510
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj25
ABSTRACT
The development of resistance to anthelmintic drugs has prompted researches into alternative methods for controlling intestinal nematodes in ruminants. This study aimed to evaluate the anthelmintic efficacy, proteolytic activity, and toxicity of bromelain encapsulated in chitosan within the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of Small East African goats in Kenya. Twelve healthy indigenous male goats were divided into four groups contained three goats in each groups. Treatment groups included: G1, chitosan-encapsulated bromelain (90 mg/kg); G2, chitosan-encapsulated bromelain (270 mg/kg); G3, positive control (albendazole 7.5 mg/kg); and G4, negative control. The animals were orally treated with the drugs in a single dose. The hematological and serum biochemical parameters were determined using standard methods. The strongyle fecal egg count was evaluated weekly using a modified McMaster technique. To determine the proteolytic activity of nanoencapsulated bromelain within the GIT, another set of twelve goats was used and administered 270 mg/kg of encapsulated bromelain. Every four hours, three goats were sacrificed and the proteolytic activity of the drug was determined in the different organs of the GIT. Significant differences were observed between the mean PCV of goats treated with 270 mg/kg encapsulated bromelain and non-treated goats on days 21 and 28 post-treatment. The mean aspartate aminotransferase, urea, and creatinine levels of treated and control goats did not significantly differ during the experiment period. Also, no significant difference was observed between the mean alanine aminotransferase level of treated and untreated goats 28 days post-treatment. The administration of encapsulated bromelain was not associated with any clinical sign and mortality. The reduction in fecal egg count in G1 and G2 at 28 days post-treatment was 9.5% and 22.6%, respectively. The encapsulated bromelain remained proteolytically active along the goat GIT but its protease activity varied according to the type of GIT organ and time elapsed since administration. In conclusion, chitosan-encapsulated bromelain is safe, but have low efficacy against GIT strongyle nematodes when given as a single dose. Future studies should evaluate higher and repeated doses of encapsulated bromelain for controlling GIT nematodes.
Key words: Bromelain, Chitosan, Efficacy, Goats, Nanoencapsulation, Proteolytic activity.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
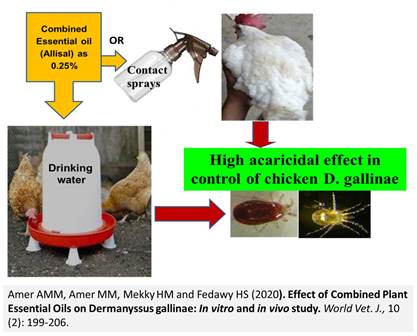
Effect of Combined Plant Essential Oils on Dermanyssus gallinae: In vitro and in vivo study
Amer AMM, Amer MM, Mekky HM and Fedawy HS.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 199-206, 2020; pii:S232245682000026-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj26
ABSTRACT
The present study was carried out to evaluate the effect of plant essential oils on Dermanyssus gallinae (D. gallinae). In vitro six groups of red mites, 20 mites in each group were exposed to direct spray of combined plant essential oils (Alisal) in rate of 0.25% on mites. activity and changes under stereomicroscope showed that sprayed mites completely stopped movements at both 1- and 2- h after treatment with completely stretched legs and white bead-like spots of oils accumulation on legs and bodies at 1- and 2- h. while, the non-treated mites were active with pale light brown colour. In vivo effect of Allisal to control red mite infestation in laying hens was investigated. In case of drinking water method mite count reduction rate on the bird was 60 %, 10%, and 0% as well as 0%, 0% and 10% in their traps at 4,7, and 12 days respectively, from the start of treatment in drinking water. While, in spray method mite reduction was 40%, 20%, and 10% on birds and 0%, 0% and 30% in the traps. On the other hand, water intake, feed intake, general health condition, skin health, and feather condition scores were improved at 4th day post treatment (DPT). Total lesion score at 12 DPT was improved. The present study concluded that in vitro combined plant essential oils have rapid and strong acaricide effect in contact sprays. In vivo, there was obvious improvement in groups treated with plant oils than non-treated group. Drinking water treated birds showed good results than spray treated group. Therefore, it is recommended to use combined plant essential oils in D. gallinae control strategies in poultry.
Key words: Acaricides, Chickens mite, Dermanyssus gallinae, Plant essential oils, Red mite.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
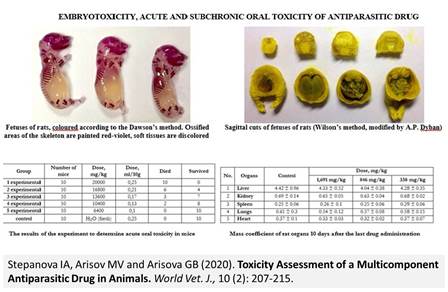
Toxicity Assessment of a Multicomponent Antiparasitic Drug in Animals
Stepanova IA, Arisov MV and Arisova GB.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 207-215, 2020; pii:S232245682000027-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj27
ABSTRACT
The important aspect of the high quality new pharmaceuticals is safety assessment in animals in practical conditions. Toxicity assessment of the new antiparasitic multicomponent drug (Inspector Quadro Tabs) composed of lufenuron, praziquantel and moxidectin in the form of tablets for cats and dogs was carried out. The parameters of acute oral toxicity were determined on white mice and white rats and subchronic toxicity was observed after repeated oral administration to rats. Embryotoxicity and teratogenicity of the drug were also evaluated. As a result of toxicological studies, median lethal doses (LD50) of the drug during oral administration to the 60 white mice were established which were equal to the following: LD50 = 14800 mg/kg (Karber's method), 13800 mg/kg (Miller and Tatener’s method); to the white rats LD50 ˃ 16912 mg/kg; according to the generally accepted classification, the drug belongs to the fourth class of hazard (low hazard substances). It was established that doses of 1691 mg/kg, 846 mg/kg and 338 mg/kg were threshold in a subchronic experiment on the rats. Moreover, it was found that the drug did not possess embryotoxic and teratogenic properties in pregnant female rats. Experimental results have confirmed the low toxicity of a new antiparasitic multicomponent drug.
Key words: Acute toxicity, Antiparasitic Drug, Embryotoxicity, Mice, Rats, Subchronic Toxicity
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
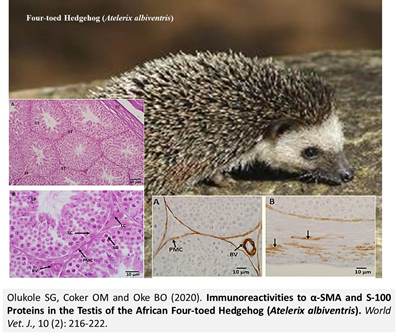
Immunoreactivities to α-SMA and S-100 Proteins in the Testis of the African Four-toed Hedgehog (Atelerix albiventris)
Olukole SG, Coker OM and Oke BO.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 216-222, 2020; pii:S232245682000028-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj28
ABSTRACT
The African four-toed hedgehog is a small nocturnal mammal, characterized by a short-grooved brown or grey spine covering the dorsum of the body with a band of whitish fur running across their forehead, little is known about the reproductive biology of this animal. The present study aimed to evaluating the validity of immunohistochemistry in the differential labelling of the different cellular components of the testis of the African four-toed hedgehog. Paraffin-embedded testicular sections were stained by conventional histological technique using ten male African four-toed hedgehogs captured from the wild animals in Ibadan, Nigeria. Primary antibodies against alpha smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and S-100 were applied on paraffin sections. The peritubular myoid cells, the testicular capsule and vascular endothelium expressed strong immunostaining for α-SMA. The spermatogenic cells, Sertoli and Leydig cells, peritubular myoid cells, the testicular capsule, straight tubules as well as rete testis and vascular endothelium all expressed positive immunostaining for S-100. α-SMA and S-100 proteins play active roles in cytoskeletal physiology of testis of the African four-toed hedgehog while S-100 protein plays additional role in the structural formation and maintenance of the blood-testis barrier during the process of spermatogenesis in the animal. It is concluded that α-SMA and S-100 proteins has active roles in the cytoskeletal structure of testis and physiology of the African four-toed hedgehogs.
Keywords: African four-toed hedgehog, Immunoreactivities, Spermatogenic cells, Sertoli cells, Testis.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
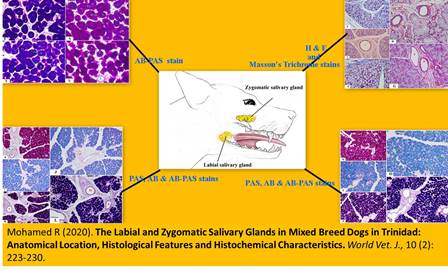
The Labial and Zygomatic Salivary Glands in Mixed Breed Dogs in Trinidad: Anatomical Location, Histological Features and Histochemical Characteristics
Mohamed R.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 223-230, 2020; pii:S232245682000029-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj29
ABSTRACT
The objective of this investigation was to give detailed descriptions of the anatomical location, histological features and histochemical characteristics of the labial and zygomatic salivary glands in mixed breed dogs. This study was performed on five heads of adult mixed breed dogs of both sexes. The heads were dissected to detect in situ position of the labial and zygomatic salivary glands. The glands were dissected and examined grossly. Samples of the glands were taken, processed and stained using hematoxylin and eosin and Masson's Trichrome for histological examination as well as Periodic Acid-Schiff, Alcian Blue (pH 2.5 and 1.0) and a combination of Periodic Acid-Schiff and Alcian Blue (pH 2.5 and 1.0) techniques for histochemical examination. The labial and zygomatic salivary glands were located in the lower lip and in the orbit respectively and they were surrounded by fibrous capsules containing collagen fibers. They were minor, compound, mixed tubuloalveolar glands. They composed of mucous acini, mucous acini with serous demilunes and isolated serous acini. The secretion of the glands (chiefly mucous) consisted of neutral mucins, acid carboxylated mucins and acid sulphated mucins. The duct system of the glands was intralobular (intercalated and striated ducts) and interlobular ducts. The anatomical location as well histological and histochemical structures of the labial and zygomatic salivary glands were important to classify the glands and their secretion as well as to give veterinarians knowledge during clinical examination of the oral and orbital regions, and to recognize normal and pathological conditions.
Keywords: Anatomy, Dog, Labial, Salivary glands, Zygomatic
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
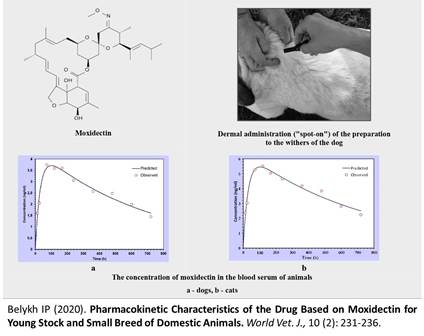
Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of the Drug Based on Moxidectin for Young Stock and Small Breed of Domestic Animals
Belykh IP.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 231-236, 2020; pii:S232245682000030-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj30
ABSTRACT
The pharmacokinetic characteristics of moxidectin in the blood serum of dogs and cats after a single cutaneous (spot-on) application of drug for veterinary use “Inspector Mini” to prevent and treat arachnoses, entomoses and intestinal nematodes in kittens and puppies as well as in small breed dogs and cats were investigated. Twelve outbred dogs and cats of different ages and weights were involved in present study. All the animals were weighed to determine the exact dosage of the drug. The determination of moxidectin in blood serum was carried out by high performance liquid chromatography with pre-column modification of N-methylimidazole and trifluoroacetic anhydride followed by fluorescence detection. According to the results of the study, it was found that moxidectin was well absorbed into the systemic circulation and reached to maximum concentration in the blood serum of dogs and cats after 4-10 days. After treatment with the drug, moxidectin was determined in the blood serum of animals after 12 hours at concentration of 2 ng/ml. Significant concentrations of moxidectin in the blood serum of animals remained for 28 days after topical application (spot-on). Moxidectin was detected in the blood serum of animals at the end of the experiment (after 30 days) which indicates its therapeutic effect for at least one month after the application of the drug.
Key words: Blood Serum, Cats, Dogs, Moxidectin, Pharmacokinetics
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
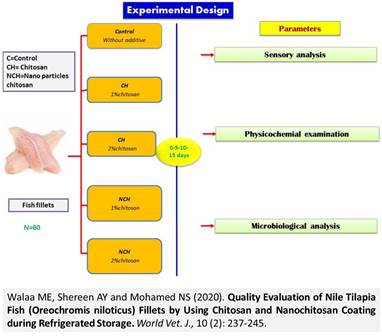
Quality Evaluation of Nile Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis niloticus) Fillets by Using Chitosan and Nanochitosan Coating during Refrigerated Storage
Walaa ME, Shereen AY and Mohamed NS.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 237-245, 2020; pii:S232245682000031-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj31
ABSTRACT
Using natural preservatives has a probability to improve the quality and integrity of fish products. Such research investigated the antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles casing on the quality of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fish fillets through refrigerated storage. In the present investigation solutions of chitosan (1 and 2%) and nanochitosan (1 and 2%) were applied for the casing of tilapia fish slices thereafter stored at 4°C for 15 days. Uncoated (control) and coated fish fillets pieces were examined intermittently for bacteriological parameters (Total bacterial count, Proteolytic bacterial count, Lipolytic bacterial count, and Staphylococcus aureus count), quality parameters (pH, total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N), and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, TBARS) and sensory features. Results showed that 2% chitosan and 2% chitosan nanoparticle solutions were the optimal concentrations for improving the quality of tilapia fish fillets until 10 days of refrigerated storage period compared to the control group. However, using 2% chitosan nanoparticles showed higher antimicrobial activity, strong ability in preventing protein degradation, retarding lipid oxidation, accepted pH values and delay in declining of sensory score more than 2% chitosan solution during the storage period. Therefore, 2% chitosan nanoparticles as a natural preservative can be utilized for the conservation of quality properties and expanding the shelf life of tilapia fish slices through chilled storage.
Key words: Bacteriological and quality parameters, Chitosan, Nanochitosan, Tilapia fish fillets
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
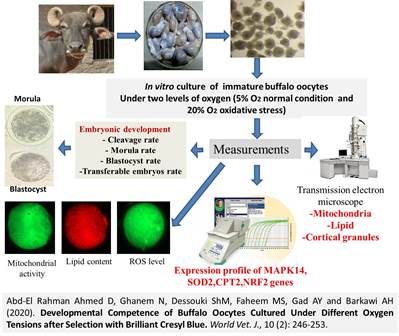
Developmental Competence of Buffalo Oocytes Cultured Under Different Oxygen Tensions after Selection with Brilliant Cresyl Blue
Abd-El Rahman Ahmed D, Ghanem N, Dessouki ShM, Faheem MS, Gad AY and Barkawi AH.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 246-253, 2020; pii:S232245682000032-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj32
ABSTRACT
The aim of this investigation was to follow up in vitro preimplantation development of buffalo cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs) after BCB test and followed by in vitro maturation under two different levels of oxygen tension. Cumulus-oocyte complexes (n=1045) were selected with BCB staining (oocytes with any degree of blue color in cytoplasm was defined as BCB+, oocytes without any degree of blue color in cytoplasm was defined as BCB-) in addition to a third control group. The previous experimental groups (BCB+, BCB-, control) were matured in vitro under low (5%) and high oxygen tension (20%), followed by in vitro fertilization and in vitro culture of presumptive zygotes. There were no differences (P ≤ 0.05) in cleavage, morula and transferable embryos rates among BCB+, BCB- and control group. However, blastocyst rate was greater significantly in control group (14.4 ± 2.0) than BCB- COCs (8.4 ± 1.9). According to the oxygen tension effect, the rate of morula and transferable embryos was increased (P ≤ 0.05) in buffalo COCs developed under low oxygen tension (11.6 ± 1.4 and 23.8 ± 1.9) compared to high oxygen tension group (7.4 ± 1.4 and 17.9 ± 2.1). In addition, cleavage, morula, blastocyst and transferable embryos rates were greater in BCB+ under low (43.6 ± 3.9, 14.9 ± 2.5, 14.1 ± 2.9 and 28.4 ± 3.6) than high oxygen tension group (33.5 ± 3.9, 7.1 ± 2.5, 11.6 ± 2.9 and 18.8 ± 3.6) which may reflect enhanced biological processes controlling early development. Moreover, blastocyst rate was significantly higher in control group cultured under high (12.0 ± 2.9) and low (16.9 ± 2.8) oxygen level than their counterparts of BCB- group (9.3 ± 2.9 and 7.6 ± 2.6, respectively). In conclusion, there was no differences in embryo development between BCB+ and BCB-, COCs; therefore, oocyte selection based on BCB staining is not an effective tool to select developmental competent buffalo COCs. Buffalo morula and transferable embryos prefer low oxygen tension for early development, which should be applied during in vitro embryo production of this species.
Keywords: Brilliant cresyl-blue staining, Cumulus-oocyte complex, Morula, Preimplantation.
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
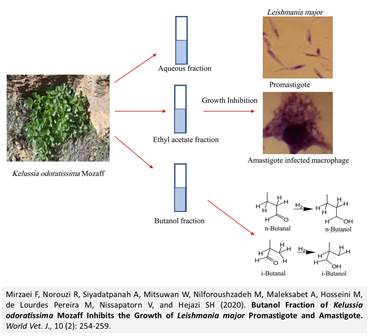
Butanol Fraction of Kelussia odoratissima Mozaff Inhibits the Growth of Leishmania major Promastigote and Amastigote
Mirzaei F, Norouzi R, Siyadatpanah A, Mitsuwan W, Nilforoushzadeh M, Maleksabet A, Hosseini M, de Lourdes Pereira M, Nissapatorn V, and Hejazi SH.
World Vet. J. 10(2): 254-259, 2020; pii:S232245682000033-10
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.36380/scil.2020.wvj33
ABSTRACT
Naturally derived compounds have been used to treat several infectious diseases including leishmaniasis. The study aimed to investigate the in vitro effects of Kelussia odoratissima Mozaff extract on Leishmania major promastigote and amastigote. Dried leaves of K. odoratissima were fractionated by 3 solvents including aqueous, butanol, and ethyl acetate. The results showed that the butanol fraction of K. odoratissima showed the highest anti-Leishmania effects against L. major promastigotes. Ninety four percent growth inhibition of the promastigote was observed when cells were treated with the 1,280 µg/mL butanol fractions. Moreover, 100% inhibition of amastigotes was detected after treatment with the butanol fraction. Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of the butanol fraction in promastigotes and amastigotes was 264.1 and 154.1 µg/mL, respectively. The obtained results suggested the potential medicinal benefits of K. odoratissima butanol fraction as an alternative treatment for leishmaniasis caused by L. major infections.
Key words: Amastigotes, Butanol fraction, Leishmania major, Kelussia odoratissima Mozaff, Promastigotes
[Full text-PDF] [XML] [Google Scholar] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).