Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 14 (3); September, 2024 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 14 (3); September, 2024 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Biochemical Studies on Efficiency of Natural Gum in Chronic Kidney Failure and Liver Cirrhosis in Rats
Lotfy MM, Abdel-Mobdy E, Abdel-Mobdy YE, Salem HM, and Ali HFM.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 293-310, 2024; pii:S232245682400036-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj36
ABSTRACT: It is well-established that apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation are associated with several disorders, including chronic renal disease and hepatic disease. Oxidative stress (OS) is a major cause of death from end-stage renal disease which also contributes to atherosclerosis and cardiac issues. The present study aimed to assess the efficacy of Gum Arabic (GA) in mitigating renal damage and hepatotoxicity in rats induced by Chloropyrifos-methyl (CPM). A total of 42 male Wistar rats were divided into seven groups, with four groups (group 2 [IC], group 5 [GA1+IC]a, group 6 [GA2+IC], and group 7 [GA1+IC]b treated with CPM for eight weeks to induce hepatic and renal damage. Two models of GA administration, including the standard oral model in drinking water (15% w/v) and the oral model by gavage at a dose of 1 g/kg body weight were administered. Physiological parameters of kidney and liver functions, including urea, creatinine, AST, and ALT along with anti-oxidant factors (Melaodialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, reduced glutathione, and catalase) were measured in plasma, and homogenates of renal and hepatic tissues on day 57 of the experiment. In addition, histopathological examination was conducted on liver and kidney tissues using hematoxylin and eosin stain to evaluate the efficacy of GA on damaged tissues. Gum Arabic was found to significantly reduce CPM toxic effects in the liver and kidney in groups treated with CPM as liver and kidney parameters were reduced to normal levels. Furthermore, GA reduced histological indicators of inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis, as well as renal morphological damage. Additionally, it reduced OS in liver and kidney homogenates. In conclusion, GA effectively reduced the damage that CPM inflicted on liver and kidney tissue by stabilizing physiological parameters to normal levels and repairing cellular structures damaged by OS.
Keywords: Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, Gum Arabic, Kidney, Liver, Oxidative stress
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
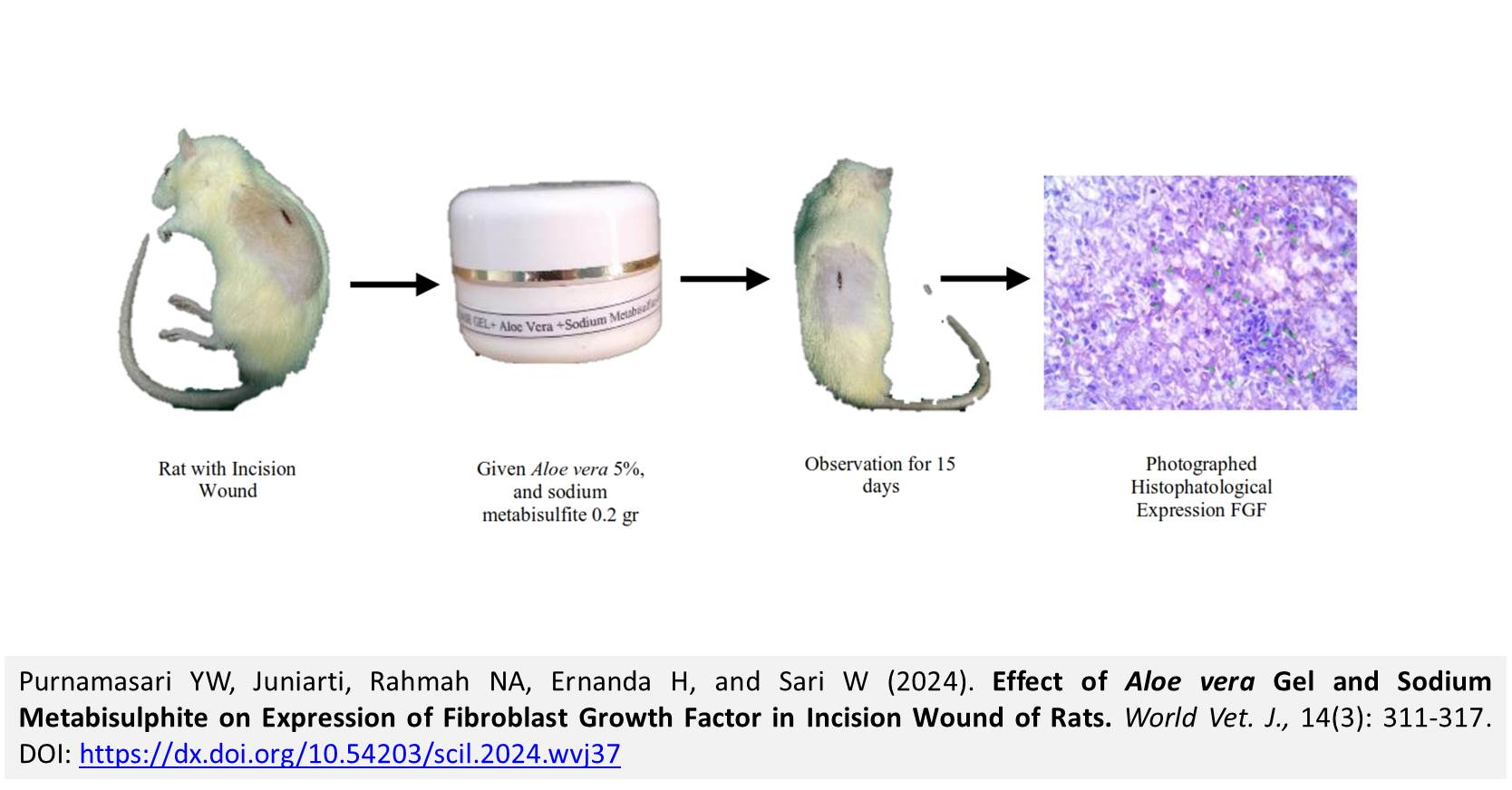
Effect of Aloe vera Gel and Sodium Metabisulphite on Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Incision Wound of Rats
Purnamasari YW, Juniarti, Rahmah NA, Ernanda H, and Sari W.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 311-317, 2024; pii:S232245682400037-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj37
ABSTRACT: An incision wound is a wound caused by being sliced. Two ingredients that play a key role in the wound-healing process are glucomannan and acemannan, which are rich in polysaccharides and growth hormones. Growth hormones stimulate fibroblast activity and proliferation. The present study involved 35 Sprague Dawley male rats, aged 2-3 months old and weighing 200-300 grams. The study comprised seven groups including, negative control group (G1), positive control (aquades, G2), betadine 10% (G3), gel base (0.5 mg, G4), gel base + sodium metabisulfite 0.2 gr (G5), gel base + Aloe vera 5% (G6), and gel base + Aloe vera 5% + sodium metabisulfite 0.2 gr (G7). Each group had five replications. Initially, a 4-cm incision was made on the dorsal skin of each rat. The study lasted 15 days with observations made on days 3, 7, and 15. After the observation period, the rats were anesthetized and then terminated to collect skin tissues for microscopic examination. The tissue samples were then stained immunohistochemically to assess fibroblast growth factor (FGF) expressions. The results showed that the highest FGF expression was observed in the 5% Aloe vera + 2% metabisulfite group (G7), while the lowest FGF expression was in the negative control group (G1). It is concluded that Aloe vera L. extract gel at 5% + 2% metabisulfite (G7) significantly enhances the expression of FGF.
Keywords: Aloe vera L, Fibroblast growth factor, Incision wound, Skin, Sodium metabisulfite
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
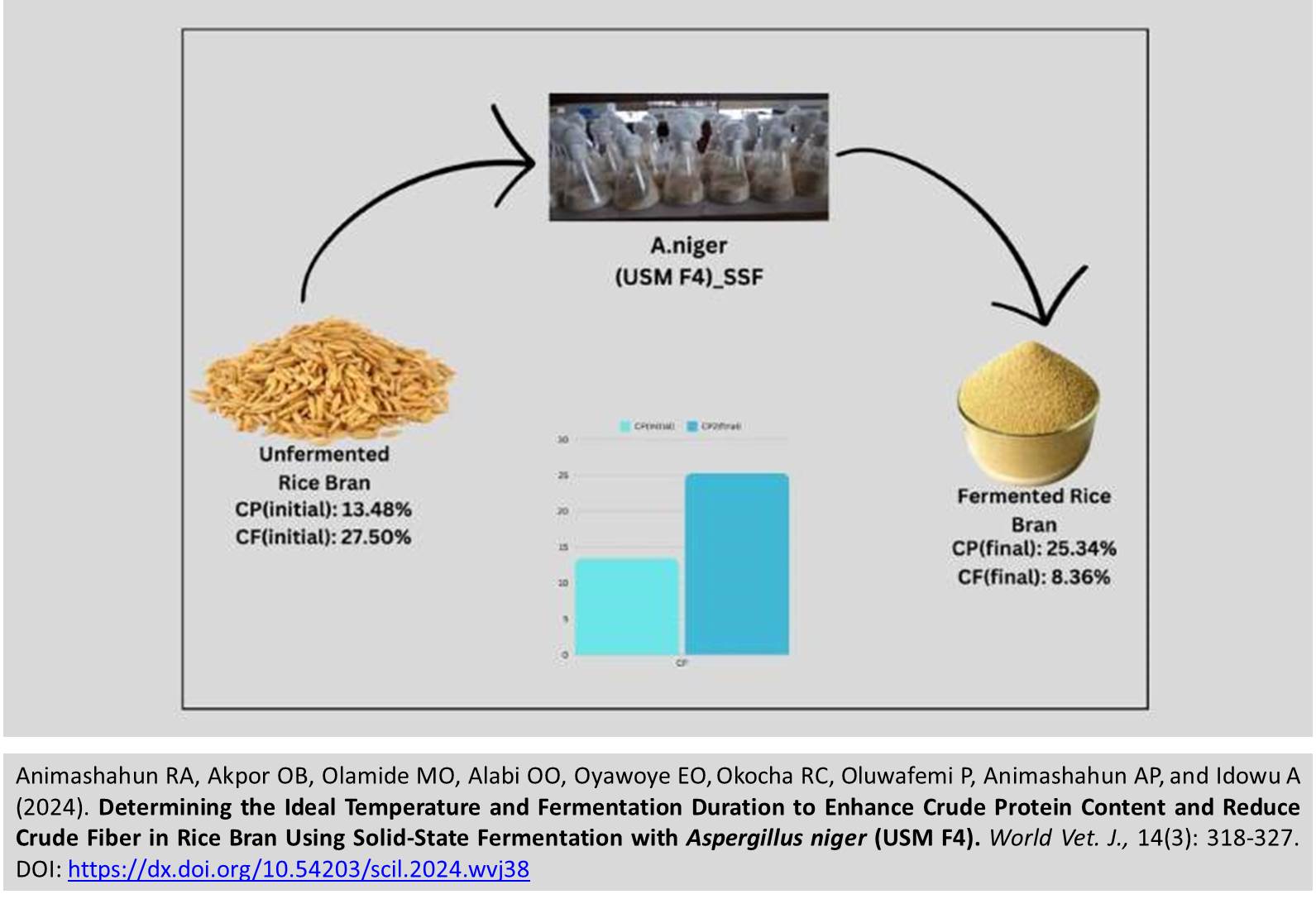
Determining the Ideal Temperature and Fermentation Duration to Enhance Crude Protein Content and Reduce Crude Fiber in Rice Bran Using Solid-State Fermentation with Aspergillus niger (USM F4)
Animashahun RA, Akpor OB, Olamide MO, Alabi OO, Oyawoye EO, Okocha RC, Oluwafemi P, Animashahun AP, and Idowu A.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 318-327, 2024; pii:S232245682400038-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj38
ABSTRACT: Solid-state fermentation (SSF) offers a sustainable method for enhancing the nutritional quality of agricultural residues such as red rice bran. This study aimed to determine the optimal temperature and duration for SSF of red rice bran, focusing specifically on increasing the crude protein (CP) content and reducing the crude fiber (CF) content. SFF of rice bran with Aspergillus niger (A. niger) USM F4 was conducted over 14 consecutive days at three different temperatures (25°C, 35°C, and 45°C). A total of 63 samples of rice bran were divided into three temperature groups, each containing 21 samples. Three samples per group were collected at 48-hour intervals over the 14-day fermentation period. The fermentation process for the collected samples at 48-hour intervals was halted by oven drying at 60°C for 24 hours. The fermented products were subjected to proximate analysis for crude protein (CP), ash, ether extract (EE), and crude fiber (CF) contents using the methods outlined by the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). The results revealed a significant effect of temperature and fermentation duration on CP, ash, EE, and CF content when compared to the unfermented rice bran kept at room temperature (25oC). The peak values of CP and the highest degradation of CF across all temperature levels were observed on day 10 while the maximum increase in ash and EE content occurred on day 8. Among the temperature conditions, the highest CP values and the lowest CF values were recorded at 35°C. Conversely, the lowest improvements in CP and CF degradation were observed at 25°C on day 10. In conclusion, the optimal conditions for SSF of rice bran with A. niger to enhance CP content and degrade CF are a temperature of 35°C and a fermentation duration of 10 days.
Keywords: Alternate feed resource, Animal production, Aspergillus niger, Proximate component, Solid-state fermentation, Value- addition
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
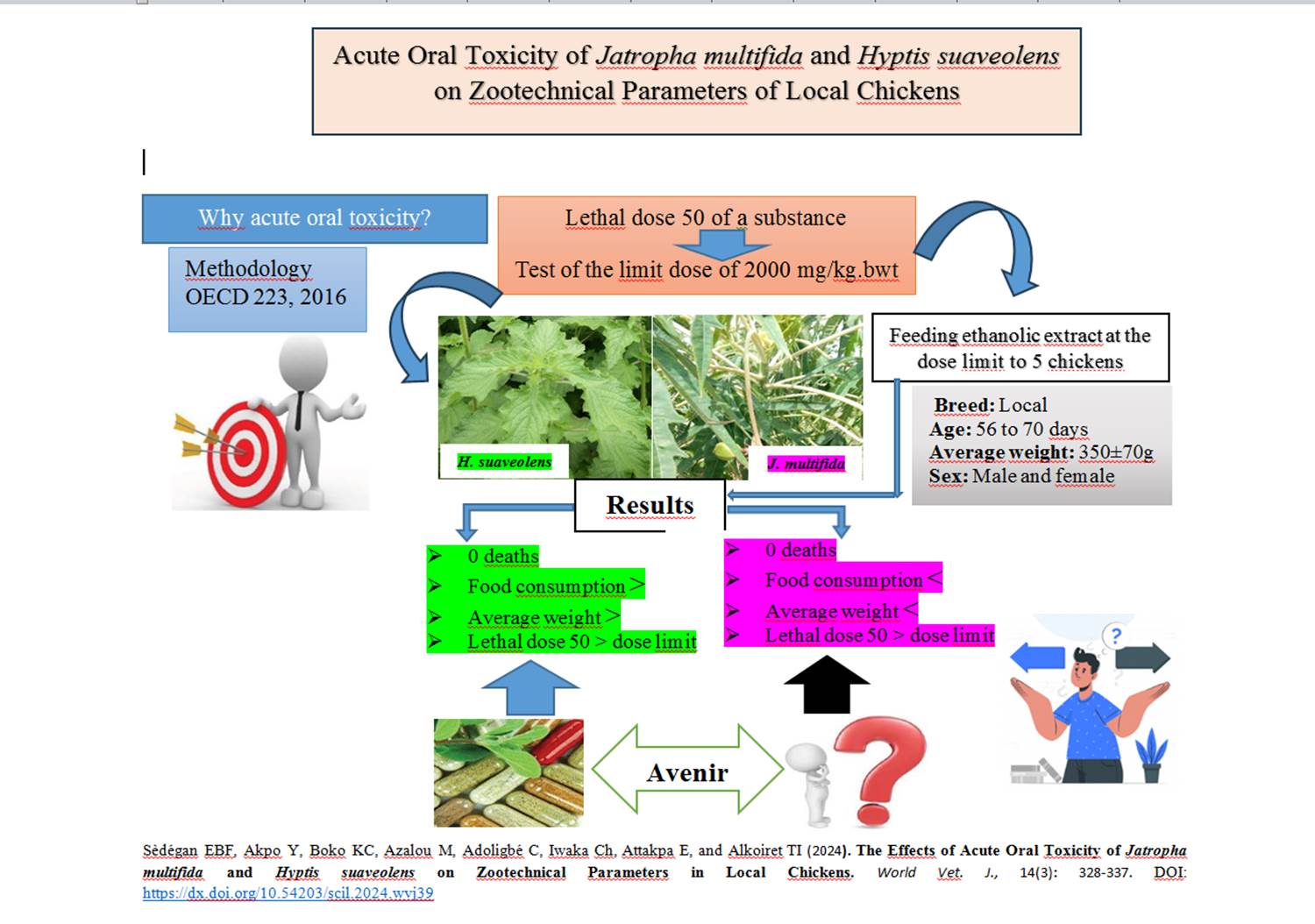
The Effects of Acute Oral Toxicity of Jatropha multifida and Hyptis suaveolens on Zootechnical Parameters in Local Chickens
Sèdégan EBF, Akpo Y, Boko KC, Azalou M, Adoligbé C, Iwaka Ch, Attakpa E, and Alkoiret TI.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 328-337, 2024; pii:S232245682400039-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj39
ABSTRACT: The substantial use of medicinal plants in traditional poultry farming is a well-established practice. The present study aimed to determine the median lethal dose (LD50) of ethanolic extracts of Jatropha multifida and Hyptis suaveolens in local chickens and to assess the effects of these extracts on feed intake, water intake, and average body weight. The methodology followed OECD Directive 223, which involves administering the highest dose of the extract to the chickens and assessing any mortality. Three homogeneous groups of five chickens each were formed for the limit dose test. The control group received distilled water, while batches 1 and 2 received 700 mg of ethanolic extract of J. multifida and H. suaveolens, respectively. The average body weight of the chickens was 350g ± 20, and the extracts were administered via gavage at a suspension of 2000 mg/kg.bwt of the extract dissolved in water. The results of the phytochemical tests indicated the presence of several chemical compounds known for their therapeutic effects. The productivity of the extract was 2.75 ± 0.19 for J. multifida and 3.3 ± 0.27 for H. suaveolens. After administration of the suspensions, observation for 14 days revealed no mortality. This finding indicated that the LD50 of the utilized ethanolic extracts exceeds the limit dose (2000 mg/kg.bwt). However, feed intake (49 ± 3 > 46±4) and average body weight (436 ± 31 > 388 ± 37) in batch 2 were significantly higher than those in batch 1. Future research should explore the subacute toxicity of J. multifida and H. suaveolens across various chicken breeds.
Keywords: Body weight, Lethal Dose, Local chicken, Medicinal plant, Mortality, Toxicity
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
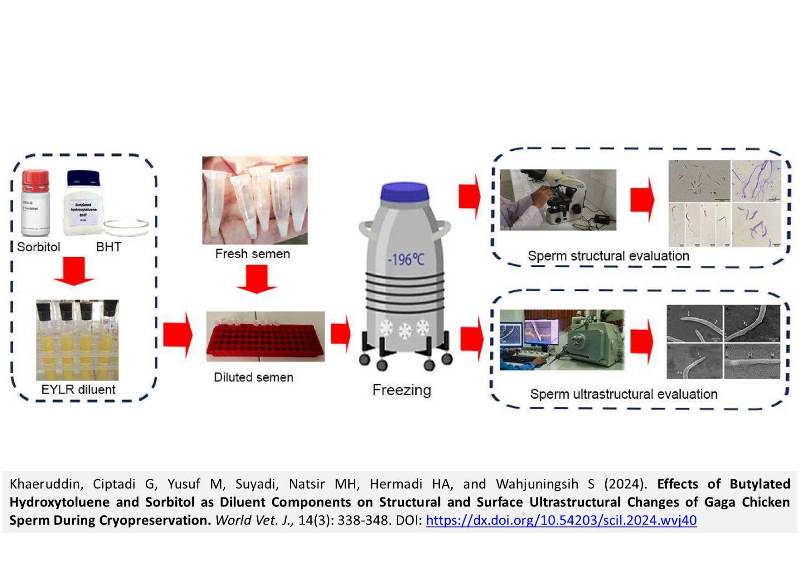
Effects of Butylated Hydroxytoluene and Sorbitol as Diluent Components on Structural and Surface Ultrastructural Changes of Gaga Chicken Sperm During Cryopreservation
Khaeruddin, Ciptadi G, Yusuf M, Suyadi, Natsir MH, Hermadi HA, and Wahjuningsih S.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 338-348, 2024; pii:S232245682400040-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj40
ABSTRACT: The Gaga chicken is an indigenous Indonesian breed that is important to preserve using semen cryopreservation technology. The study was conducted to determine the effect of adding sorbitol and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) in the diluent on the structural and surface ultrastructure of cryopreserved Gaga chicken sperm during cryopreservation /frozen storage. The study aimed to assess how adding sorbitol and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) to the diluent affects the structure and surface ultrastructure of cryopreserved Gaga chicken sperm. A completely randomized design was employed with four treatments and 10 replications including egg yolk-lactate ringer diluent (EYLR) as the control group, EYLR diluent with 3 mM BHT, EYLR diluent with 2% sorbitol, and EYLR diluent with both 3 mM BHT and 2% sorbitol. Semen was collected using a massage technique from 4 male chickens aged approximately 10 months, pooled semen was diluted, packaged in 0.25 mL straws, equilibrated for 2 hours at 5 °C, pre-freeze for 10 minutes, frozen for 24 hours, and thawed for 30 seconds at 37 °C. The parameters evaluated were sperm plasma membrane integrity, acrosome integrity, DNA damage, mitochondrial functionality, and surface ultrastructure. The results showed that the treatment had a significant effect on plasma membrane integrity and post-thawing mitochondrial functionality compared to the control, but no effect was observed on acrosome integrity or DNA damage. The results showed that the combination treatment of BHT with sorbitol had a significant effect on plasma membrane integrity and post-thawing mitochondrial function, but did not affect acrosome integrity or DNA damage when compared to the control group. Ultrastructural observations indicated that cryopreservation caused damage to the head, middle, and tail of the sperm in the control groups. However, these changes were prevented by the diluent containing a combination of BHT and sorbitol. The addition of both components (BHT 3 mM + sorbitol 2%) effectively maintained plasma membrane integrity, mitochondrial functionality, and surface ultrastructure of Gaga chicken sperm during cryopreservation.
Keywords: Butylated hydroxytoluene, Chicken sperm, Cryopreservation, Sorbito, Structure, Sperm ultrastructure
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
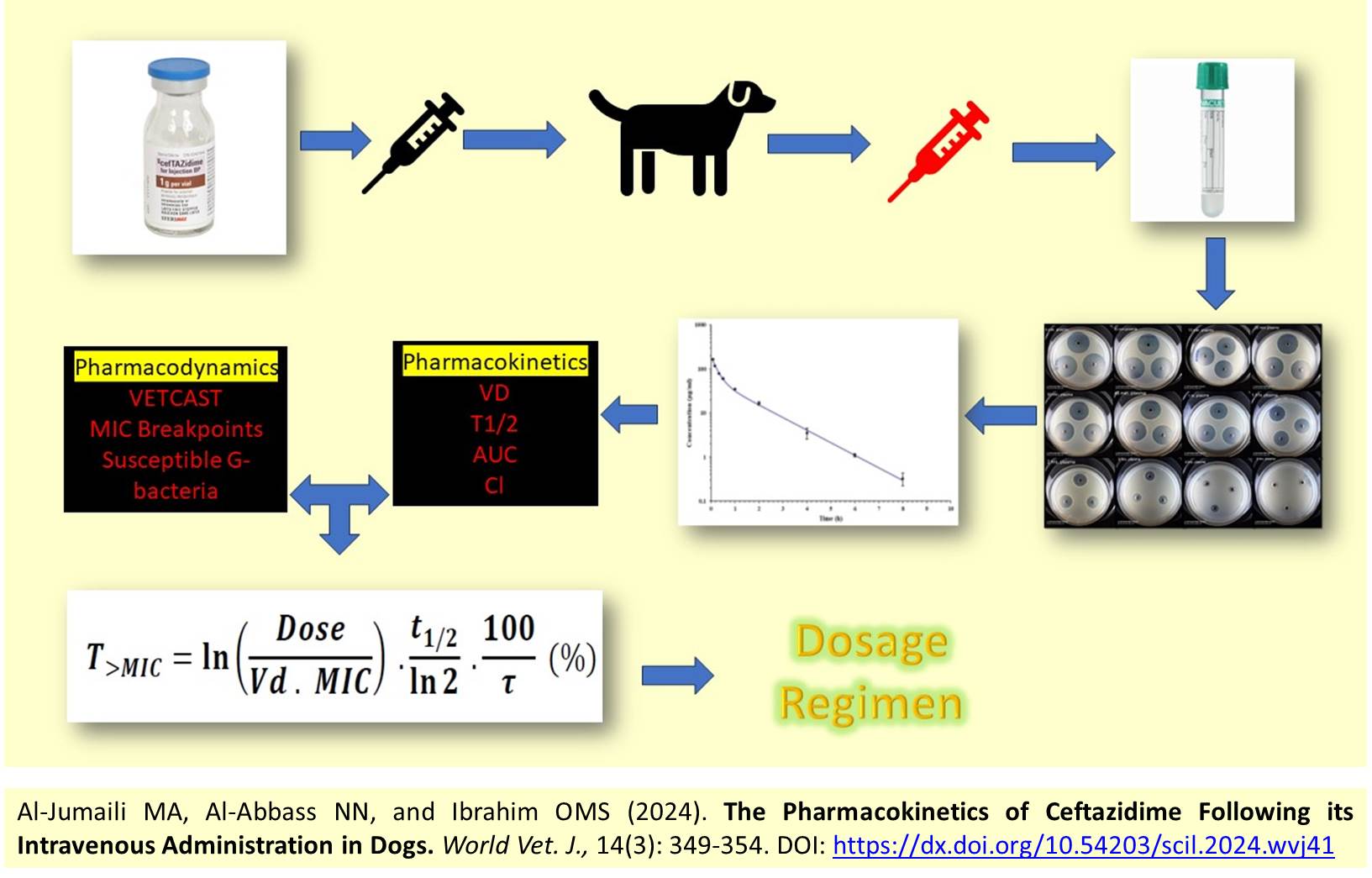
The Pharmacokinetics of Ceftazidime Following its Intravenous Administration in Dogs
Al-Jumaili MA, Al-Abbass NN, and Ibrahim OMS.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 349-354, 2024; pii:S232245682400041-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj41
ABSTRACT: Ceftazidime is a beta-lactam that is used in the treatment of bacterial infections in humans and companion animals, such as dogs and cats. It is prescribed to treat gram-negative infections, especially those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This study aimed to compare the pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime using a microbiological assay to evaluate the adequacy of the proposed dosage regimens for susceptible gram-negative bacteria. For this purpose, five healthy mongrel male dogs, with a mean age of four years and an average weight of 19.1 kg, were administered a single intravenous bolus dose of ceftazidime (20 mg/kg). Plasma concentrations were measured using a microbiological assay, and dosage regimens were established by integrating pharmacokinetics data with pharmacodynamics parameters. The results showed that ceftazidime was rapidly distributed to the peripheral tissues (0.189 L/kg), with a half-life of 1.15 hours and a clearance rate of 0.166 L/hr./kg. The results obtained from the pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamic integration suggested 20 mg/kg q8 hours of ceftazidime for susceptible gram-negative bacteria with a Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of ≤ 8 µg/ml, and 20 mg /kg q12 hours of ceftazidime for susceptible gram-negative bacteria with a Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of ≤ 4 µg/ml. In conclusion, a mild correlation was observed between the dogs’ weight and the ceftazidime half-life, which led to an adjustment of the proposed dosage regimen to 20 mg/kg q8 hours.
Keywords: Ceftazidime, Dog, Dosage regimen, Gram-negative microbe, Pharmacokinetic
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
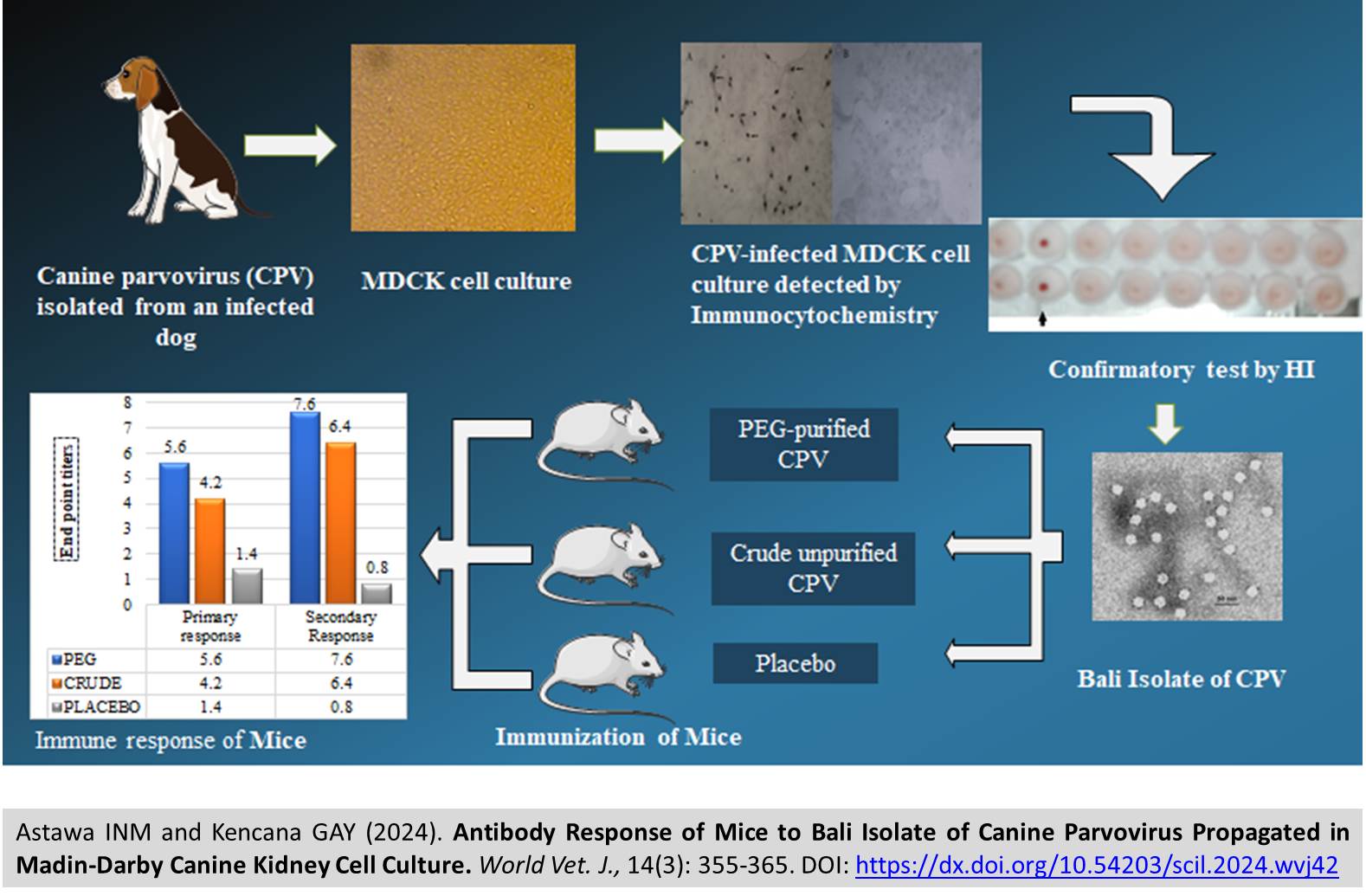
Antibody Response of Mice to Bali Isolate of Canine Parvovirus Propagated in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney Cell Culture
Astawa INM and Kencana GAY.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 355-365, 2024; pii:S232245682400042-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj42
ABSTRACT: Canine parvovirus (CPV) infection is still common among dogs, leading to severe disease with high mortality. The potential of a local isolate of CPV as an effective vaccine to prevent the disease warrants investigation. This study aimed to determine the antibody response in mice against a Bali isolate of CPV propagated in the Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cell culture. The virus was purified using polyethylene glycol (PEG)-6000 and mixed with an Aluminum hydroxide adjuvant. Fifteen 7-week female mice were divided into three treatment groups: treatment group 1 (PEG-purified virus and Adjuvant), treatment group 2 (crude unpurified virus and adjuvant), and treatment group 3 (adjuvant without virus), with five replicates per group. The Bali isolate of CPV was successfully replicated in MDCK cells, achieving a titer of 210-211 hemagglutination (HA) units after eight serial passages through the cell culture. The virus was confirmed as CPV by immunocytochemistry test using a monoclonal antibody and hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test using chicken anti-CPV polyclonal antibody. Following the first immunization, the antibody endpoint titer in mice immunized with PEG-purified CPV (5.6) was significantly higher than those immunized with crude unpurified CPV (4.2) and adjuvant without CPV (1.4). Similarly, after the second immunization, the antibody endpoint titer in mice immunized with PEG-purified CPV (7.6) also remained significantly higher than those immunized with crude unpurified CPV (6.4) and adjuvant without CPV (0.8). Significant increases in antibody endpoint titer were observed after the second immunization in mice immunized with PEG-purified CPV and crude unpurified CPV, but not in those given adjuvant without CPV. The Bali isolate of CPV propagated in MDCK cell culture induced a robust antibody response in mice, suggesting it’s a potential as an alternative vaccine candidate for preventing CPV infection in dogs.
Keywords: Bali, Canine parvovirus, Madin-Darby Canine Kidney, Mice, Vaccines
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Two Types of Estrogen on the Follicular Wave for in Vivo Oocyte Collection in Brown Swiss Cows
Payano IU, Eulogio CQ, Gómez EA, Carhuas JN, Villar FA, Fermín JU, and Sánchez NM.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 366-372, 2024; pii:S232245682400043-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj43
ABSTRACT: The manipulation of follicular waves through hormonal treatments, such as estrogen administration, plays a crucial role in optimizing in-vivo oocyte collection for assisted reproductive technologies. The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of two specific types of estrogen on follicular wave dynamics and their impact on in-vivo oocyte collection in Brown Swiss cows. Fourteen cows, in their first lactation, weighing approximately 340 kg were randomly assigned to one of two treatments including T1 (estradiol cypionate) and T2 (estradiol benzoate). Both treatments were administered at 1.2 mg of estrogen, at day 0 of the experiment. All Brown Swiss cows were provided with a diet entirely consisting of alfalfa grazing. On day 7, follicular wave dynamics were assessed using a DP-50 vet ultrasound device equipped with a 7.5 MHz transducer for transvaginal follicular aspiration guidance. Follicle counts were categorized into three size ranges including 2-4 mm (small), 4-8 mm (medium), and greater than 8 mm (large). Additionally, the quantity and quality (viable oocytes) of the collected oocytes were evaluated by the Ovum Pick Up (OPU) team for oocyte viability on day 7. The study assessed the follicular dynamics (number of follicles) and efficiency of oocyte collection (viable oocytes) in cows treated with Estradiol Cypionate (T1) and Estradiol Benzoate (T2). The average number of small, medium-sized, and large follicles size were 6.048 ± 6.037, 3.16 ± 2.01, and 0.53 ± 0.67 respectively. The total number of follicles was 9.59 ± 3.56. The mean number of viable oocytes recovered was 3.024 ± 1.66, while the mean number of non-viable oocytes was 1.47 ± 1.01. The results indicated no significant differences between treatments in the size of small, medium, and large follicles, nor in the total number of follicles and viable oocytes recovered. However, a significant difference was observed in the number of non-viable oocytes recovered, with a higher mean in T2 (1.86) compared to T1 (1.09). The results indicated an adequate follicular response and viable oocyte recovery in both treatment groups (estradiol cypionate and estradiol benzoate). However, variations in oocyte viability were observed, with estradiol cypionate showing a slight advantage.
Keywords: Follicle count, Follicular wave dynamic, Oocyte collection, Transvaginal follicular aspiration
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Multidrug Resistance in Stray Cats of The North Surabaya Region, East Java, Indonesia
Wibisono FJ, Widiasih DA, Mentari AO, Isnaeni M, Qurratu'ain SH, Jalal I, Islam AF, Al Fardiansyah, and Nguyen-Viet H.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 373-379, 2024; pii:S232245682400044-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj44
ABSTRACT: Stray cats survive by getting food or drink that is available in the environment, correspondingly, stray cats have relatively high exposure to antibiotic resistance obtained from resistant bacteria found in the environment. The present study was conducted to determine patterns of multidrug resistance and Escherichia coli resistance in stray cats. A total of 50 stray cat anal swab samples were taken randomly from the previously recorded stray cat population in the Surabaya area, East Java, Indonesia. Samples were brought using buffered peptone water. They were cultured on MacConkay Agar differential selective media, and all suspicious colonies of Escherichia coli were examined by biochemical tests. Isolates were then identified, and susceptibility testing was performed according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. The results of the resistance test indicated that the multidrug resistance in Escherichia coli bacteria taken from cats was 14.6% (7/48). The high antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli bacteria in stray cats, which were resistant to many drugs, provides an early warning of environmental health. Environmental health is closely related to animal and human health, especially antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Antibiotic, Antimicrobial resistance, Escherichia coli, Multidrug resistance, Stray cat
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
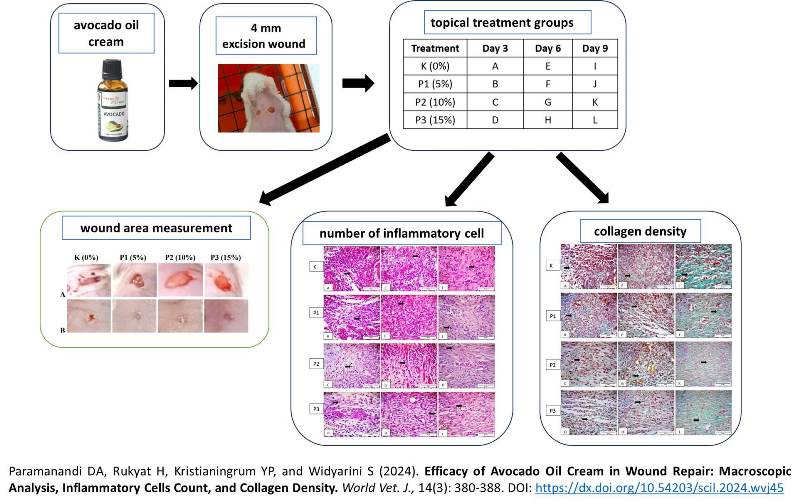
Efficacy of Avocado Oil Cream in Wound Repair: Macroscopic Analysis, Inflammatory Cells Count, and Collagen Density
Paramanandi DA, Rukyat H, Kristianingrum YP, and Widyarini S.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 380-388, 2024; pii:S232245682400045-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj45
ABSTRACT: The wound healing process goes through a series of complex stages that are mutually continuous, namely inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. Following wound formation and the release of proinflammatory cytokines and growth factors, inflammation occurs immediately after the hemostasis phase. Proliferation occurs when products processed by the growth factors are present. The final stage, maturation, is portrayed by the plan of the extracellular network. This study utilized oil from avocado fruit (Persea americana), which contains linoleic and oleic acid content that supports skin tissue repair. The study aimed to explore the effects of using avocado oil cream on the area of wound healing, the number of inflammatory cells, and the collagen density. Twenty-four female mice, aged eight weeks, were used as experimental animals by making excision wounds using a 4 mm biopsy punch on the dorsal skin on the left and right sides. The mice were divided into four groups based on the percentage of avocado oil in the topical cream included Group K (control, topical cream without avocado oil), Group P1 (5% topical avocado oil cream), Group P2 (10% topical avocado oil cream), and Group P3 (15% topical avocado oil cream). Macroscopic examination of the wounds was conducted daily on days 3, 6, and 9 after topical cream treatment using a digital caliper. A total of 48 skin tissue samples were collected from days 3, 6, and 9 after cream application, which were then processed for histopathology evaluations using hematoxylin-eosin staining and Masson’s Trichrome staining. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to count the inflammatory cells, and Masson's Trichrome staining was employed to assess collagen density. The results revealed that avocado oil had a great impact on wound closure after 9 days of 15% avocado oil cream treatment, reducing the inflammatory cells after 3-6 days of 10% avocado oil cream therapy, and increasing collagen density after 9 days of 15% avocado oil cream application, as compared to the control, non-avocado oil cream group. Avocado oil can help close wounds, reduced the number of inflammatory cells, and increased collagen density when used in topical pharmaceutical formulations. Avocado oil cream may, therefore, be considered a viable option for wound repair treatment.
Keywords: Avocado oil, Collagen, Inflammatory cell, Wound repair
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
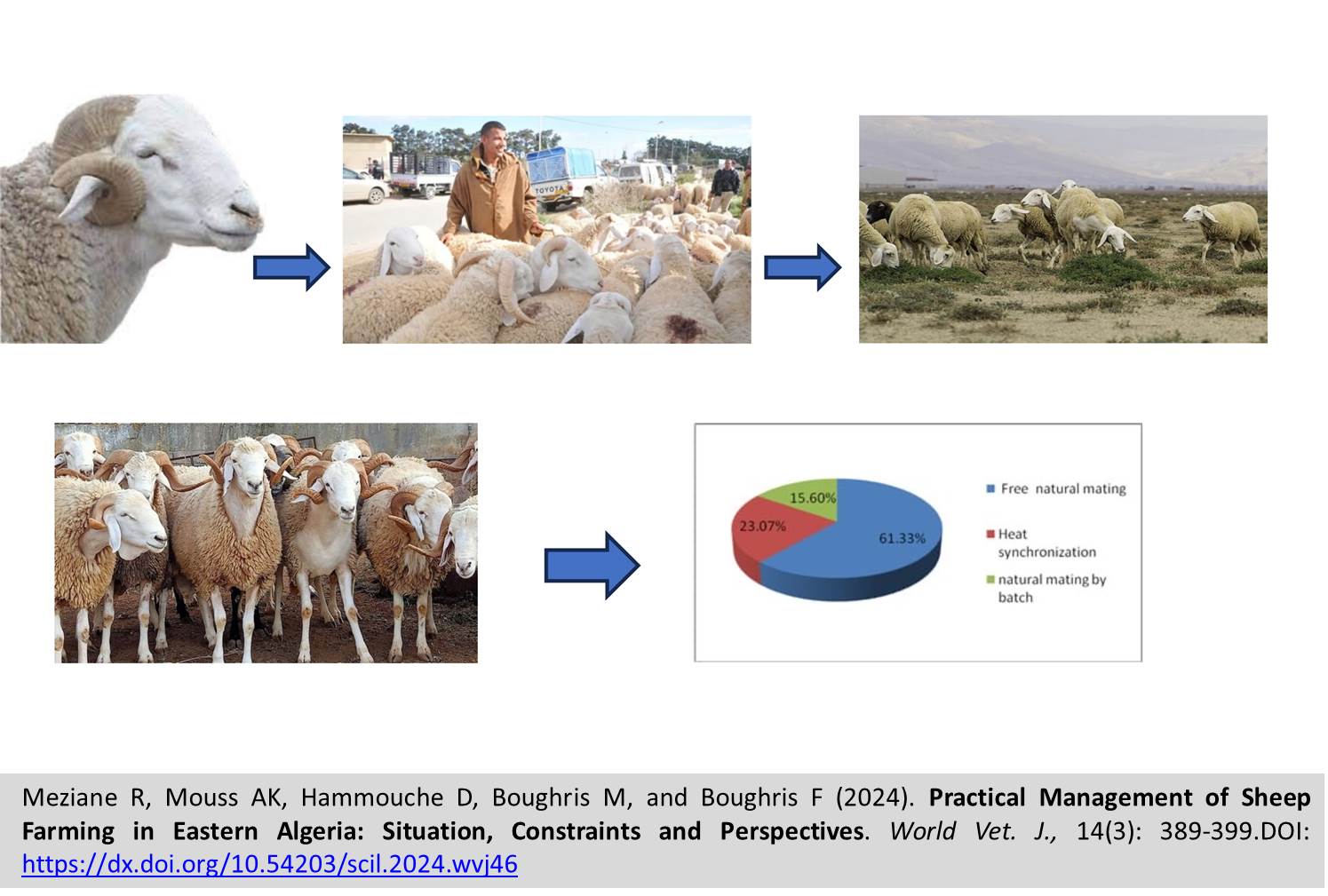
Practical Management of Sheep Farming in Eastern Algeria: Situation, Constraints and Perspectives
Meziane R, Mouss AK, Hammouche D, Boughris M, and Boughris F.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 389-399, 2024; pii:S232245682400046-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj46
ABSTRACT: Successful sheep farming requires hands-on management and a thorough understanding of the factors that influence it. This necessitates a practical, well-organized approach to ensure the flock's health, productivity, and profitability. Various factors, such as climate, available resources, and management strategies, play a crucial role in determining the success of sheep farming. This study, conducted in the Batna region of Algeria, aimed to assess sheep breeding practices and production performance through a questionnaire distributed to farmers and veterinarians. The study encompassed 14,124 sheep, including 9,435 ewes, from 33 Batna region farms to evaluate production and reproduction performance. The findings revealed that the Ouled Djellal breed is the most prevalent, comprising 61.02% of the sheep population. The results indicated that sheep farming in the region largely relies on traditional extensive grazing systems. It is worth noting that breeding practices have not consistently followed recommended guidelines, as evidenced by a suboptimal sex ratio of 36.28. Additionally, only 21.94% of breeders had employed heat synchronization methods, and artificial insemination was not utilized. The low adoption of artificial insemination is primarily attributed to factors, including a lack of knowledge regarding reproductive management, along with challenges related to illiteracy and limited access to essential resources. The analysis further demonstrated that all categories of sheep were profitable; however, profitability was influenced by factors, such as environmental conditions, feed availability, and the age of the animals. The study underscored significant findings, including the prevalence of the Ouled Djellal breed and the limited use of advanced breeding practices, such as artificial insemination, in the Batna region. The value of the current study lies in its comprehensive examination of traditional sheep farming practices and its recommendations for enhancing productivity. These include improving management practices, increasing access to resources, and promoting genetic improvement by adopting advanced breeding technologies.
Keywords: Ewe, Livestock management, Nutrition, Ouled Djellal, Performance
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
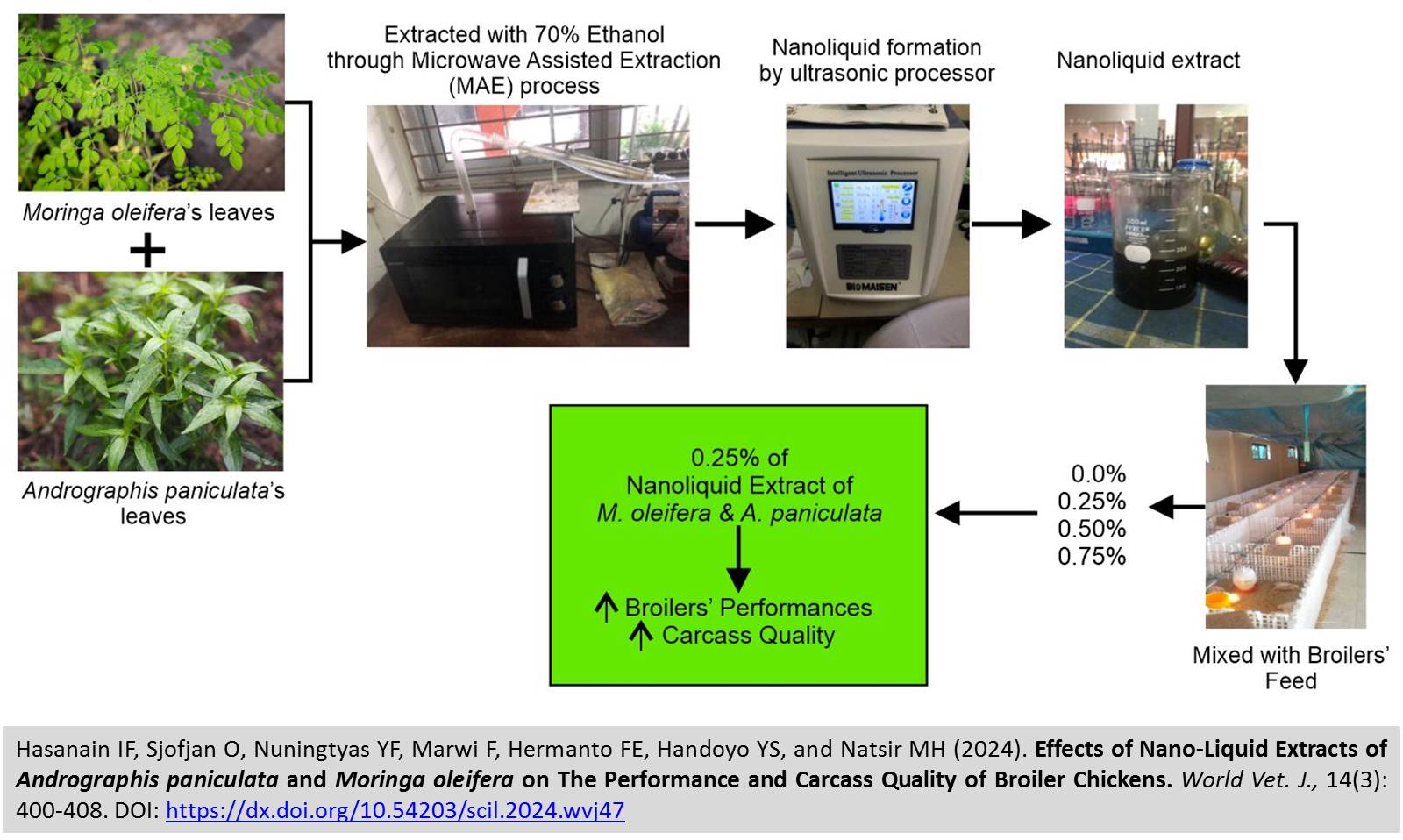
Effects of Nano-Liquid Extracts of Andrographis paniculata and Moringa oleifera on The Performance and Carcass Quality of Broiler Chickens
Hasanain IF, Sjofjan O, Nuningtyas YF, Marwi F, Hermanto FE, Handoyo YS, and Natsir MH.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 400-408, 2024; pii:S232245682400047-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj47
ABSTRACT: Feed was crucial for achieving optimal productivity in broiler chickens, which required ongoing monitoring of its quantity and quality. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of nanoliquid extracts from Andrographis paniculata and Moringa oleifera used as photobiotic on the performance and carcass quality of broiler chickens. The research involved 128 broiler chickens, which were divided into four treatment groups, each with four replications of eight broiler chickens. The treatments included a control group (T0), a 0.25% nano liquid extract mixture of Andrographis paniculata and Moringa oleifera (T1), a 0.50% nanoliquid extract mixture (T2), and a 0.75% nanoliquid extract mixture (T3). The study utilized an in vivo method and analysed the data using a completely randomized design. The optimal level of nano liquid extract was determined based on chicken performance (feed consumption, body weight, feed conversion ratio (FCR), income-over-feed cost (IOFC)) and carcass quality (carcass percentage, cooking loss, meat color, water-holding capacity, and texture). The findings indicated that the addition of combined Andrographis paniculata and Moringa oleifera (1:1, w/w) nano-liquid extract in the chickens’ feed significantly influenced body weight, FCR, and IOFC. However, there was no significant effect on feed consumption. Furthermore, the use of Andrographis paniculata and Moringa oleifera combination had a significant impact on all carcass quality parameters beyond *b carcass color. It was concluded that the addition of 0.25% of combined Andrographis paniculata and Moringa oleifera nano liquid extract yielded the most favorable outcomes for the performance and carcass quality of broiler chickens.
Keywords: Andrographis paniculata, Broiler chicken, Carcass quality, Moringa oleifera, Nano liquid, Performance
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
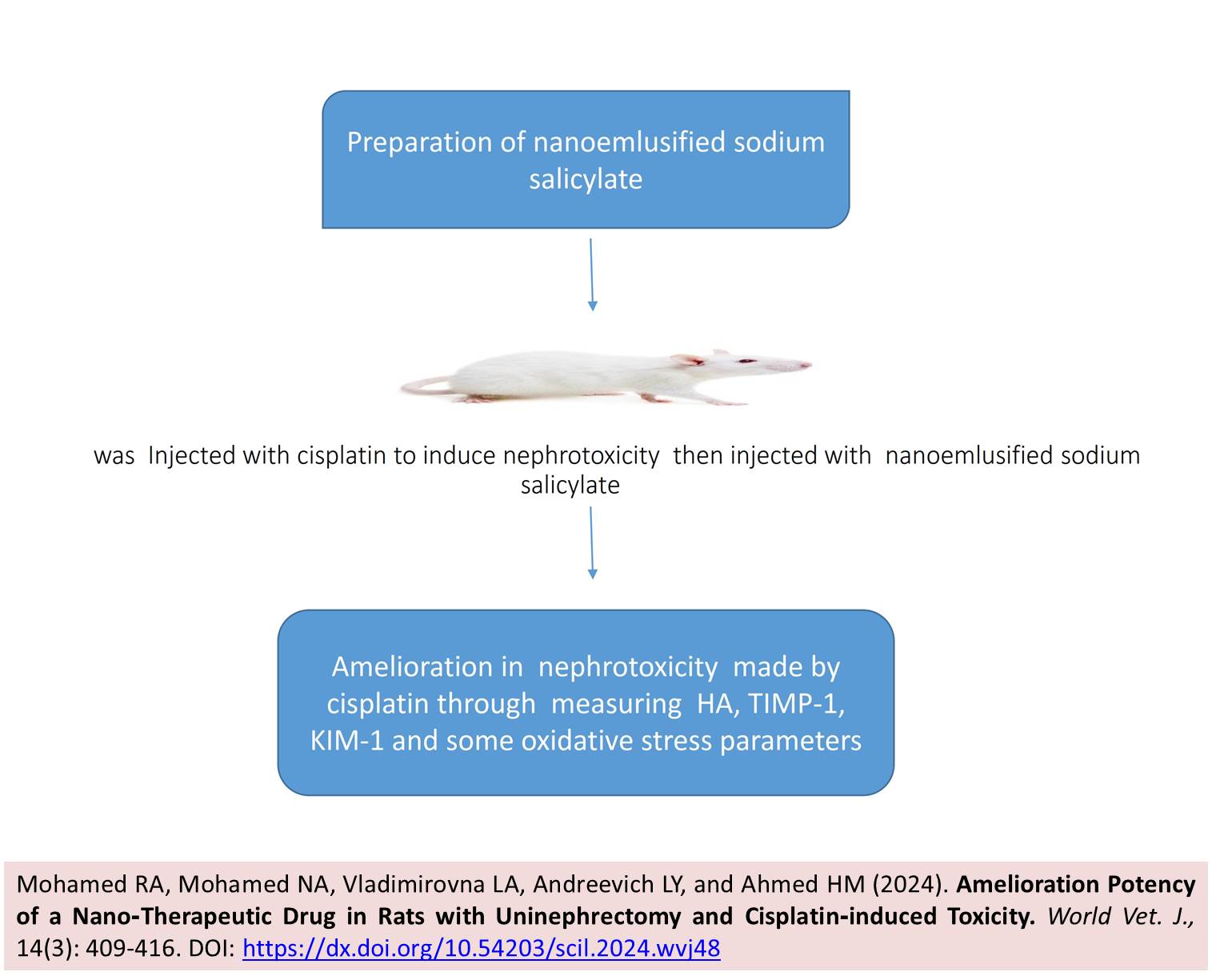
Amelioration Potency of a Nano-Therapeutic Drug in Rats with Uninephrectomy and Cisplatin-induced Toxicity
Mohamed RA, Mohamed NA, Vladimirovna LA, Andreevich LY, and Ahmed HM.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 409-416, 2024; pii:S232245682400048-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj48
ABSTRACT: While physicians describe drugs to treat diseases, these medications may have cytotoxic effects on certain organs, necessitating the use of some drugs to ameliorate such adverse effects. The study was conducted to investigate the protective behavior of nanoemulsified sodium salicylate on uninephrectomized rats injected with cisplatin to induce nephrotoxicity. Fifty adult male albino rats, aged five weeks and weighing approximately 100-120 g, were divided into five groups. The first group received 200 mg/kg/day i.p normal saline for 30 days. The second group was administrated 200 mg/kg/day of nanoemulsified salt of salicylic acid for 30 days. The third group, comprising uninephrectomized rats, was injected with two doses of cisplatin (20 mg/kg body weight) on alternate days from the start of the experiment to induce nephrotoxicity. The fourth group, also uninephrectomized, received 200 mg/kg/day i.p of nanoemulsified sodium salicylate for 30 days. The fifth group, uninephrectomized and treated with 200 mg/kg/day sodium salicylate nanoemlusion for 21 days, was subsequently injected with two doses of cisplatin, followed by continued nanoemulsified sodium salicylate treatment until day 30 from the start of the study. The results showed a significant increase in tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1), Hyaluronic acid (HA), malondialdehyde, kidney injury molecule -1(KIM-1), and nitric oxide in the nephrotoxic group injected with cisplatin compared to the control group. Additionally, there was an elevation in the mRNA expression of nephrotoxic group with uninephrectomy. However, nephrotoxic rats treated with nanoemulsified sodium salicylate exhibited only a modest increase in TIMP-1, HA, and KIM-1 levels, along with elevated expressions of podocin and nephrin compared to the healthy control group. These findings suggest that nanoemulsified sodium salicylate exerts a protective effect against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in uninephrectomized.
Keywords: Cisplatin, Lateral nephrectomy, Nanoemlusion, Podocyte, Rat, Surgery
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
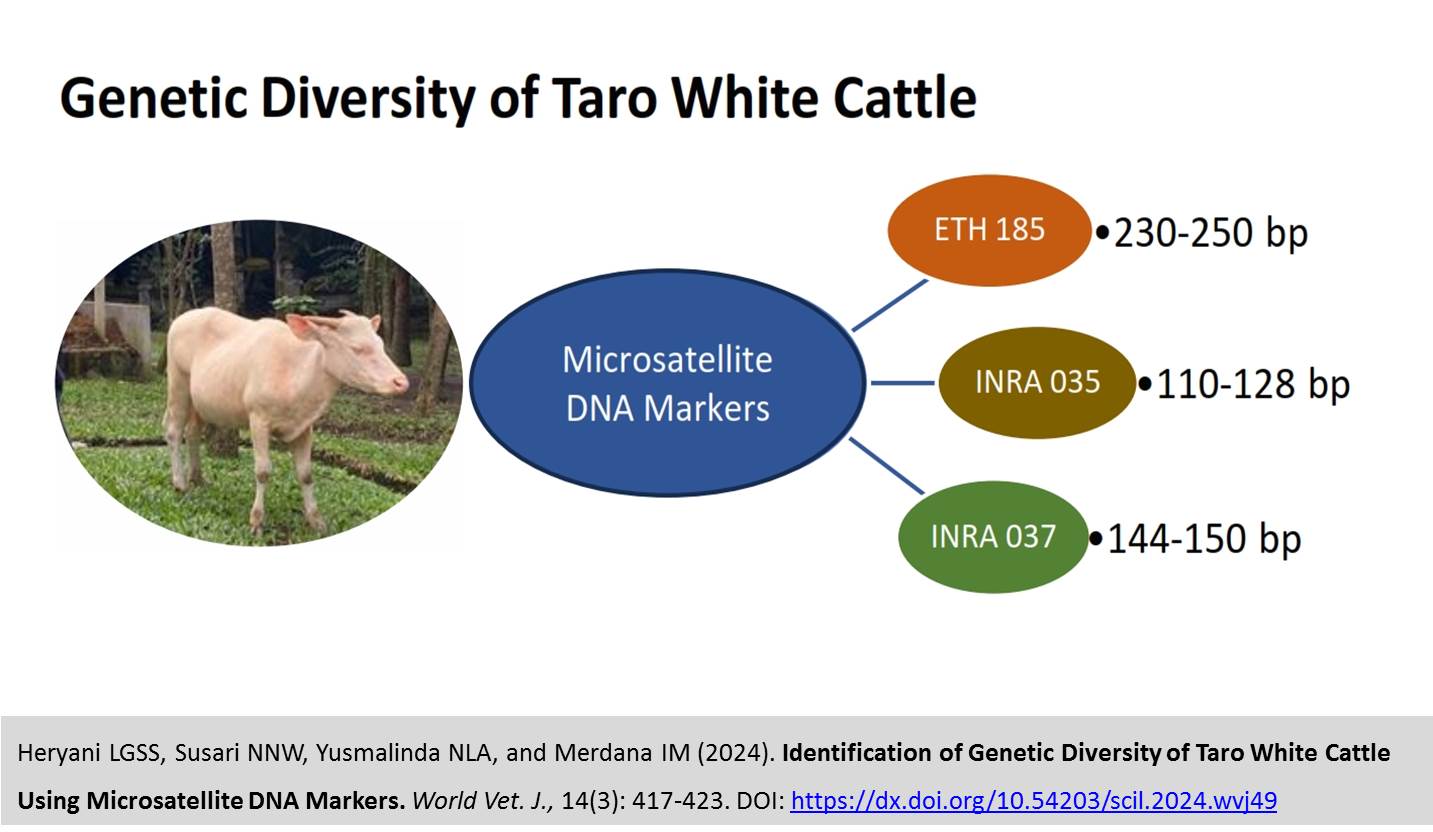
Identification of Genetic Diversity of Taro White Cattle Using Microsatellite DNA Markers
Heryani LGSS, Susari NNW, Yusmalinda NLA, and Merdana IM.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 417-423, 2024; pii:S232245682400049-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj49
ABSTRACT: Taro white cattle have a small population found in Taro Village, Tegalalang, and Gianyar, Bali, which must be protected as one of the most valuable biological resources for the Hindu community in Bali. White cattle require conservation efforts, with morphometric characterization and genetics providing the first phases of an animal conservation program. The purpose of this study was to identify the genetic diversity of Taro white cattle based on allele frequency, heterozygosity, and fixation index (FIT) using different microsatellite DNA loci so that it can be used as a study and reference in determining policies for the conservation of Taro white cattle in Indonesia, particularly in Bali. This cross-sectional observational study utilized ETH 185, INRA 035, and INRA 037 microsatellite DNA markers. Polymerase chain reaction amplified a total of 22 Taro white cattle blood samples with an average of 4.33 alleles; the average observed heterozygosity and expected heterozygosity were 0.288 and 0.637, respectively, with an average fixation index value of 0.55. In conclusion, there is a significant deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium with the likelihood of inbreeding, as indicated by the Hardy-Weinberg balance. The microsatellite loci used in this study can be further used to evaluate the genetic diversity of Taro white cattle.
Keywords: Conservation, Genetic diversity, Microsatellite DNA, Taro white cattle
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
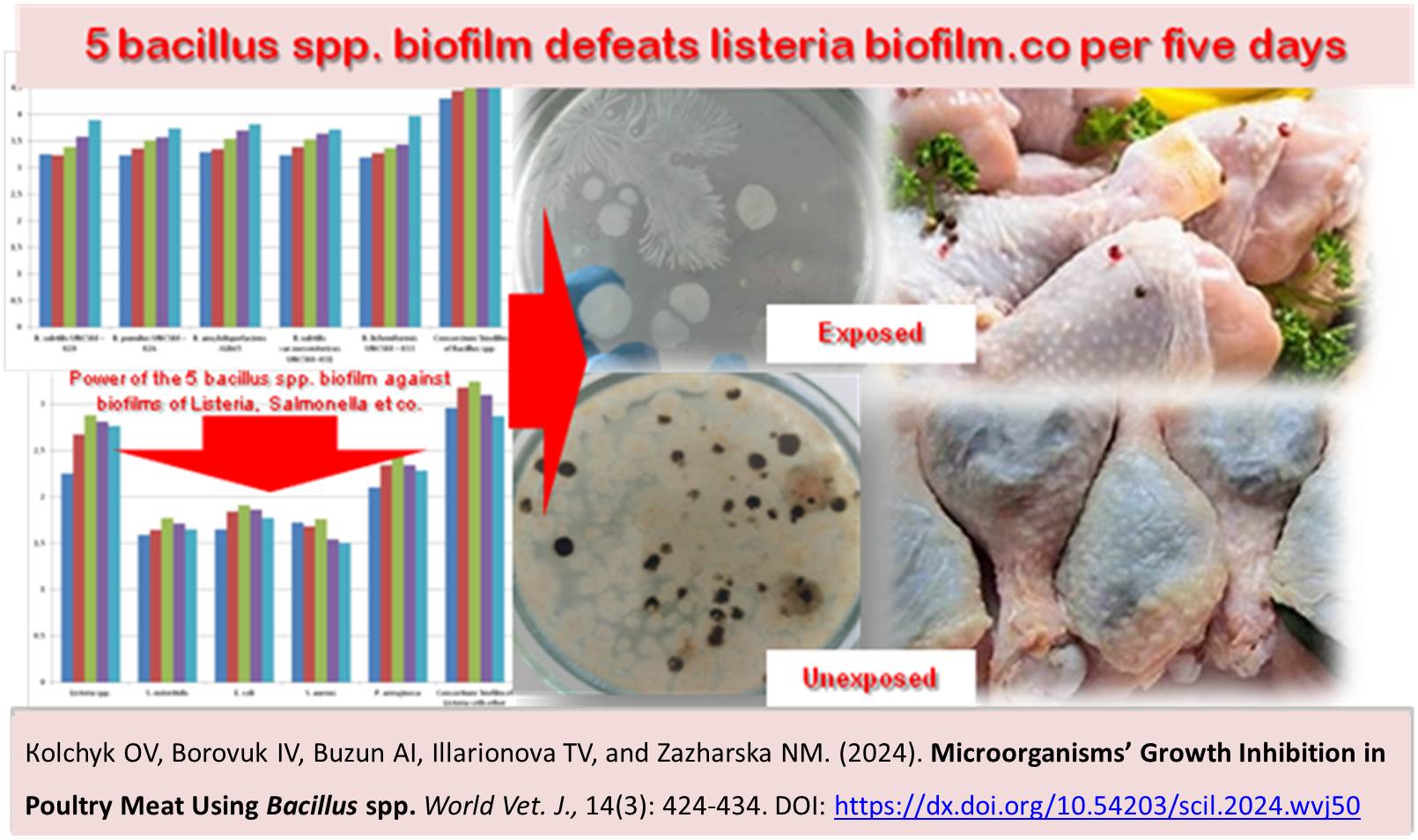
Microorganisms’ Growth Inhibition in Poultry Meat Using Bacillus spp.
Кolchyk ОV, Borovuk IV, Buzun АI, Іllarionova ТV, and Zazharska NM.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 424-434, 2024; pii:S232245682400050-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj50
ABSTRACT: Meat processing enterprises are currently seeking ways to improve the efficiency of their operations. This study aimed to assess the presence of harmful microorganisms in poultry meat treated with a probiotic complex of Bacillus spp. bacteria during storage. Of the 2,516 meat samples collected from broiler chickens across six poultry processing enterprises in the Dnipropetrovsk region over three years, 1,845 samples tested positive for pathogens. Listeria spp. were isolated in 52.7% of meat samples, S. aureus in 28.7%, P. aeruginosa – in 6.9%, E. coli in 4.2%, and Salmonella spp. in 7.5%. The next stage of the study was the infection of 10 samples of poultry meat with pathogens of test cultures (Escherichia coli UNCSM - 007, Pseudomonas aeruginosa UNCSM - 012, Staphylococcus aureus UNCSM - 017, Listeria ivanovii UNCSM - 042, Salmonella Enteritidis UNCSM - 081), followed by aerosol treatment with a probiotic complex of Bacillus spp. (1.5×108 in ml (0.5 Mac Farland) administered at a dose of 1 ml per sample with daily registration of colony growth. Following pathogen contamination and a single aerosol treatment with the probiotic complex of Bacillus spp., the growth of E. coli and S. aureus was already suppressed on the second day of meat storage. The probiotic complex of Bacillus spp. was able to displace Salmonella Enteritidis on the third day and P. aeruginosa on day 4, but the growth of L. ivanovii could be observed only on day 5. The probiotic complex of Bacillus spp. formed visible biofilms from the five strains of microorganisms and remained viable for five days, forming a dense biofilm with a high accumulation rate of 4.73 D620. A distinctly noticeable ability to form microbial biofilms within three days was observed in planktonic forms of L. ivanovii up to 2.88 D620, followed by P. aeruginosa at 2.28 D620. Low biofilm density was observed for Salmonella Enteritidis (1.77 D620) and S. aureus (1.76 D620). The probiotic complex of bacteria of the genus Bacillus spp. shows potential for use in meat processing plants to prevent the growth of harmful microbial biofilms on meat products stored under refrigeration.
Keywords: Antagonistic activity, Biofilm formation, Microbial biofilm, Pathogen, Probiotic complex of Bacillus spp.
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
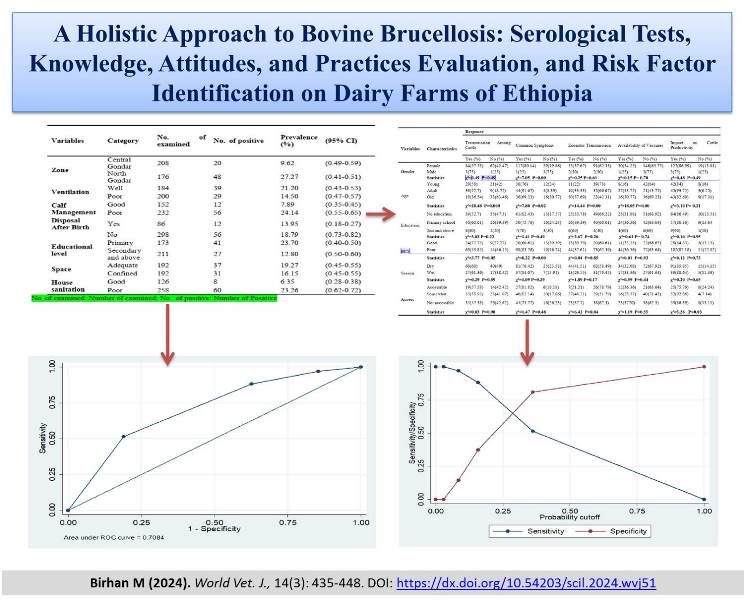
A Holistic Approach to Bovine Brucellosis: Serological Tests, Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Evaluation, and Risk Factor Identification on Dairy Farms of Ethiopia
Birhan M.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 435-448, 2024; pii:S232245682400051-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj51
ABSTRACT: Brucellosis, a contagious bacterial disease affecting animals globally presents a substantial zoonotic risk that is frequently underestimated, hinders animal trade, and endangers livestock and human health. The present study was conducted from November 2023 to June 2024 in Central and North Gondar Zone, Ethiopia. The current cross-sectional study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of brucellosis and to explore the related knowledge, attitudes, and practices within the specified region. A total of 384 serum samples were collected via random sampling from 20 dairy farms located in Ethiopia. Both local and cross-breed samples screened using the Rose Bengal Plate test and confirmed through an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The seroprevalence of bovine brucellosis for both tests was 17.71% overall, with 9.62% for Central Gondar and 27.27% for North Gondar. Extensive farms exhibited notably higher odds of brucellosis compared to intensive farms, with unadjusted crude odds ratios of 3.01 and adjusted odds ratios of 2.37, respectively. Medium-sized herds also demonstrated increased odds in the multivariate analysis compared with small herds. Young respondents displayed the highest awareness levels, followed by adults and older individuals, with statistically significant differences observed across all categories. Regarding a semi-structured survey from 150 farmers on the association between sociodemographic data and knowledge, females exhibited higher awareness levels, with 117 (80.14%) responding positively. Young respondents showed a higher positive response rate of 58% compared to adults (52.7%) and the elderly (36.54%). In conclusion, these results emphasize the need for comprehensive strategies to address the factors influencing bovine brucellosis prevalence and respondent awareness.
Keywords: Brucellosis, Central Gondar, Dairy Farm, North Gondar, Seroprevalence
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
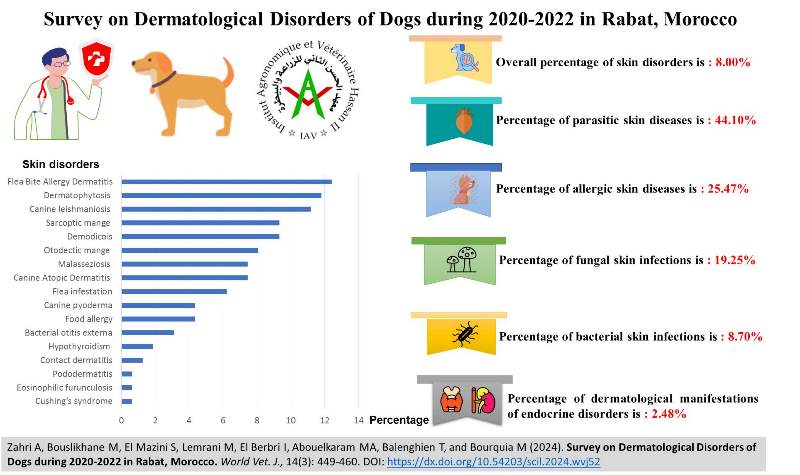
Survey on Dermatological Disorders of Dogs during 2020-2022 in Rabat, Morocco
Zahri A, Bouslikhane M, El Mazini S, Lemrani M, El Berbri I, Abouelkaram MA, Balenghien T, and Bourquia M.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 449-460, 2024; pii:S232245682400052-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj52
ABSTRACT: Dermatology is an important specialty in veterinary medicine, focusing on the skin and its appendages. Therefore, the present study highlighted the percentage of skin disorders, as well as their associated risk factors, from cases received at the Parasitology-Dermatology clinic of the Hassan II Institute of Agronomy and Veterinary Medicine (IAV Hassan II), Rabat, Morocco for two years. A total of 1561 dogs (1450 dogs were in 28 different pure breeds and 111 dogs were mongrels, 805 males, and 756 females, with an average age of 6.5 years old) were presented at the University Veterinary Teaching Hospital (UVTH) of the IAV Hassan II from the end of October 2020 to the end of May 2022 (including vaccinations) and 125 dogs were assessed and 161 skin diseases were found (a few dogs had more than one skin disease). Dermatological examinations represented an average of 8.00% (125/1561) of all canine cases received at the University Veterinary Teaching Hospital. The most common clinical signs were pruritus, alopecia, erythema, onychogryphosis, and visible ectoparasites. Parasitic dermatoses were the most frequent, representing 44.10% of all dermatological cases, followed by allergic dermatoses (25.47%) and fungal skin infections (19.25%). Bacterial skin infections and dermatological manifestations of endocrine disorders were infrequent, representing 8.70% and 2.48%, respectively of all observed cases. Risk factors contributing to the occurrence of canine skin disorders included age and lifestyle for sarcoptic mange. An apparent predilection for the living environment was observed in the case of canine leishmaniosis, and an apparent predilection for sex regarding otodectic mange was also demonstrated. Similar results were found for the living environment and lifestyle concerning canine atopic dermatitis. Data reported herein fill gaps in knowledge of skin disorders and their associated risk factors in dogs in Morocco, demonstrating the dominance of skin diseases of zoonotic interest, including flea bite allergy dermatitis (FBAD), dermatophytosis, and canine leishmaniosis.
Keywords: Dog, Morocco, Rabat, Skin disease, Survey
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
How to Design a Biomonitoring Study – A Practical Guide for Veterinary Professionals under a One Health approach
Jota Baptista C, Seixas F, Gonzalo-Orden JM, and Oliveira PA.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 461-463, 2024; pii:S232245682400053-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj53
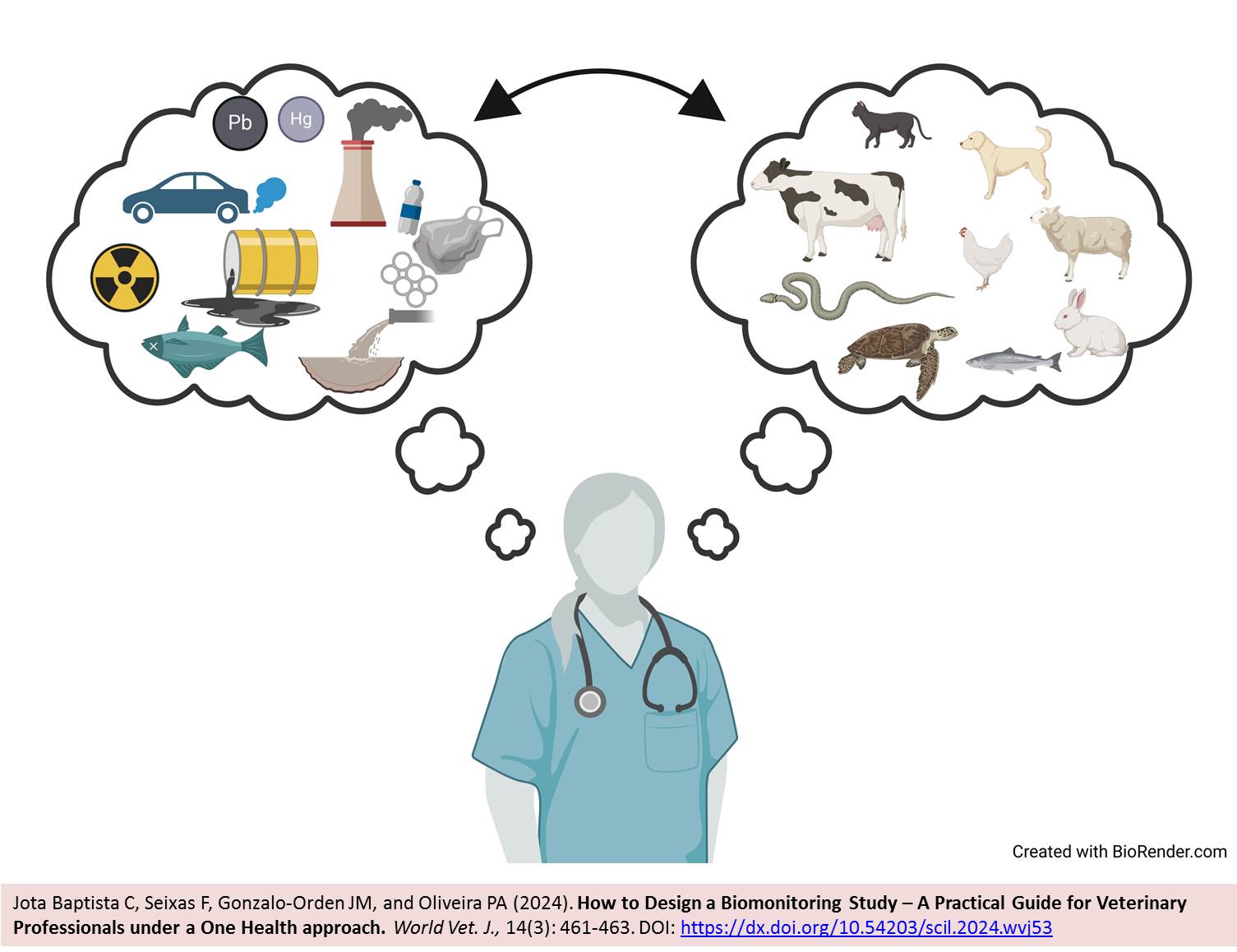
ABSTRACT: Currently, veterinarians can see their daily practice and medical tasks as constant opportunities for passive surveillance of One Health threats, such as infectious zoonotic diseases and chemical pollution effects on living beings. The present study aimed to provide a practical guide to designing a biomonitoring study during veterinary clinical practice without time-consuming procedures or significant costs. The constant access to several species' specimens provides the necessary samples to perform a biomonitoring study of environmental pollutants at the regional or national level. Generally, most health professionals know what to do (or where to find information) to report a disease outbreak. However, a summarized background to perform a biomonitoring study of a chemical hazard is missing. The authors of the current study provided a flow chart with the main steps to conduct a biomonitoring study in different fields of veterinary medicine. Thus, a biomonitoring study might give veterinarians (as other health professionals) a positive contribution to the clinical cases’ resolution, while improving the general knowledge about the impact of environmental contamination on animals and human health.
Keywords: Contamination, Guideline, Monitoring, One Health, Pollution
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide and Cardiovascular Diseases in Dogs and Cats
do Carmo JLP, Soares GSL, Vieira LS, and Oliveira D.
World Vet. J. 14(3): 467-475, 2024; pii:S232245682400054-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2024.wvj54
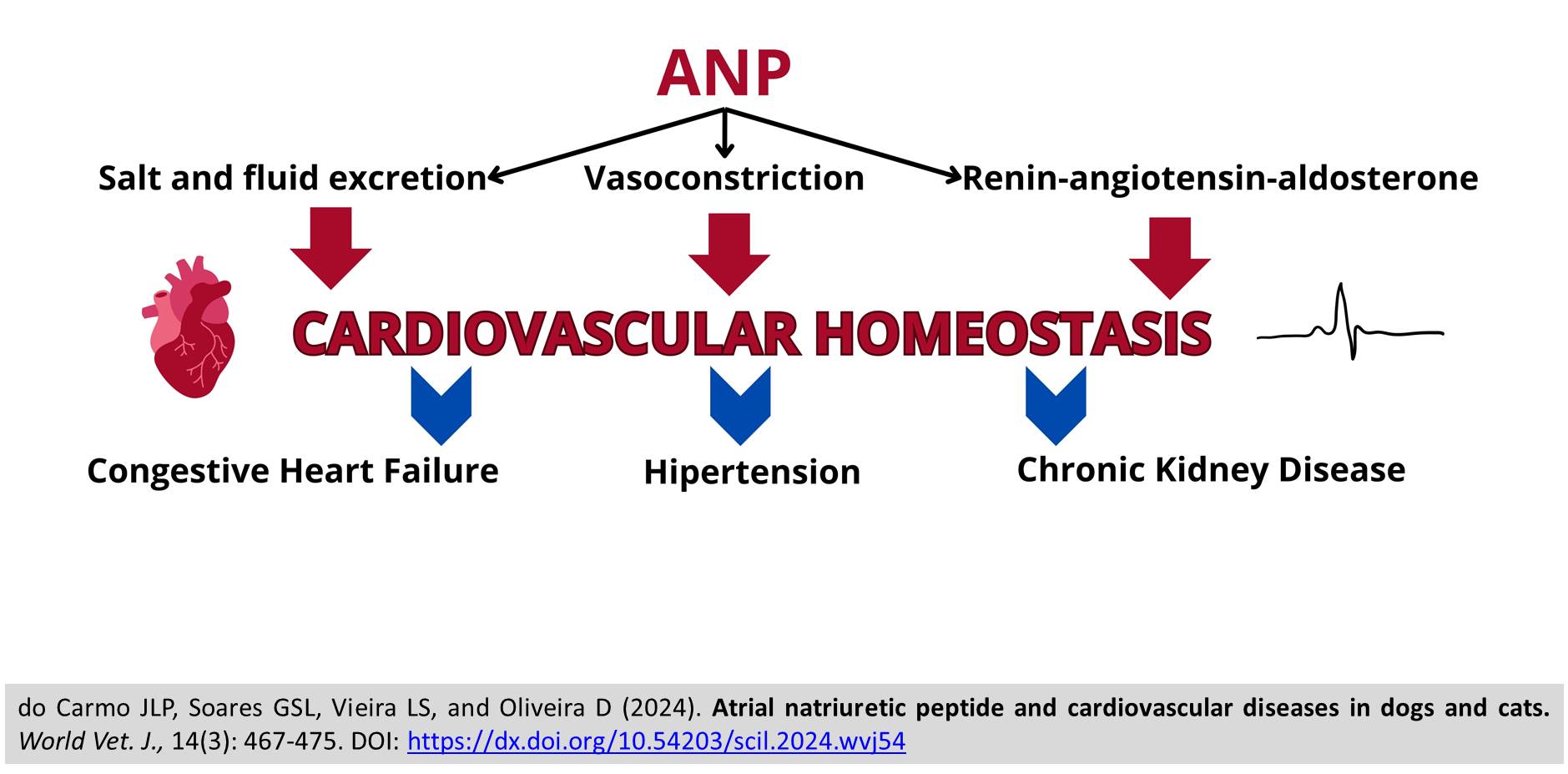
ABSTRACT: The term biomarker encompasses various biological indicators that objectively reflect a patient's medical status with precision and reproducibility. These indicators range from basic measurements like pulse and blood pressure to more intricate laboratory tests. Cardiac markers are crucial for accurate and prompt diagnosis of heart diseases in animals. Given the challenge of diagnosing cardiac diseases in small animals due to nonspecific clinical signs, cardiac markers provide quantitative indicators of biological processes. These markers include cardiac troponins for myocardial injury, natriuretic peptides for myocardial function, lipoproteins for serum homeostasis, and markers for inflammation of the cardiovascular system. Among natriuretic peptides, atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) has emerged as a significant tool in diagnosing and monitoring cardiac diseases. ANP, primarily synthesized in cardiac atria, regulates salt and fluid excretion, counteracts vasoconstriction, and inhibits the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, contributing to the maintenance of cardiovascular homeostasis. Additionally, it functions as a biomarker for ventricular hypertrophy and congestive heart failure (CHF) in animals. Furthermore, it protects against hypertension and cardiac remodeling by demonstrating antagonism to the same system. This review addresses the definition of biomarkers within the context of molecular biology, elucidates their multifaceted functions in the animal organism in light of integrative physiology, and explores the pathologies correlated with ANP, with an emphasis on its etiopathogenesis and clinical manifestations.
Keywords: Biomarker, Canine, Feline, Heart physiology
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).