Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 15 (3); September 2025 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 15 (3); September 2025 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Effects of Food Waste Fermented with Rhizopus oligosporus on the Performance and Carcass Quality of Alabio Ducks
|
|
Rusfidra, Maulana F, Prima HS, Susalam MK, Agasi SY, and Fajri F.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 549-557, 2025; pii:S232245682500055-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj55
ABSTRACT: The incorporation of food waste as an alternative feed ingredient has attracted considerable academic attention, owing to its potential to decrease feed costs and promote sustainable practices within livestock production systems. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of food waste from Pesantren (FWP), Indonesia, fermented with Rhizopus oligosporus (R. oligosporus) as feed on the performance and carcass quality of Alabio ducks. A completely randomized design with four replications was used in the present study. A total of 200 one-day-old male Alabio ducks, with an average initial body weight of 39 ± 2 grams, were raised for eight weeks and randomly divided into five dietary groups, consisting of 40 ducks per group and five ducks per replicate with different FWP inclusion levels. The treatments varied based on the inclusion levels of FWP fermented with R. oligosporus in the diets of Alabio ducks which included FWP 0% (Treatment A, the control group), FWP 10% (Treatment B), FWP 20% (Treatment C), FWP 30% (Treatment D), and FWP 40% (Treatment E). Different parameters were observed at 56 days of age, including feed consumption, final body weight, feed conversion ratio (FCR), protein intake, carcass percentage, and abdominal fat percentage. The current results indicated that FWP significantly affected feed consumption, final body weight, FCR, and protein intake. Treatment D resulted in the highest body weight, protein intake, and the best FCR. However, there were no significant differences among treatments in carcass and abdominal fat percentages. In conclusion, incorporating up to 30% of FWP fermented with R. oligosporus, based on dry matter, into the diet of male Alabio ducks does not negatively impact their performance or carcass quality. Using FWP fermented with R. oligosporus as part of the duck feed offered a sustainable and cost-effective method for organic waste management in Pesantren poultry systems.
Keywords: Alabio duck, Carcass quality, Fermented feed, Growth performance, Rhizopus oligosporus
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
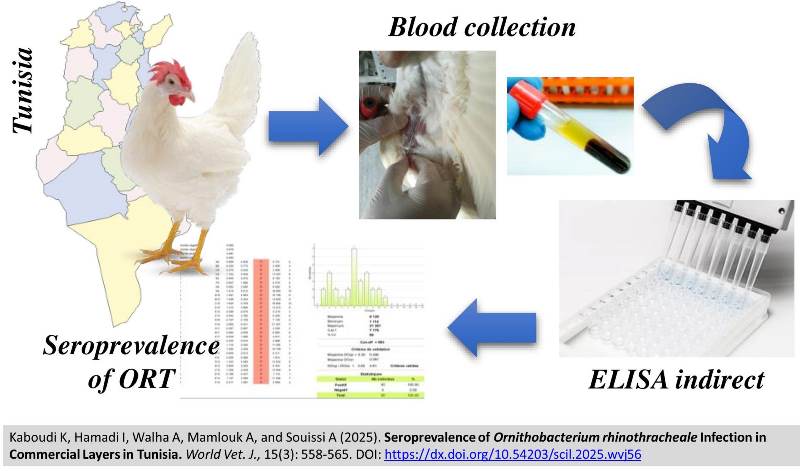
Seroprevalence of Ornithobacterium rhinothracheale Infection in Commercial Layers in Tunisia
|
|
Kaboudi K, Hamadi I, Walha A, Mamlouk A, and Souissi A.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 558-565, 2025; pii:S232245682500056-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj56
ABSTRACT: Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT) infection is a worldwide disease in commercial poultry production. It is caused by a gram-negative bacterium, inducing respiratory and articular infections. The present study investigated the seroprevalence of ORT in commercial laying chicken farms in the Sfax region of South-eastern Tunisia. Diagnosis of ORT is based on the clinical signs such as respiratory distress, sneezing, cough, and limping, gross pathology in post-mortem examination (fibrinous tracheitis, fibrinous pneumonia, caseous arthritis, and tendinitis), and laboratory investigations, including isolation and identification, molecular and serological analysis. In the current study, 470 serum samples were collected from 25 commercial layer flocks (18 to 20 blood samples/flock) and tested using an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which revealed that all 25 flocks (100%) demonstrated evidence of past or recent ORT infection. Seropositivity of the tested sera indicated the presence of antibodies against ORT, ranging widely from 7.69% to 100% within individual layer hens flocks. The average antibody levels varied considerably among flocks, from 1425.67 to 15233 in different flocks. The current findings indicated widespread ORT exposure in commercial layer farms in the Sfax region of South-eastern Tunisia, signifying the potential for horizontal transmission of ORT, particularly in multi-age layer integrations where older flocks can act as a source of infection for younger pullets.
Keywords: Biosecurity, Commercial layer, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
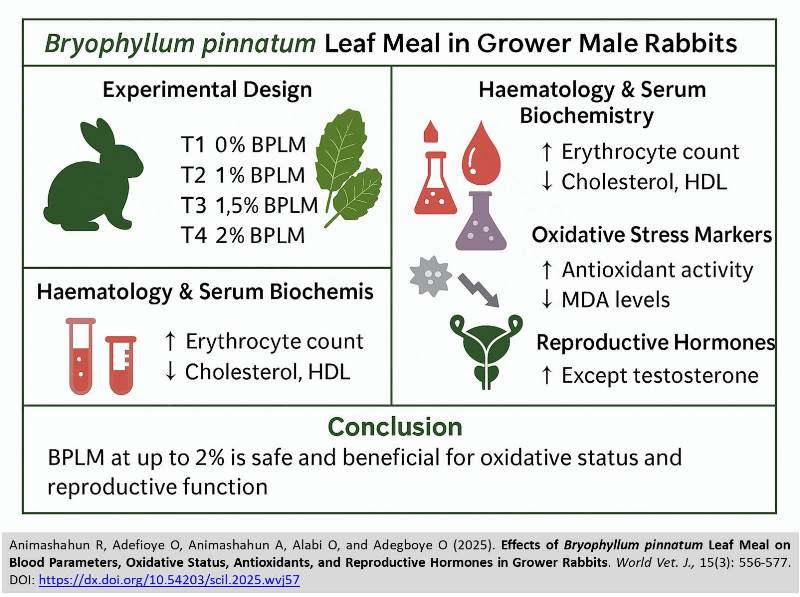
Effects of Bryophyllum pinnatum Leaf Meal on Blood Parameters, Oxidative Status, Antioxidants, and Reproductive Hormones in Grower Rabbits
|
|
Animashahun R, Adefioye O, Animashahun A, Alabi O, and Adegboye O.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 566-577, 2025; pii:S232245682500057-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj57
ABSTRACT: In the search for safe and effective phytogenic alternatives to synthetic additives in rabbit nutrition, Bryophyllum pinnatum has shown promising biological potential. This study investigated the effects of dietary inclusion of Bryophyllum pinnatum leaf meal (BPLM) on hematological parameters, serum biochemistry, oxidative stress markers, and reproductive hormone levels in grower male rabbits. A total of 48 Hyla grower male rabbits, aged 7–8 weeks, were randomly allotted to four dietary treatments in a completely randomized design (CRD): T1 (0% BPLM), T2 (1% BPLM), T3 (1.5% BPLM), and T4 (2% BPLM), with 12 rabbits per group, further subdivided into three replicates of four animals each. After an 10-week feeding trial, blood samples were collected and analyzed for hematological indices (erythrocyte count, packed cell volume, hemoglobin concentration, erythrocyte indices, total and differential white blood cell counts), biochemical parameters (liver enzymes, total protein, glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein, and high-density lipoprotein [HDL]), oxidative stress markers (malondialdehyde [MDA] and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl scavenging activity [DPPH]), and reproductive hormones. The majority of hematological and biochemical parameters were not significantly affected by BPLM inclusion, indicating no adverse impact on physiological homeostasis. However, erythrocyte count, serum cholesterol, and HDL levels showed significant differences. Erythrocyte count increased progressively from 0% to 1.5% BPLM inclusion, but declined at the 2% level. Serum cholesterol decreased gradually with increasing BPLM inclusion, with the lowest value observed at 2%. Antioxidant activity improved significantly with increasing BPLM levels, as evidenced by enhanced DPPH scavenging capacity and reduced MDA concentrations, particularly at 1.5% and 2% inclusion. Furthermore, reproductive hormones, apart from testosterone, were significantly elevated in rabbits fed diets containing 1.5% and 2% BPLM, suggesting enhanced reproductive function. Overall, these findings indicate that dietary inclusion of BPLM up to 2% is safe and beneficial for growing male rabbits, with positive effects on antioxidant defense and reproductive performance. The functional phytogenic properties of Bryophyllum pinnatum (B. pinnatum) leaves highlight their potential as a natural feed additive for improving rabbit health and productivity.
Keywords: Functional nutrition, Male fertility, Medicinal plant, Oxidative stress, Phytogenic feed additive, Rabbit
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
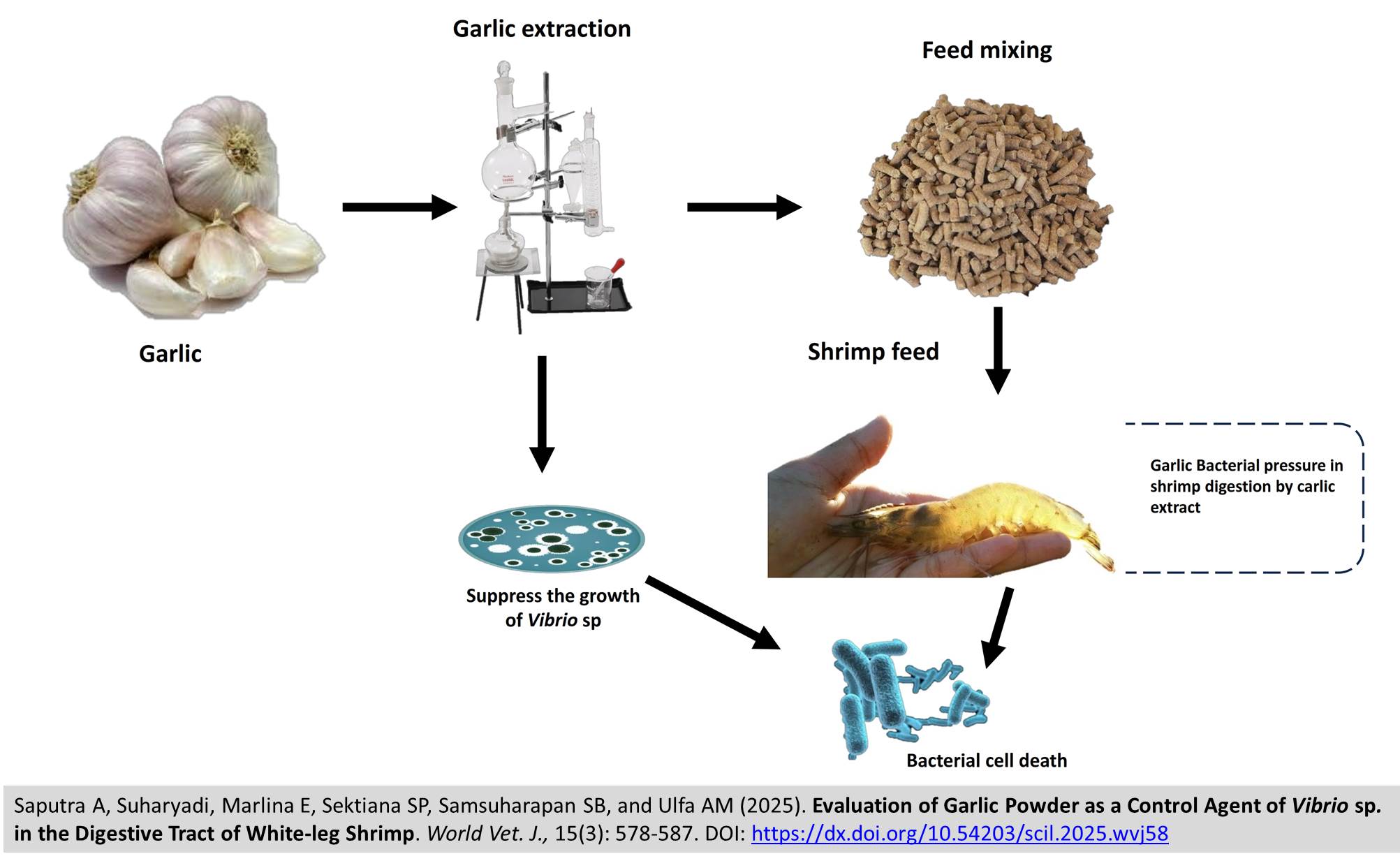
Evaluation of Garlic Powder as a Control Agent of Vibrio sp. in the Digestive Tract of White-leg Shrimp
|
|
Saputra A, Suharyadi, Marlina E, Sektiana SP, Samsuharapan SB, and Ulfa AM.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 578-587, 2025; pii:S232245682500058-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj58
ABSTRACT: Garlic (Allium sativum) is a natural plant recognized for its active compounds, such as allicin, which possess antibacterial properties that can combat pathogenic microorganisms. Vibrio sp. bacteria can be pathogenic to vannamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei), causing mortality marked by necrosis and melanization in the hepatopancreas cells. The present study aimed to examine the chemical compositions of garlic powder and its potential to inhibit the growth of Vibrio sp. bacteria in vannamei shrimp. Vannamei shrimp, with a population of 400 shrimp/m3, were orally administered garlic powder mixed into their feed. The experimental doses were 0.1 mg of garlic powder (Group A), 0.5 mg of garlic powder (Group B), and 1 mg of garlic powder in 1 g of shrimp feed (Group C), along with shrimp that did not receive garlic powder (K, control group). Vannamei shrimp at the post-larva stage were used with a density of 1000 shrimp in each tank. Phytochemical analysis of the garlic powder revealed the presence of compounds such as flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins, phenols, and saponins. Thin-layer chromatography using quercetin as the reference standard yielded a positive result, indicated by a retention factor of 0.66. Notably, there was a significant reduction in total bacterial counts of Vibrio sp. in 40 days of treatment. A garlic powder at a dose of 0.5 mg/g was particularly effective in inhibiting the growth of Vibrio sp. bacteria. The current results indicated that shrimp not given garlic powder (control group) exhibited significant atrophy and hepatopancreas infiltration.
Keywords: Garlic, Hepatopancreas, Vannamei Shrimp, Vibrio sp.
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
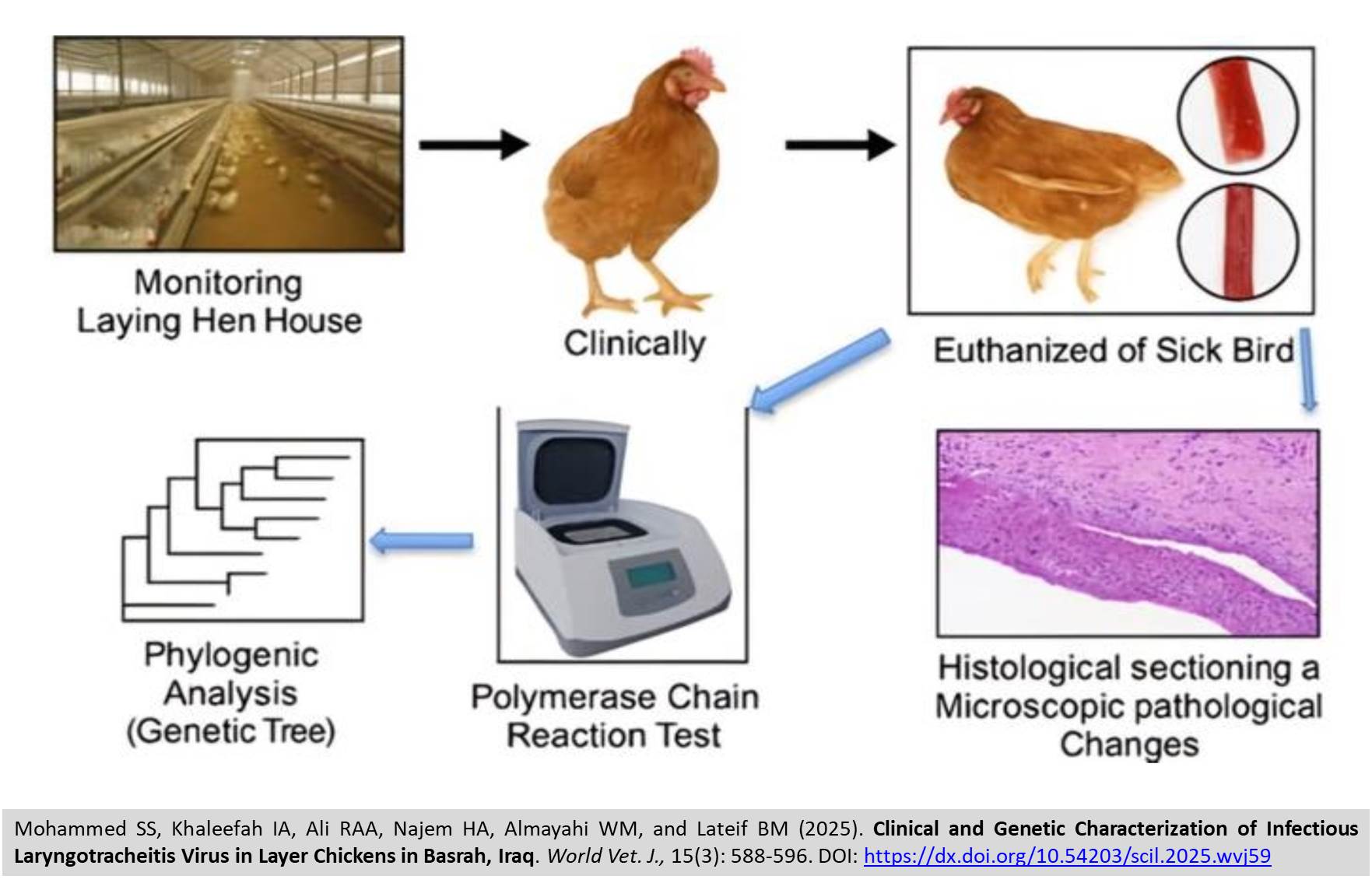
Clinical and Genetic Characterization of Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus in Layer Chickens in Basrah, Iraq
|
|
Mohammed SS, Khaleefah IA, Ali RAA, Najem HA, Almayahi WM, and Lateif BM.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 588-596, 2025; pii:S232245682500059-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj59
ABSTRACT: Infectious Laryngotracheitis (ILT) has been widely prevalent in numerous countries in recent years. The present study aimed to detect ILT in chickens exhibiting clinical suspicion, utilizing molecular analytical techniques in Basrah, Iraq. Clinical signs, histological changes, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) were used to diagnose thirty-five samples collected from clinically suspected chickens, including trachea and lungs for histopathology and PCR testing for the p32 gene. The present study demonstrated that the three isolates of ILTV, including ILT-BASRAH 1, ILT-BASRAH 2, and ILT-BASRAH 3, caused the typical signs and pathological changes of ILT in layers chickens. Phylogenetic analyses indicated that ILT-BASRAH 1 exhibited a distant relationship with other current local isolates. Conversely, the isolates ILT-BASRAH 2 and ILT-BASRAH 3 exhibited a close relationship with each other. The initial results indicated that ILT-BASRAH 1 exhibited high nucleotide similarity to MK895003.1, MK895000.1, and MK894999.1 from Australia, which are representative of recombinant strains derived from live attenuated vaccine strains, as well as PQ232589.1 from Georgia. Furthermore, ILT-BASRAH 2 and ILT-BASRAH 3 were identified as vaccine-related isolates. These isolates demonstrated a high level of genetic similarity and a close phylogenetic relationship to the Gallid alphaherpesvirus 1 isolate TJ2019 (GenBank accession no. PP062931.1), originating from Chinese source flocks. The current study determined that ILT-BASRAH isolates 1, 2, and 3 exhibited genetic similarity, suggesting that they likely originated from the same or closely related sources. Their difference from vaccine strains, including the minor variation in ILT-BASRAH 1, might indicate regional viral adaptation.
Keywords: Gallid alphaherpesvirus, Histological change, Layer chicken, Phylogenetic
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
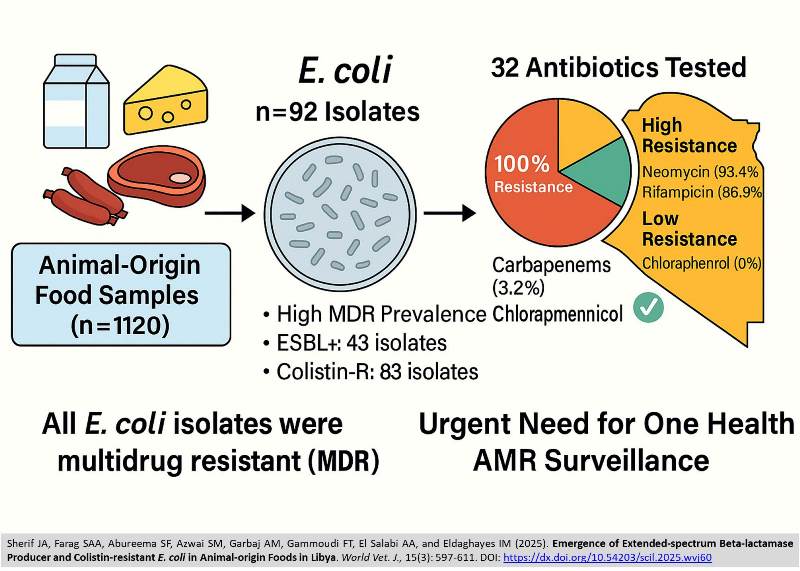
Emergence of Extended-spectrum Beta-lactamase Producer and Colistin-resistant E. coli in Animal-origin Foods in Libya
|
|
Sherif JA, Farag SAA, Abureema SF, Azwai SM, Garbaj AM, Gammoudi FT, El Salabi AA, and Eldaghayes IM.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 597-611, 2025; pii:S232245682500060-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj60
ABSTRACT: The increasing prevalence of Escherichia coli (E. coli) infection poses significant health challenges worldwide. Understanding the genetic, pathogenic, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of E. coli is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. The present study aimed to assess the prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of E. coli isolated from different samples of food products from animals, with specific attention to identifying and characterizing extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing isolates. The present study analyzed 92 E. coli isolates obtained from 1120 food samples, including milk, dairy products, meat, and meat products, collected randomly from retail markets in Libya. The isolates were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility, and the antibiotic resistance profiles were evaluated using 32 antibiotics from 12 different classes. Multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) and antibiotic resistance index were calculated, with MAR ≥ 0.2 indicating high antibiotic resistance. Isolates were categorized as multidrug resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), or pan drug-resistant (PDR) based on standard definitions. The ESBL production was assessed using the double-disc synergy test, and colistin resistance was tested using the agar diffusion method. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of E. coli isolates revealed 100% resistance to penicillin and cloxacillin, with high resistance rates observed against neomycin (93.4%), rifampicin (86.9%), and methicillin (75%). However, all isolates were susceptible to chloramphenicol, whereas carbapenems (imipenem, meropenem, ertapenem) indicated the lowest resistance (3.2%). Cefepime demonstrated the highest effectiveness among cephalosporins, with a resistance rate of 1.08%. The MAR ranged from 0.09 to 0.6, with the highest MAR value (0.6) observed in isolates resistant to 20 antibiotics. All isolates were MDR, but no XDR or PDR strains were detected. Among the 92 isolates, 43 were confirmed as ESBL producers, primarily originating from raw milk, lben (fermented milk), and other dairy products. In addition, 83 isolates demonstrated phenotypic resistance to colistin. The present study highlighted the significant presence of MDR E. coli in food products of animal origin, particularly raw milk, fermented milk, and chicken meat in Libya, emphasizing the urgent need for antimicrobial stewardship, stronger regulatory frameworks, and integrated One Health surveillance approaches to combat AMR in Libya.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance, Colistin, Escherichia coli, Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases, Food sample
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effectiveness of Guava Leaf Fraction on Phagocytosis Activity and Leukocyte Differentiation in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila
|
|
Wardani LMDK, Andayani S, and Maimunah Y.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 612-621, 2025; pii:S232245682500061-15
DOI:https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj61
ABSTRACT: One obstacle to the sustainability of fisheries is the bacterial infection caused by Aeromonas hydrophila (A. hydrophila). To overcome the sustainability issues posed by antibiotic use against A. hydrophila in fisheries, guava leaf (Psidium guajava L.) immunostimulants offer a promising natural alternative. The present study aimed to examine the impact of dynamic compounds derived from guava leaves on leukocyte differentiation and phagocytosis in tilapia infected with A. hydrophila. A completely randomized design was established, consisting of three treatment groups and two controls, with three replications. The groups included 150 ppm of guava leaf fraction (Group A), 125 ppm of guava leaf fraction (Group B), and 100 ppm of guava leaf fraction (Group C), which were injected into tilapia. The negative control group was infected with A. hydrophila bacteria without receiving the guava leaf fraction, and the positive control group was not infected with A. hydrophila bacteria and did not receive the guava leaf fraction. The dosage determination of the guava leaf fraction was conducted using the lethal concentration 50% test. The results demonstrated that Fraction 5 of guava leaf extract significantly enhanced the non-specific immune response of tilapia. The optimal dose of 150 ppm led to a substantial increase in lymphocyte counts and phagocytic activity following infection with A. hydrophila. Consequently, all treatment groups (100, 125, and 150 ppm) exhibited survival rates statistically equivalent to those of the positive control group, which was significantly higher than the 39% survival rate in the negative control group. Thus, guava leaf Fraction 5, particularly at 150 ppm, serves as an effective immunostimulant and natural antibiotic alternative for controlling A. hydrophila in tilapia.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila, Guava leaf fraction, Immune response, Immunostimulant
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
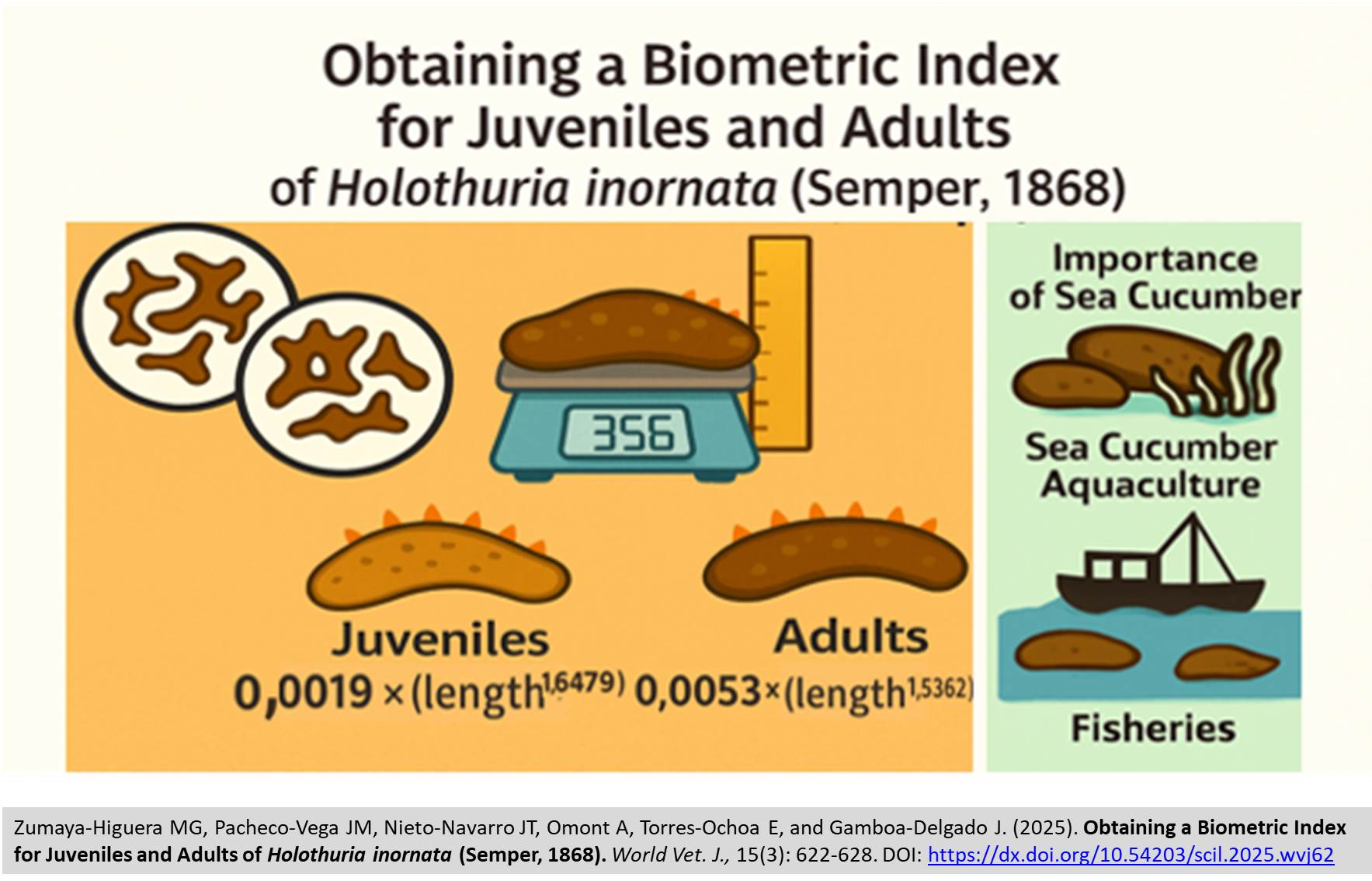
Obtaining a Biometric Index for Juveniles and Adults of Holothuria inornata (Semper, 1868)
|
|
Zumaya-Higuera MG, Pacheco-Vega JM, Nieto-Navarro JT, Omont A, Torres-Ochoa E, and Gamboa-Delgado J.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 622-628, 2025; pii:S232245682500062-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj62
ABSTRACT: The sea cucumber Holothuria inornata (H. inornata) is a species at risk in Mexico. To help protect this species, it is important to provide information related to biological and fisheries management. The present study aimed to predict the weight of the sea cucumber (H. inornata) using biometric measurements such as wet weight and dry weight. A total of 267 H. inornata were manually collected from El Borrego Beach in the municipality of San Blas, Nayarit, Mexico. Species identification involved characterizing calcareous ladders. Each specimen was sedated using xylazine 10%, and measurements were taken out of water with a digital scale. Multiple linear regressions were performed, with size serving as the independent variable and wet weight, dry weight, and humidity percentage as dependent variables. A general equation was developed to predict the wet weight of the H. inornata at the juvenile stage. For correlations based on dry weight, the following equations were established. In immature adults, including dry weight, the equation was 0.0019 × (length^1.6479); and in mature adults, including dry weight, it was 0.0053 × (length^1.5362). The biometric parameters used for weight estimation exhibited a high degree of correlation with actual weight. Wet weight was the biometric parameter that showed the best fit among the studied parameters. Utilizing these biometric indices facilitates the recording of wet and dry weights for interested parties, thereby supporting population and biomass evaluations within the H. inornata fishery and aquaculture sectors.
Keywords: Biometric index, Dry weight, Holothuria inornata, Wet weight
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
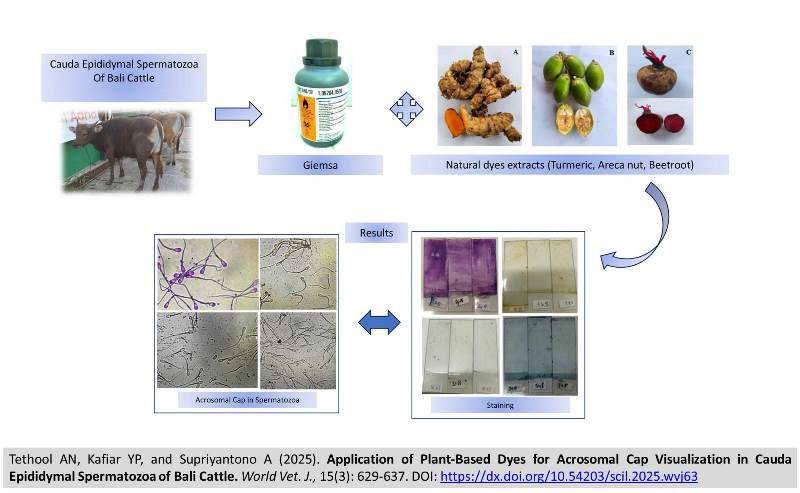
Application of Plant-Based Dyes for Acrosomal Cap Visualization in Cauda Epididymal Spermatozoa of Bali Cattle
|
|
Tethool AN, Kafiar YP, and Supriyantono A.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 629-637, 2025; pii:S232245682500063-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj63
ABSTRACT: The cauda epididymis contains mature spermatozoa capable of fertilization, with acrosomal integrity being a crucial factor in their function. Damage to the acrosome impairs the viability and fertilizing ability of spermatozoa. Conventional staining methods, such as Giemsa or fluorescence microscopy, are effective but less practical in low-resource settings. The present study aimed to evaluate damage to the acrosomal cap of cauda epididymal spermatozoa in Bali cattle and to assess the integrity of the acrosomal cap using Giemsa and natural dyes such as turmeric, beetroot, and areca nut extract. The present study utilized cauda epididymal spermatozoa from Bali cattle aged 3-4 years and weighing 316-412 kg. The study employed a completely randomized design with four treatments, each replicated 20 times. The treatments were Giemsa stain 100% (Control, P0), 10% Giemsa + 90% turmeric extract (P1), 10% Giemsa + 90% beetroot extract (P2), and 10% Giemsa + 90% areca nut extract (P3). Using Giemsa and natural dyes resulted in different colors of spermatozoa acrosomes. The P0 preparations exhibited a dark purple coloration, P1 appeared yellowish, corresponding to the turmeric pigment, and P3 appeared bluish, while P2 demonstrated no detectable staining on the slides. The acrosomal caps of spermatozoa in P0 were dark purple, those in P1 were yellowish, and those in P2 and P3 were unstained (Transparent or faint). The average acrosomal cap integrity was the highest in P0, followed in order by P1, P2, and P3. Based on the current findings, it can be concluded that P1, P2, and P3 signified acrosomal cap integrity in cauda epididymal spermatozoa of Bali cattle. However, P1 produced the best results, showing a distinguishable color and the highest acrosomal cap integrity score (86.9 ± 2.0%). Beetroot and areca nut extracts produced weaker staining and lower acrosomal integrity values. Therefore, turmeric extract may serve as a practical, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly alternative for acrosome evaluation in veterinary reproductive laboratories, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Giemsa, Intact acrosomal cap, Natural dye, Spermatozoa
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
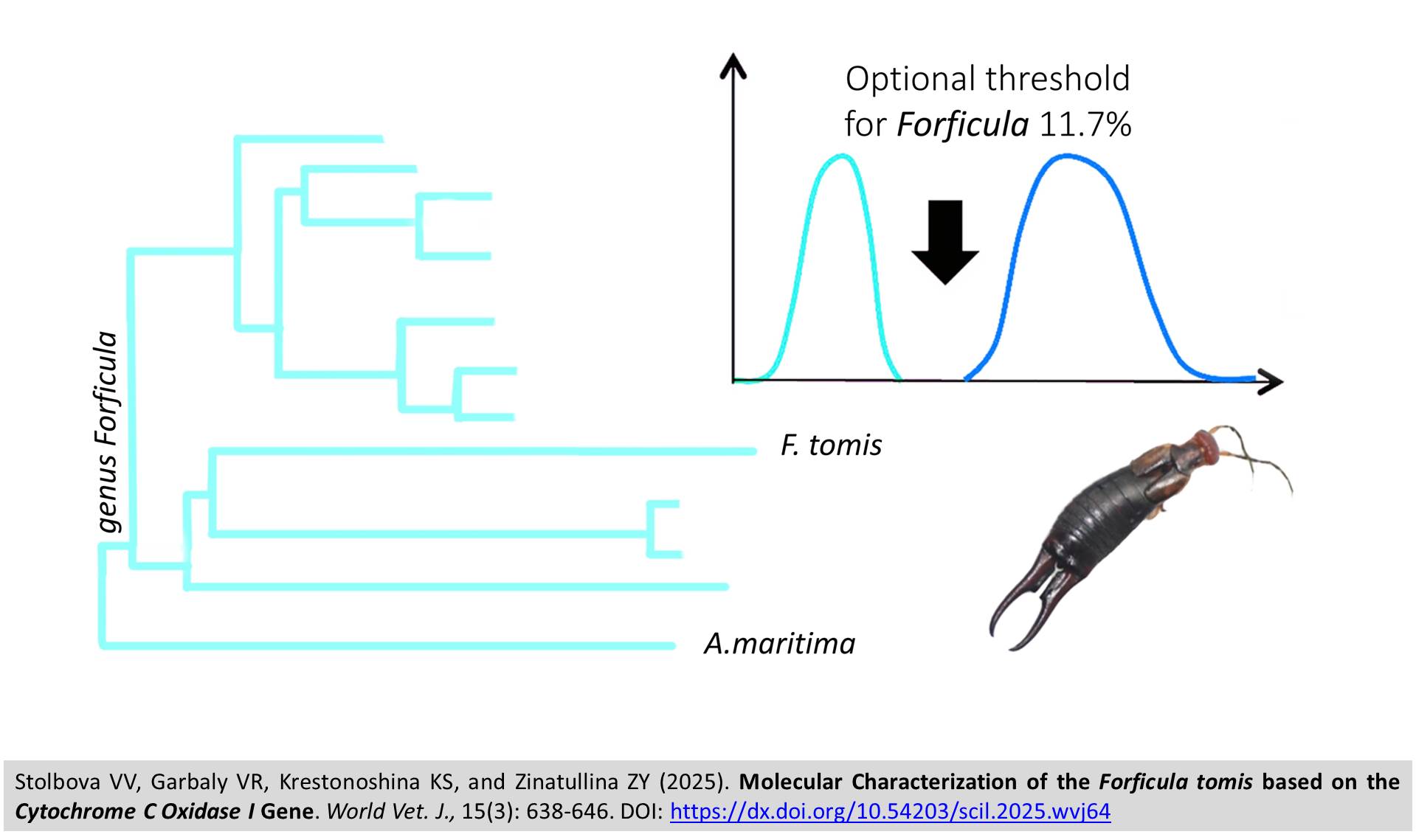
Molecular Characterization of the Forficula tomis based on the Cytochrome C Oxidase I Gene
|
|
Stolbova VV, Garbaly VR, Krestonoshina KS, and Zinatullina ZY.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 638-646, 2025; pii:S232245682500064-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj64
ABSTRACT: The ovine Earwigs of the genus Forficula play a significant role in agriculture and beekeeping, acting as pests and vectors of honey bee pathogens. Despite the ecological and agricultural significance, nucleotide sequences of the species Forficula tomis (F. tomis) are absent in genetic databases, which complicates its molecular identification. The present study aimed to perform the molecular characterization of the earwig F. tomis using the cytochrome c oxidase I (COI) gene fragment as a molecular marker. A total of 18 earwig specimens were hand-collected from Apis mellifera hives in the Tyumen region, Russia. During the cultivation, 9 adults were obtained, which were used in the present study. Morphological analysis confirmed that F. tomis is the predominant species of bee hives in the Tyumen region. Sequencing of the COI gene fragment made it possible to obtain a reference sequence of F. tomis, which, in phylogenetic analysis, formed a separate clade and demonstrated a significant genetic distance (up to 22.9%) with other representatives of the genus Forficula. The optimal species differentiation threshold for the group was 11.7%, which significantly exceeds the standard barcode gap (3%) and may indicate long-term evolutionary isolation or the presence of cryptic diversity. The obtained results expand the present understanding of the genetic structure of the genus Forficula and have practical significance for monitoring apiary pests, developing methods for molecular identification of bee pests, and understanding their role in the spread of pathogens.
Keywords: Beekeeping, Cytochrome c oxidase I gene, DNA barcoding, Earwigs, Forficula tomis
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
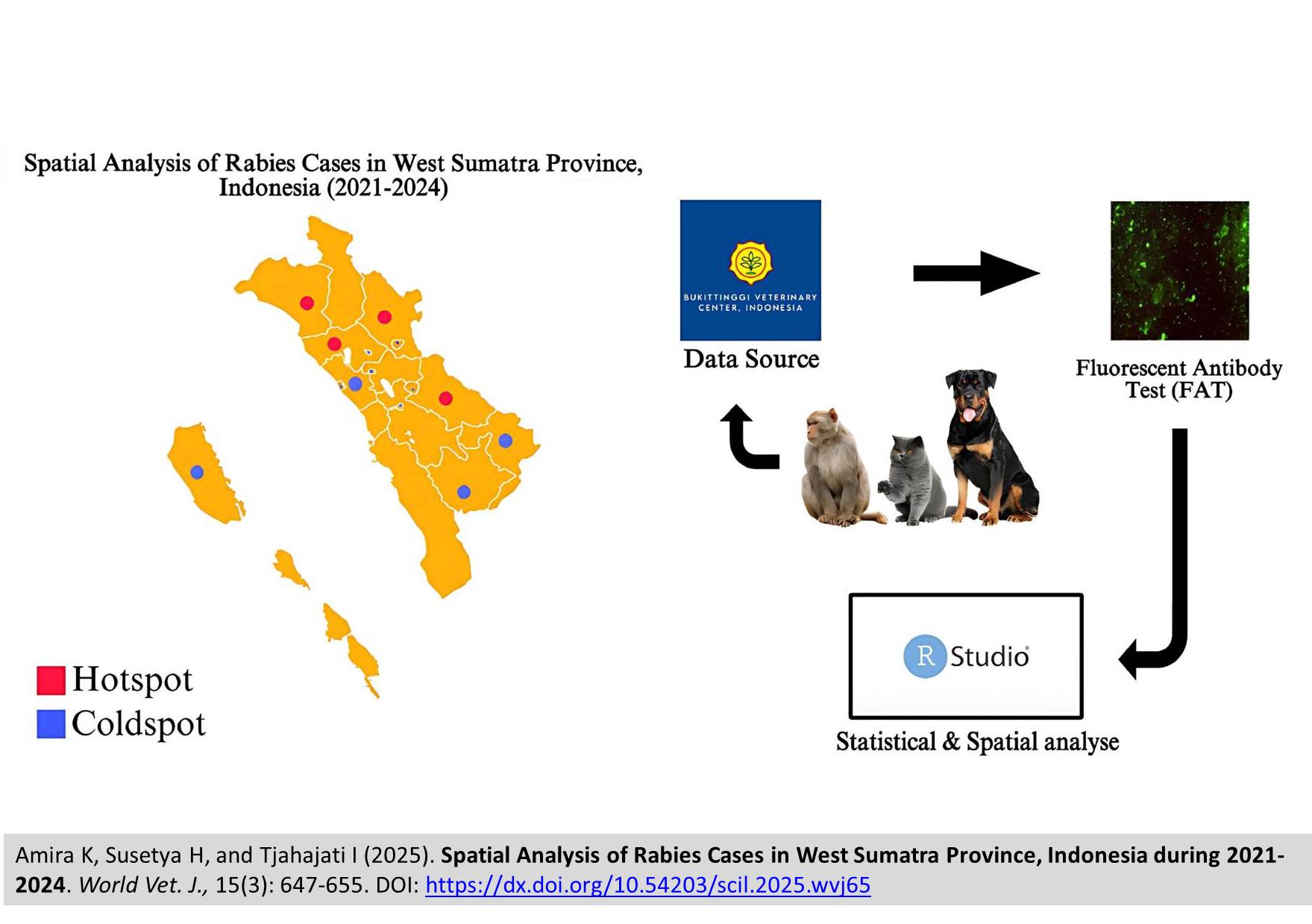
Spatial Analysis of Rabies Cases in West Sumatra Province, Indonesia during 2021-2024
|
|
Amira K, Susetya H, and Tjahajati I.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 647-656, 2025; pii:S232245682500065-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj65
ABSTRACT: The West Sumatra Province, Indonesia, has been an endemic rabies region since its initial rabies incident in 1953. This study aimed to analyze spatial patterns for rabies cases in animals in 19 districts/cities in West Sumatra Province, Indonesia. Secondary data on rabies-positive cases in animals were identified in 198 samples through the Fluorescent Antibody Test (FAT) obtained from the Bukittinggi Veterinary Center’s database from 2021 to 2024. Statistical and spatial analyses were conducted in R Software v.4.4.2. The Moran’s Index revealed a cluster distribution of rabies cases throughout the study period. The highest prevalence occurs in Lima Puluh Kota District (28.79%). The index indicated four regions as high-high quadrants, three regions as low-high quadrants, 11 regions as low-low quadrants, and one region as a high-low quadrant. However, Lima Puluh Kota District was consistently found as a region with substantial local spatial autocorrelation. In conclusion, the prevalence of rabies cases in animals in West Sumatra Province fluctuated during 2021-2024. Spatial analysis with Moran’s Index and Local Indicator of Spatial Autocorrelation (LISA) indicated a cluster distribution of the disease. The current study underscored the need for targeted, location-specific control measures in these high-risk clusters to effectively mitigate the spread of the disease.
Keywords: Fluorescent Antibody Test, Moran’s Index, Rabies, Spatial analysis
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
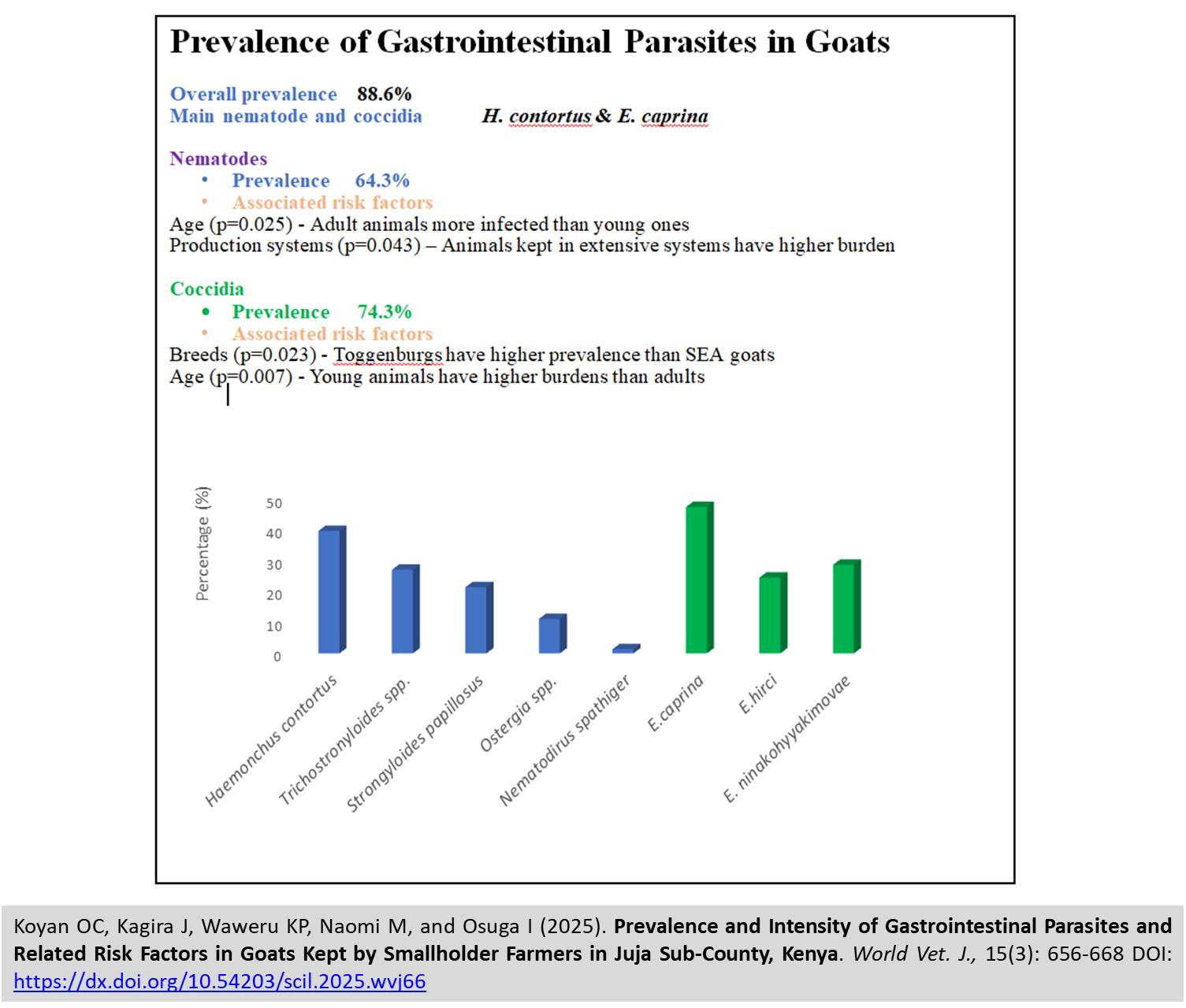
Prevalence and Intensity of Gastrointestinal Parasites and Related Risk Factors in Goats Kept by Smallholder Farmers in Juja Sub-County, Kenya
|
|
Koyan OC, Kagira J, Waweru KP, Naomi M, and Osuga I.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 656-668, 2025; pii:S232245682500066-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj66
ABSTRACT: Gastrointestinal parasites (GIP) negatively impact the health and productivity of goats. Regular screening of the animals for these parasites is crucial for implementing effective control strategies. A cross-sectional study was conducted to determine the prevalence of GIP and its risk-related factors in goats owned by smallholder farmers in Juja Subcounty, Kiambu County, Kenya. A total of 210 goats consisting of both males and females, of different breeds including Boer, Toggenburg, Alpine, and Small East African were randomly sampled from 80 farms. Fresh fecal samples were collected and analyzed for parasites using McMaster techniques for egg/oocyst examination. A structured questionnaire was administered to assess the risk factors such as age, sex, breed, origin of the goats, production system, and purpose and frequency of cleaning goat houses in relation to the prevalence of the parasites. The overall prevalence of the GIP was 88.6%, with nematodes and coccidia detected in 64.3% and 74.3% of the goats, respectively. The mean eggs per gram was 67.72, while the mean oocysts per gram was 243. Goat fecal samples positive for gastrointestinal nematodes (GIN) eggs were cultured and identified after recovery of third-stage larvae (L3) using the Baermann technique, whereas the coccidian oocysts were sporulated in 2.5% potassium dichromate solution, followed by microscopic examination based on morphological features of the parasites. The identified GIN nematodes included Haemonchus contortus, Trichostrongylus spp., Strongyloides papillosus, Ostertagia spp., and Nematodirus spathiger, while the coccidians were Eimeria caprina, Eimeria ninakohlyakimovae, and Eimeria hirci. The prevalence of GIN was significantly associated with age (higher in adults), production systems (higher in intensive systems), and body condition score (higher in animals with poor body condition). For coccidia, the prevalence was associated with the animal origin (higher in goats from Murera Ward), breed (higher in small East African goats), age (higher in younger goats), body condition score (higher in goats with poor condition), and cleaning frequency (higher in goats kept in irregularly cleaned pens). In conclusion, the overall prevalence and burden of GIP reported in the study were high, with the pathogenic gastrointestinal nematodes and Eimeria spp. being the most prevalent parasites.
Keywords: Coccidia, Goat, Nematode, Prevalence, Risk factor
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Different Levels of Raisins Pomace Powder on Productive Performance and Blood Parameters in Broiler Chickens
|
|
Mahdi AS.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 669-677, 2025; pii:S232245682500067-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj67
ABSTRACT: One of the primary concerns in poultry farming is the exploration of natural feed ingredient alternatives that are, concurrently, more cost-effective and environmentally sustainable. Raisin pomace powder (RPP), a by-product from grape processing, may contain numerous beneficial nutrients and natural compounds that contribute to optimal performance in chickens. The present study assessed the impact of incorporating RPP into broiler chicken diets concerning growth performance, carcass characteristics, economic efficiency, blood parameters, and immune indices. A total of 180 unsexed Ross 308 broiler chickens, all one day old with an initial average body weight of approximately 38 g, were randomly divided into four dietary treatments. The present study comprised a control group (T1) and three experimental groups, including 10 g/kg of RPP (T2), 20 g/kg of RPP (T3), and 30 g/kg of RPP (T4). The study duration spanned 35 days, covering both the initial and finisher phases. The present results demonstrated no statistically significant differences in body weight, weight gain, feed intake, dressing percentage, or economic efficiency among the treatment groups. However, the feed conversion ratio was notably higher in T2 in comparison to the control group. Hematological parameters, encompassing packed cell volume, hemoglobin concentration, as well as red and white blood cell counts, were not significantly influenced by the inclusion of RPP. Serum levels of total protein and globulin remained stable across groups, whereas albumin levels exhibited a significant decrease in T4. Additionally, cholesterol levels were reduced in T3 compared to T1. The current findings suggested that RPP can be included in broiler diets up to 30 g/kg without adverse effects on productivity, physiological status, or immune development. Utilizing RPP provided a sustainable strategy for poultry nutrition through the employment of agro-industrial by-products, thereby potentially improving feed resource efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Keywords: Broiler chicken, Bursa of Fabricius, Economic efficiency, Feed conversion ratio, Productive performance, Raisin pomace powder
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Assessment of Active LaSota and Inactivated Vaccines and Their Nucleotide Sequence Homology on the Virulence of Wild-type Newcastle Disease Genotype VIIi Virus
|
|
Kencana G.A.Y., Astawa I.N.M., Kendran A.A.S., and Pratomo A.A.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 678-687, 2025; pii:S232245682500068-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj68
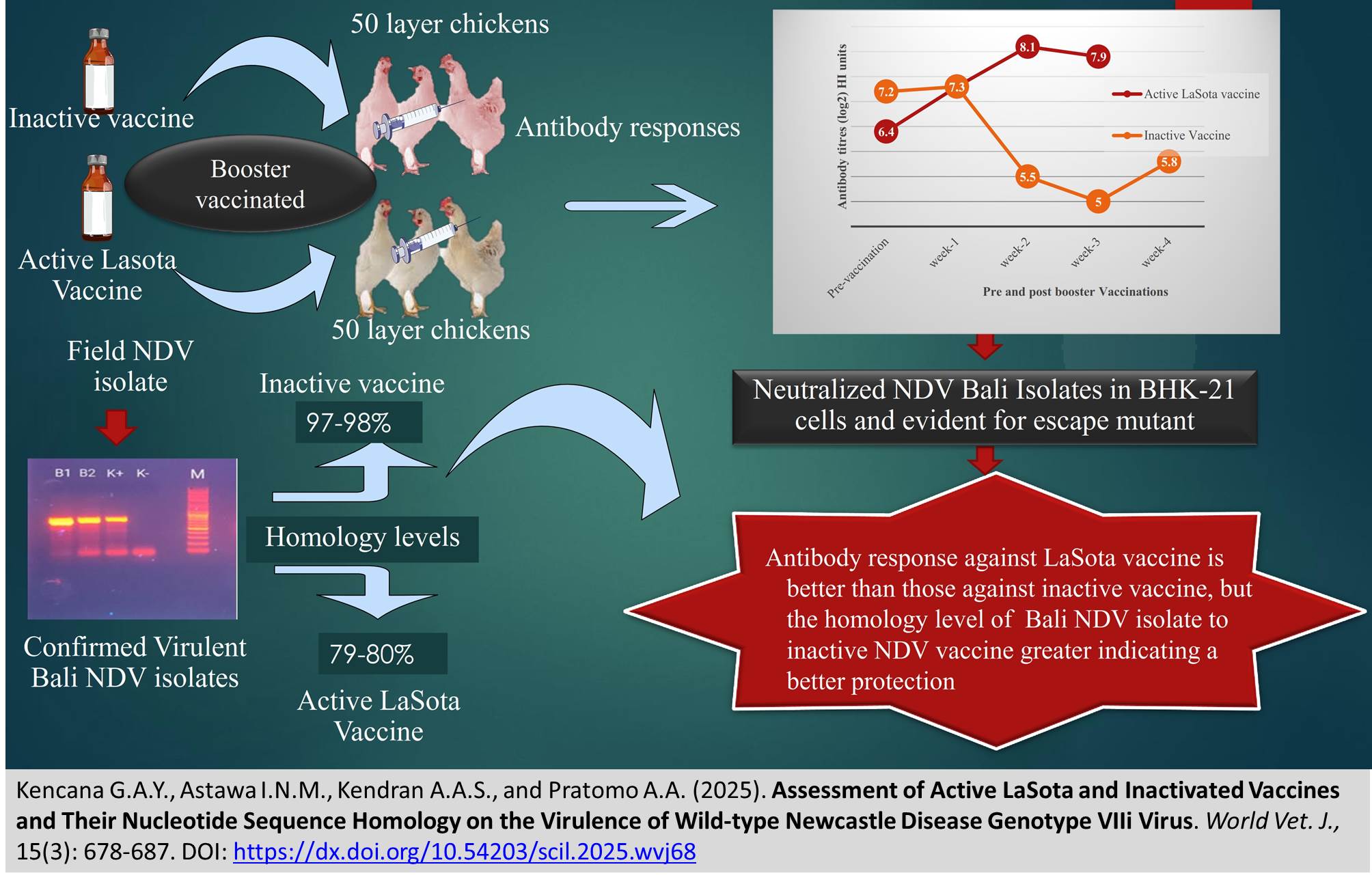
ABSTRACT: Many vaccines are commercially available to prevent Newcastle Disease (ND) in chickens, but the disease is still endemic in many countries. The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of ND vaccines in vivo and to analyze the nucleotide sequence similarity between the vaccines and the wild-type virus encountered in the field, as well as the underlying reasons for vaccination failures against ND in chickens. One hundred laying Isabrown hens, aged 22 weeks with an average weight of 1.75 kg, from two farms (Farm A and B) in Tabanan, Bali, Indonesia, served as experimental animals. All laying hens had previously been vaccinated four times orally with LaSota vaccines (Farm A) and alternately with LaSota and inactive ND vaccines (Farm B). They were then given a booster vaccination orally with live LaSota (Farm A) and intramuscularly with an inactive vaccine (Farm B). Sera samples were collected every week for four weeks in Farm A and for five weeks in Farm B, and the antibody titers were examined by hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test. The genotypes of the field isolates were determined through sequencing and bioinformatics analysis using MEGA 7. The mean log2 antibody titers for hens vaccinated with the LaSota vaccine were 7.2 HI units before vaccination, 7.3 HI units at one week post-vaccination, 8.1 HI units at two weeks post-vaccination, and 7.9 HI units at three weeks post-vaccination. In contrast, the mean log2 antibody titers for those vaccinated with the inactive NDV vaccine were 6.4 HI units at pre-vaccination, 7.3 HI units at one week, 5.5 HI units at two weeks, 5.0 HI units at three weeks, and 5.8 HI units at four weeks post-vaccination. The NDV-LaSota vaccine illustrated 80-81% similarity to a recent ND virus isolate from chickens in Bali (ND/chicken/GAYK01/Penebel Bali/2023), while inactive vaccines exhibited 96-98% similarity. Thus, vaccines were closely related to the Bali virus, whereas the active vaccine was less similar. Based on antibody responses and homology levels, the inactive NDV vaccine induced stronger protective immunity against NDV field isolates than the Active LaSota vaccine.
Keywords: Antibody titer, Field isolate, Neutralization, Newcastle disease vaccine, Sequencing
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Prevalence of Lungworms and Liver Fluke Infections in Ruminants Slaughtered at Kirkuk City, Iraq
|
|
Saleh ANA, Wahhab CM, Al-Bayati AM, Abass KS, and Akool ASK.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 688-694, 2025; pii:S232245682500069-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj69
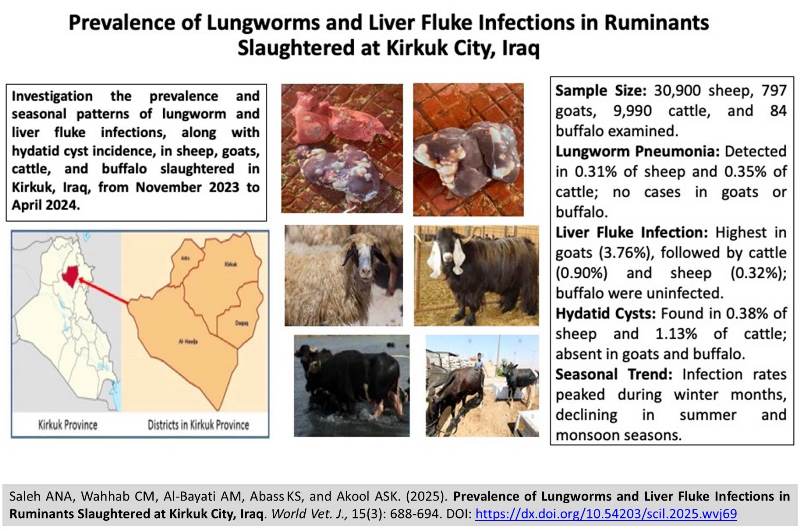
ABSTRACT: Parasitic infections represent one of the most prevalent and economically significant diseases affecting livestock worldwide. The present study aimed to investigate risk factors associated with liver fluke and lungworm infections in small ruminants, characterize the diversity of lungworm species, and determine the prevalence of infections in Kirkuk, Iraq. The study was conducted from November 2023 to April 2024 in Northeastern Iraq, examining 30,900 sheep, 797 goats, 9,990 cattle, and 84 buffalo at slaughter. All carcasses underwent thorough gross pathological examination to detect parasitic infections, including lungworms, liver flukes, hydatid cysts, and associated pulmonary lesions. Distinct pathological manifestations were particularly evident in naturally infected local sheep. The present study revealed the following disease prevalence patterns across species. Pneumonia was detected in 0.31% of sheep and 0.35% of cattle, with no cases observed in goats or buffalo. Hepatitis showed an incidence rate of 0.39% in sheep and 0.75% in cattle. Hydatid cyst occurrence in hepatic and pulmonary tissues was documented at 0.38% in sheep and 1.13% in cattle, while remaining undetectable in caprine and bovine specimens. Liver fluke infection rates varied significantly among species, with sheep exhibiting 0.32% prevalence, goats demonstrating the highest rate at 3.76%, cattle showing 0.90% infection, and buffalo populations remaining completely uninfected. The present findings revealed significantly higher disease susceptibility in ruminants during winter months, with progressively lower infection rates observed throughout summer and monsoon seasons. This seasonal pattern may reflect environmental factors influencing parasite life cycles and host immunity.
Keywords: Animal disease, Hydatid cyst, Parasitic infection, Pneumonia, Ruminant
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Veterinarians' Perceptions of Competence and Communication Skills in Bali, Indonesia
|
|
Dharmawan NS, Wulanyani NMS, and Agustina KK.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 695-702, 2025; pii:S232245682500070-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj70
ABSTRACT: Effective communication is a crucial aspect of veterinary medicine. Despite its importance, this subject has not been sufficiently studied in the specific context of Bali, Indonesia, resulting in a notable gap in the existing research literature. The present study addressed a significant gap in the literature by systematically examining how communication challenges, specifically client dissatisfaction, inadequate treatment compliance, and recurrent misunderstandings between veterinarians and pet owners, affect the quality of veterinary care. The current study explored how veterinary practitioners in Bali, Indonesia, perceive their professional skills and communication abilities. Data were collected through interviews, focus group discussions, open-ended questionnaires, and surveys, involving 218 practitioners in the study area. The participants included small animal practitioners (65%), livestock veterinarians (25%), and mixed-practice clinicians (10%), with experience ranging from recent graduates to senior professionals with over 20 years in the field. The current findings revealed that 86.2% of respondents considered communication skills as equally important as clinical knowledge in facilitating critical professional outcomes, including client trust, treatment compliance, and clinical effectiveness. Effective communication was recognized as crucial for fostering confidence, increasing job satisfaction, strengthening client relationships, and supporting important activities such as anamnesis and treatment discussions. However, practitioners encountered difficulties in discussing sensitive topics, including life-threatening diagnoses, euthanasia, and costly treatment options. Notably, 86.7% of participants indicated the necessity for post-employment communication training to maintain and advance their skills, highlighting the significance of ongoing professional development in Indonesia. The present study emphasized the critical role of communication in veterinary practice and highlighted the demand for targeted training programs to address existing gaps.
Keywords: Client, Communication skill, Perception, Veterinarian
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
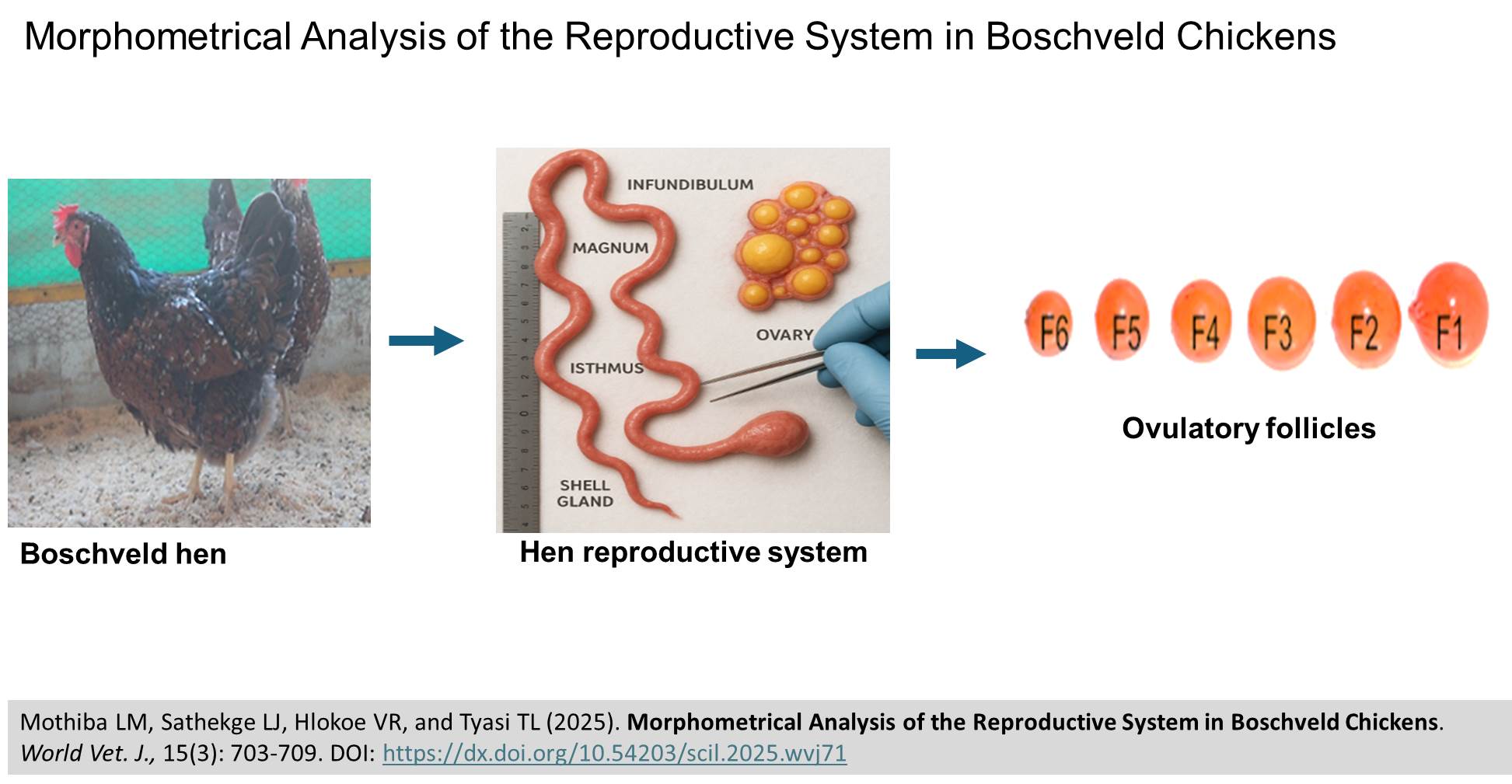
Morphometrical Analysis of the Reproductive System in Boschveld Chickens
|
|
Mothiba LM, Sathekge LJ, Hlokoe VR, and Tyasi TL.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 703-709, 2025; pii:S232245682500071-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj71
ABSTRACT: The egg yield is determined by the number of ovarian follicles that ovulate and the oviduct's capability to form a hard-shelled egg around the egg cell. However, the morphological characteristics of the reproductive organs in Boschveld chickens have not been explored. The present study aimed to evaluate the morphology of the reproductive system, including the oviduct and the developing ova in the Boschveld chicken breed. To perform a morphological analysis, ovarian follicles and oviducts were obtained from six Boschveld hens (Out of a total of twenty), aged 30 weeks, sourced from the University of Limpopo experimental farm in South Africa. The present results revealed significant differences in both the weight and number of small white (2-4 mm), large white (5-6 mm), and small yellow (7-8 mm) follicles. Among the mature follicles, Follicle 1 (F1) exhibited the highest weight, whereas F6 demonstrated the lowest weight. Additionally, the weights and lengths of the infundibulum, magnum, isthmus, and shell gland varied significantly in Boschveld chickens. The present findings indicated that the magnum was the heaviest and longest oviduct segment in Boschveld chickens, and the heaviest pre-ovulatory follicle was ovarian F1, followed by ovarian F2. The results revealed a distinct profile characterized by many small white follicles and a well-developed magnum, which is the largest part of the oviduct. These findings provided a crucial anatomical baseline for the breed, indicating that the structure of the follicular hierarchy and oviduct plays a crucial role in its egg-laying ability. Improving the development and function of these reproductive parts could boost productivity in the Boschveld breed.
Keywords: Boschveld chicken, Isthmus, Magnum, Morphology, Ovarian follicle
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
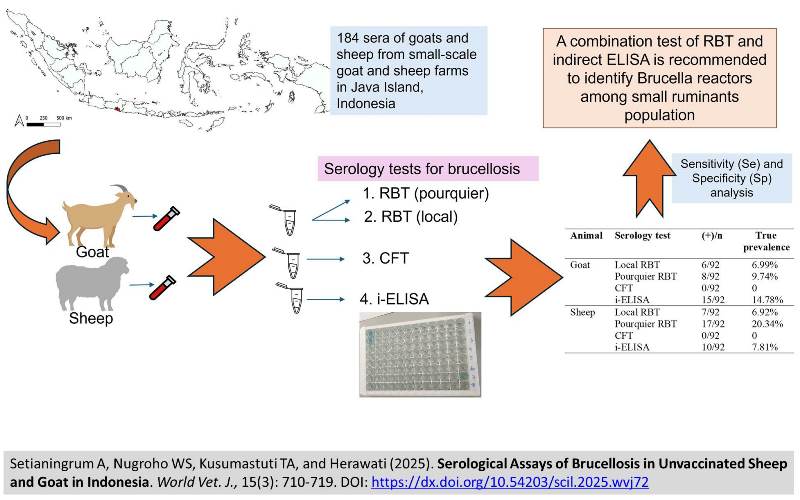
Serological Assays of Brucellosis in Unvaccinated Sheep and Goat in Indonesia
|
|
Setianingrum A, Nugroho WS, Kusumastuti TA, and Herawati.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 710-719, 2025; pii:S232245682500072-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj72
ABSTRACT: Brucellosis is recognized as one of the most widespread zoonotic diseases and is often overlooked, impacting livestock populations worldwide. Annual routine screenings utilize serological assays, such as the Rose Bengal test (RBT) and the complement fixation test (CFT), to identify the presence of brucellosis. The present study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and discriminative performance of the CFT, the locally produced RBT antigen from Indonesia, the commercial RBT antigen (Pourquier), and the indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using sera from Indonesian goats and sheep. A total of 184 serum samples were collected, including 92 from goats and 92 from sheep. The samples were obtained through jugular venipuncture from animals on small-scale goat and sheep farms in Java Island, Indonesia. The results were analyzed to determine true prevalence (TP), accuracy, and cross-tabulation with parallel interpretation to assess the sensitivity and specificity of each test analysis. The TP of brucellosis in small ruminant serum samples using local RBT, Pourquier RBT, CFT, and indirect ELISA was 6.99%, 9.74%, 0%, and 14.78% in goats, and 6.92%, 20.34%, 0%, and 7.81% in sheep, respectively. Moderate Kappa interrater reliability was observed between the local and Pourquier RBTs for both goats (0.537) and sheep (0.440). The combined RBT sensitivity in goats and sheep was 27% and 20%, respectively, while the combined RBT specificity was 92% in goats and 80.5% in sheep. Using more than one diagnostic method is essential for screening and investigating brucellosis in goat and sheep populations. A combination of RBT and indirect ELISA tests is recommended to identify Brucella reactors among small ruminants in Indonesia.
Keywords: Brucellosis, Complement fixation test, Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Rose Bengal test, Small ruminant
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Prevalence and Seasonal Survey of Tick Fauna (Acari: Ixodidae) of Domestic Ruminants in the Hauts-Bassins Region, Burkina Faso
|
|
Sidiki BHEA, Fidèle TD, Alizèta S, Adama K, and Hamani M.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 720-733, 2025; pii:S232245682500073-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj73
ABSTRACT: As in other West African countries, ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting domestic ruminants are a major constraint for livestock breeders in Burkina Faso. The present epidemiological survey study was conducted from October 2022 to September 2023 in two pastoral areas of the Hauts-Bassins region of Burkina Faso to inventory the tick genera and species present, and determine the prevalence and associated risk factors in infested ruminants, including host sex, age, and season. A total of 8,274 live ticks were collected from 800 ruminants randomly selected (300 cattle, 300 sheep, and 200 goats) across two pastoral zones (Sidéradougou and Saho pastoral zones) and three seasons (cold dry season, hot dry season, and rainy season) from the herds of 140 livestock farmers surveyed. Morphological identification identified six species within the genera Amblyomma (67.32%), Hyalomma (26.35%), and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus, 6.33%), with Amblyomma variegatum as the dominant species. The overall prevalence of tick infestation was 74.90%, including 37.25% in cattle, 23.50% in sheep, and 14.15% in goats, with an average infestation level of 10.34 ± 20.30 ticks per animal. Male ruminants (52.62%) were more infested than females (47.38%), and juveniles (41.37%) were more infested than adults (58.63%). Seasonal patterns revealed peak infestation during the rainy and cold dry seasons in both Pastoral zones, and ticks showed a predilection for the inguinal and pastern regions. These findings highlight the extensive tick burden in Hauts-Bassins region, Burkina Faso’s pastoral systems, and underscore the need for targeted, season- and host-specific control strategies to mitigate tick-borne disease risks and improve livestock productivity.
Keywords: Pastoral area, Prevalence, Ruminant, Seasonal dynamic, Tick infestation
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
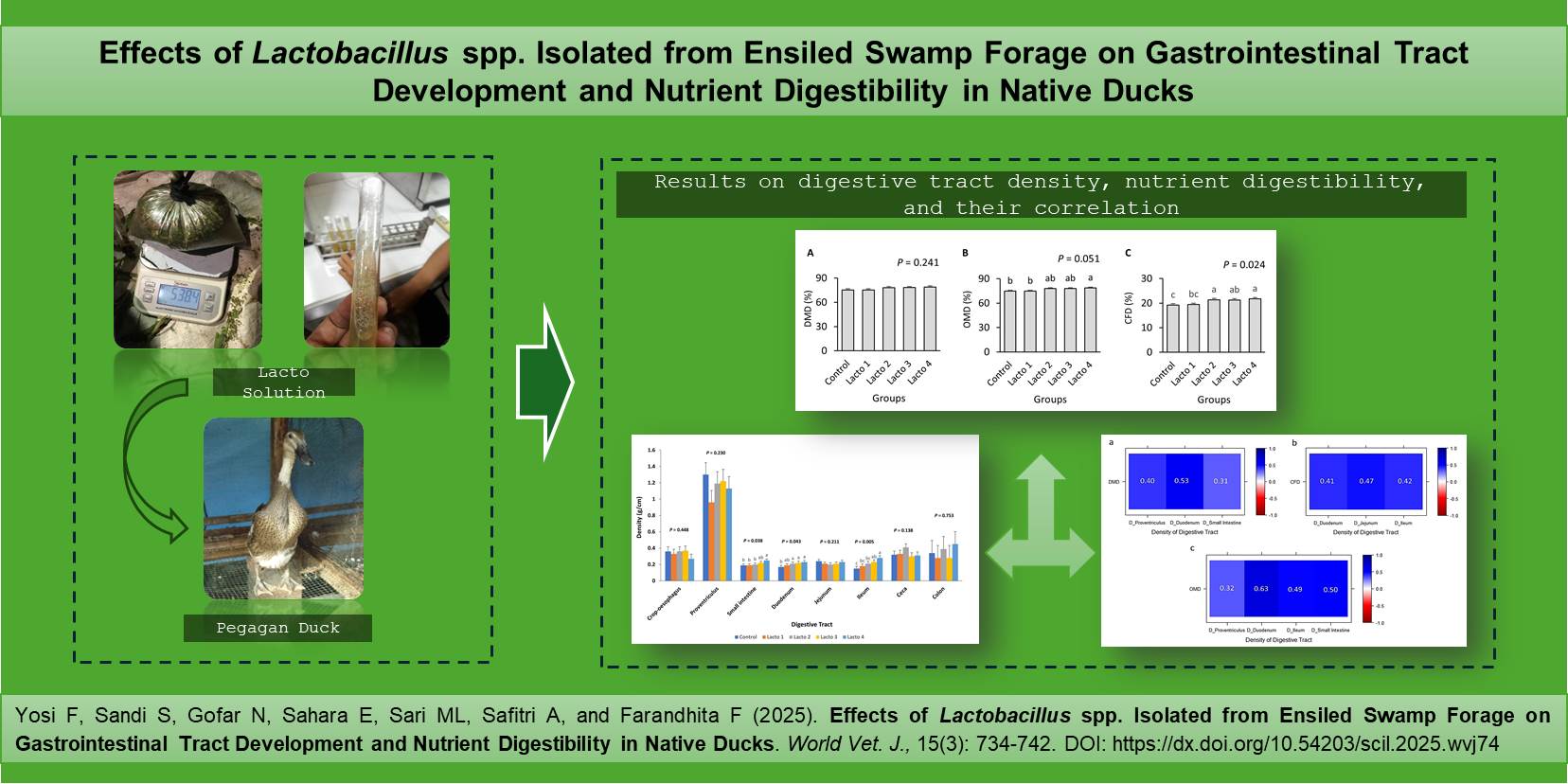
Effects of Lactobacillus spp. Isolated from Ensiled Swamp Forage on Gastrointestinal Tract Development and Nutrient Digestibility in Native Ducks
|
|
Yosi F, Sandi S, Gofar N, Sahara E, Sari ML, Safitri A, and Farandhita F.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 734-742, 2025; pii:S232245682500074-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj74
ABSTRACT: The application of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), particularly Lactobacillus, as feed additives has demonstrated benefits for poultry, including enhanced gut function and better nutrient digestion. However, studies on LAB derived from swamp grass silage remain limited. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of supplementing Lactobacillus spp. (Lacto) solution derived from ensiled swamp forage (Hymenachne acutigluma) at different concentrations through drinking water on the relative weight and length, as well as intestinal density and nutrient digestibility of native ducks. The relationship between intestinal tract density and nutrient digestibility was assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient. The present study involved sixty 24-week-old native ducks, divided into five groups with four replicates each. The groups included a control group and groups that received Lacto solutions in their drinking water. The Lacto solutions were at concentrations of 1×106 CFU/mL (Lacto 1), 1×107 CFU/mL (Lacto 2), 1×108 CFU/mL (Lacto 3), and 1×109 CFU/mL (Lacto 4). The current results indicated that supplementation of the Lacto solution in drinking water increased the relative weights of the proventriculus, small intestine, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and ceca. The relative weight and density of the intestine in the Lacto groups increased linearly with higher concentrations of Lacto solution. Compared to the control group, ducks receiving Lacto supplementation showed improved crude fiber digestibility (CFD) and a tendency to enhance organic matter digestibility (OMD). In 33-week-old ducks, a higher proventriculus density was associated with increased dry matter digestibility (DMD) and OMD. Additionally, the densities of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum were positively correlated with DMD, OMD, and CFD. The present findings indicated that the administration of Lacto solution at increasing concentrations up to 109 CFU/mL via drinking water effectively improved the development of the small intestines of ducks, which was indicated by an increase in the intestinal relative weight and density, as well as enhancing the OMD and CFD in the diets.
Keywords: Drinking water, Lactic acid bacteria, Lactobacillus, Native duck, Nutrient digestibility, Swamp forage
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
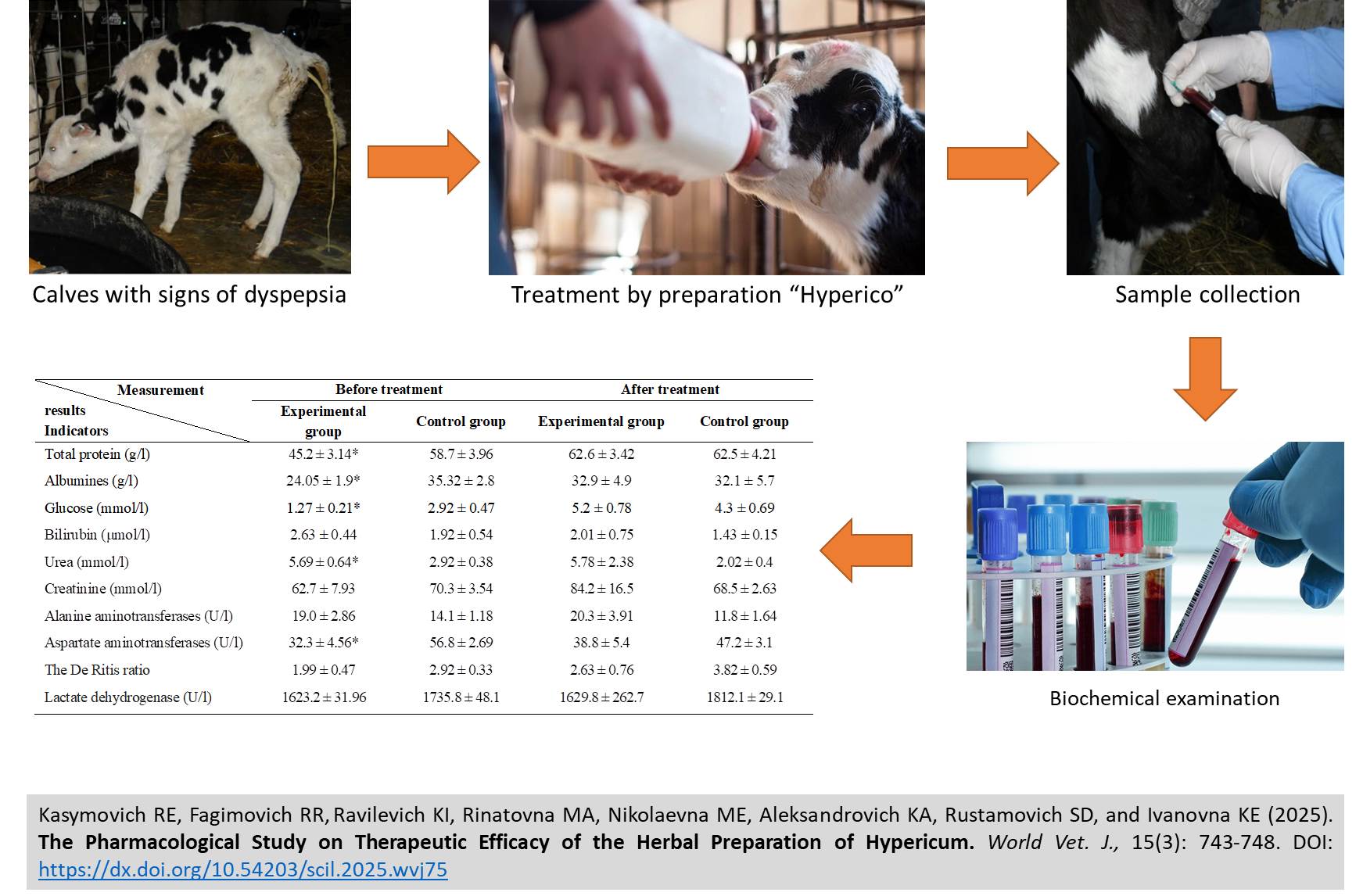
The Pharmacological Study on Therapeutic Efficacy of the Herbal Preparation of Hypericum
|
|
Rakhmatullin EK, Rakhmatullov RF, Kadikov IR, Makaeva AR, Mayorova EN, Korchemkin AA, Sagdeev DR, and Kurshakova EI
World Vet. J. 15(3): 743-748, 2025; pii:S232245682500075-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj75
ABSTRACT: Dyspepsia is a condition associated with digestive disorders, including diarrhea, weakness, dehydration, and intoxication. The investigation and application of therapeutic and prophylactic agents for managing gastrointestinal diseases in young cattle, including dyspepsia in newborn calves, is concerning. The present study aimed to investigate the biochemical mechanisms of action of Hypericum in the treatment of dyspepsia in newborn calves. Two groups of black and white breed bulls (five animals per group), aged 8-10 days, were assigned to assess the effects of Hypericum on biochemical parameters, including total protein, albumin, glucose, bilirubin, urea, creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, and lactate dehydrogenase. Calves in the first group (n = 5), exhibiting pronounced signs of dyspepsia, were administered the treatment. This treatment consisted of 250 mL of Hypericum, combined with 500-700 mL of warm water, instead of milk, during the following two feedings. Then, milk was added to each serving of this mixture until the total volume reached 1.25-1.50 liters, and it was given to calves until clinical signs of recovery appeared. Calves of the second group (n = 5) were clinically healthy and received boiled water instead of the Hypericum. The current findings demonstrated that the biochemical parameters of the experimental calves improved following the administration of Hypericum, reaching levels comparable to those of clinically healthy calves. After prophylactic administration of Hypericum at a dose of 6.5 mL/kg during the first six feedings, the general condition of the experimental calves was satisfactory. In the experimental group of calves administered Hypericum at a dosage of 6.5 mL/kg mixed with milk over a period of two days, only one out of fifteen calves exhibited signs of dyspepsia, including liquid feces and lethargic behavior within the initial four days, representing a prevalence of 6.7%. Hypericum could prevent the occurrence of dyspepsia by 93%. The utilization of Hypericum had a therapeutic influence and positively impacted the clinical condition, behavior, and appetite of the calves.
Keywords: Albumin, Biochemical indicator, Calf, Dyspepsia, Hypericum, Total protein
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Ginger, Turmeric, Teak Leaf Extracts Combined with a Probiotic on Broiler Chicken Performance
|
|
Tasya SA, Nurgiartiningsih VMA, Permata FS, Djati MS, Nuningtyas YF, Hamiyanti AA, and Natsir MH.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 749-755, 2025; pii:S232245682500076-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj76
ABSTRACT: In poultry production, the transition to antibiotic-free systems has resulted in an increased demand for effective natural growth promoters. The present study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a mash-form feed additive made from microwave-extracted ginger, turmeric, and teak leaf phytobiotics, combined with a multi-strain bacterium as a probiotic, administered at graded inclusion levels in broiler chickens. A 35-day feeding experiment was conducted with 300 broiler chickens, arranged in a completely randomized design with five dietary treatments and five replicates per treatment. In the first group, chickens received only the basal diet and served as the control (T0). The treatment groups received the basal feed top-dressed with the phytobiotic and probiotic additive at inclusion levels of 0.2% (T1), 0.4% (T2), 0.6% (T3), and 0.8% (T4). Measurements of performance, including body weight gain (BWG), feed conversion ratio (FCR), performance index, and income over feed cost (IOFC), were collected and analyzed. High-performance liquid chromatography confirmed the presence of key bioactive compounds, such as curcumin and 6-gingerol. The inclusion of 0.2% bacterium as a probiotic additive resulted in optimal BWG, FCR, and the highest IOFC, indicating that this level was biologically effective and economically efficient. In contrast, higher inclusion levels of bacteria as probiotics led to reduced performance, likely due to polyphenol-induced mineral binding and issues with feed palatability. The co-administration of probiotics may enhance the bioavailability of curcumin and promote a healthier gut environment. The present findings highlighted the potential of phytobiotic-probiotic combinations as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters when used at optimal dose levels.
Keywords: Antibiotic-free, Ginger, Performance, Probiotic, Teak leaf, Turmeric
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
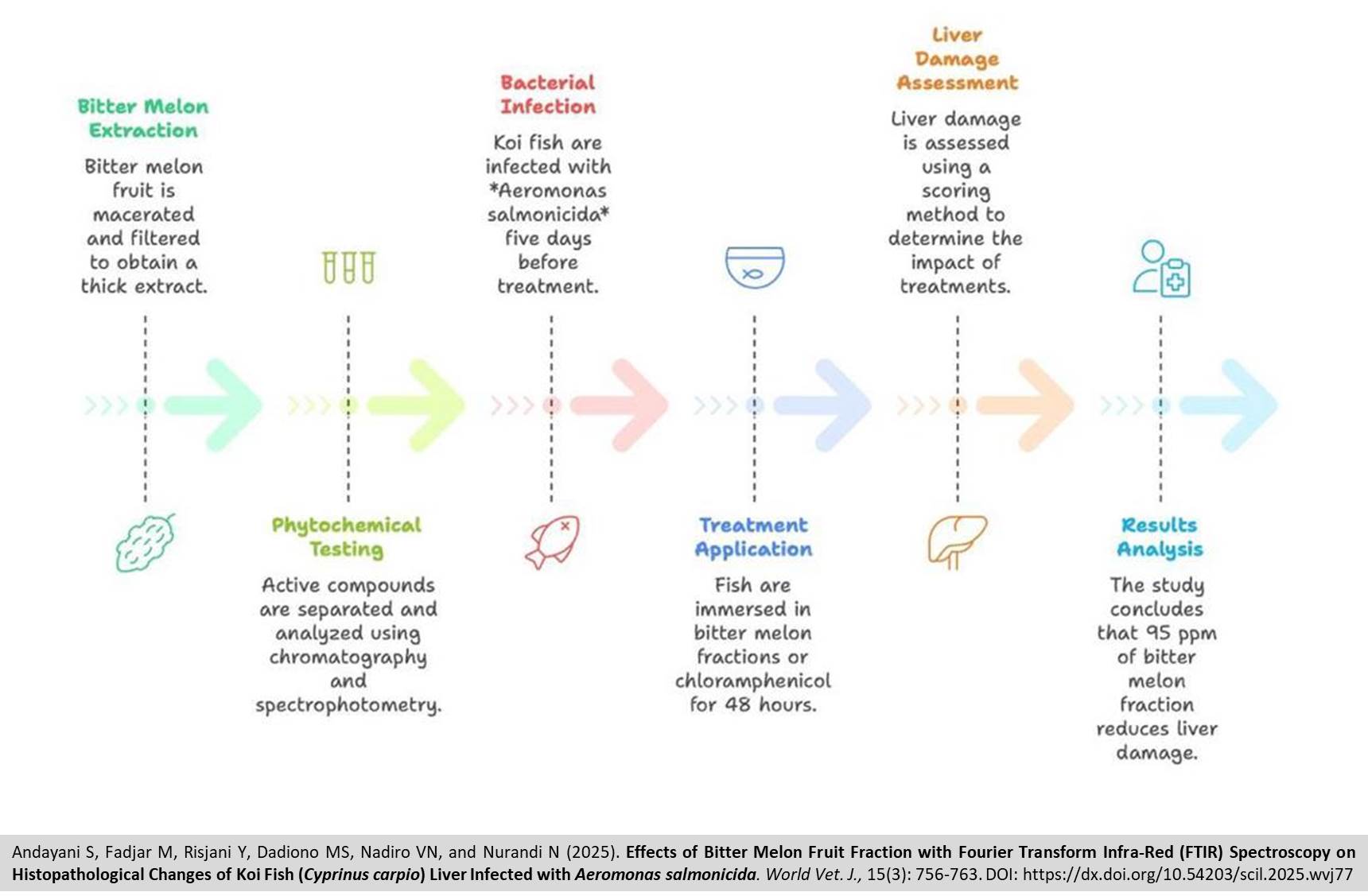
Effects of Bitter Melon Fruit Fraction with Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) Spectroscopy on Histopathological Changes of Koi Fish (Cyprinus carpio) Liver Infected with Aeromonas salmonicida
|
|
Andayani S, Fadjar M, Risjani Y, Dadiono MS, Nadiro VN, and Nurandi N.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 756-763, 2025; pii:S232245682500077-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj77
ABSTRACT: Bitter melon is widely recognized for its medicinal properties, including its potential health benefits in various species. The present study investigated the impact of the bitter melon fraction on liver histological changes of koi fish infected with Aeromonas salmonicida (A. salmonicida). Maceration of bitter melon fruit was carried out for 4 days, then filtered and evaporated to obtain a thick extract. Phytochemical testing included column chromatography for the separation of active compounds and UV-Vis spectrophotometry for the analysis of the absorbance spectra of the fractions. The A. salmonicida bacterial infection was performed five days prior to the fish being soaked in a bitter melon fraction, at a bacterial density of 10⁷ cells/ml for 48 hours. A completely randomized design was employed, featuring five treatments, including no bitter melon fraction with no infection (K -), other groups infected with A. salmonicida and supplemented with 75 ppm of bitter melon (A), 95 ppm of bitter melon (B), 115 ppm of bitter melon (C), and 5 ppm chloramphenicol (antibiotic, K +). Each treatment group consisted of 15 fish (average length and weight of Koi fish were 8 cm and 12 grams) with three replications, which were immersed in their respective solutions for 48 hours. The current study adopted the maceration method with 98% ethanol for the extraction of bitter melon fruit. To determine liver histological damage in Koi fish, the authors employed the scoring method. The findings indicated slight liver damage in histology parameters with an average score of 1.2-1.4 for treatments A and B, respectively; however, treatment C and the positive control exhibited moderate damage with an average necrosis score of 2. According to the obtained data, the bitter melon fruit fraction at a concentration of 95 ppm had the highest preventive effects on the liver of the Koi fish infected with A. salmonicida.
Keywords: Bitter melon fruit, Fraction, Koi fish, Liver
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
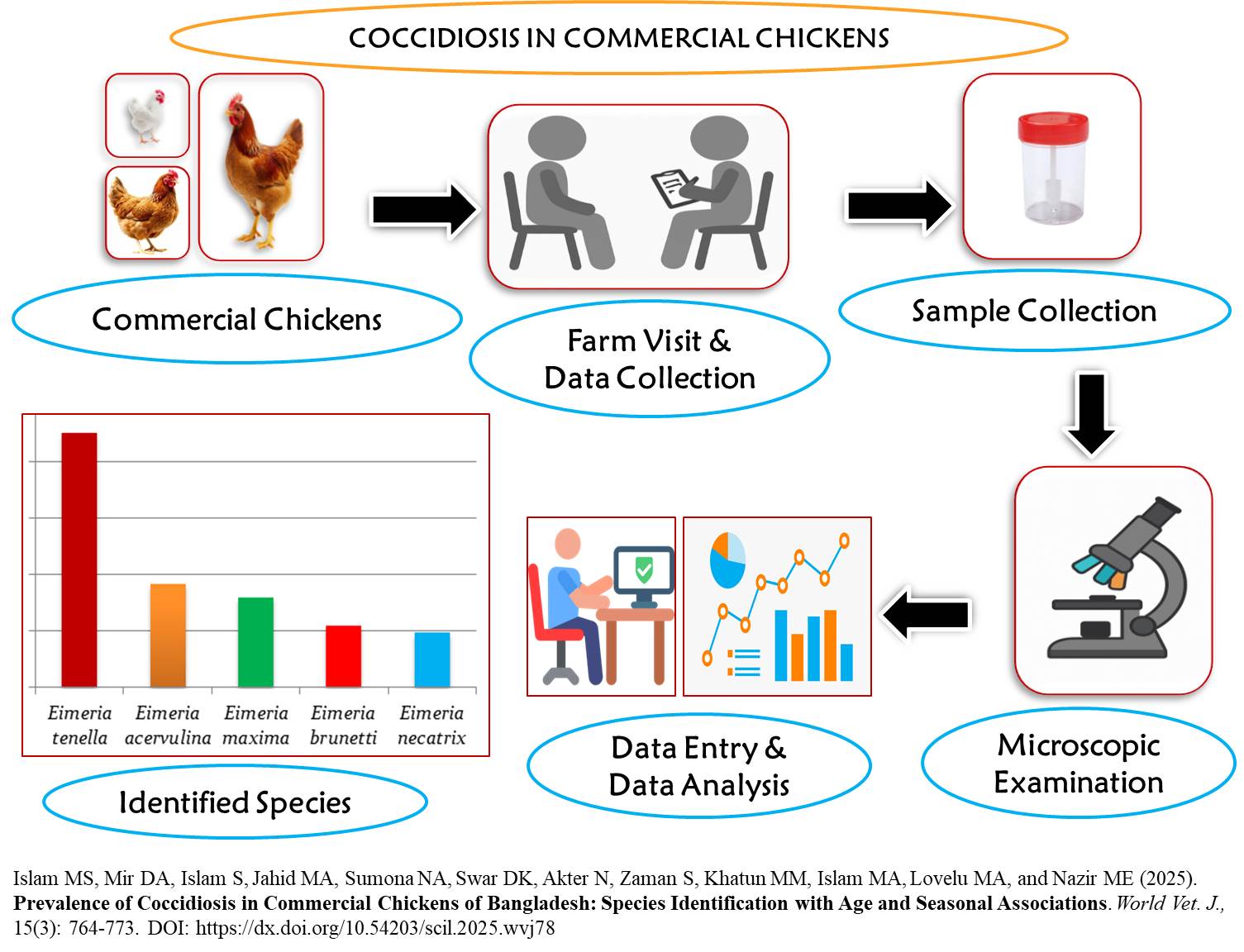
Prevalence of Coccidiosis in Commercial Chickens of Bangladesh: Species Identification with Age and Seasonal Associations
|
|
Islam MS, Mir DA, Islam S, Jahid MA, Sumona NA, Swar DK, Akter N, Zaman S, Khatun MM, Islam MA, Lovelu MA, and Nazir ME.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 764-773, 2025; pii:S232245682500078-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj78
ABSTRACT: Coccidiosis is one of the most economically significant diseases in the poultry industry, resulting in substantial economic losses through treatment costs, reduced growth rates, and decreased body weight gain. The present study aimed to determine the prevalence of different Eimeria (E.) species in commercial chickens and to assess age-specific and seasonal patterns of coccidiosis. A total of 595 chicken fecal samples were randomly collected from three different chicken types, namely broiler breeds (n = 227), layer breeds (n = 205), and Sonali (a dual-purpose crossbred, n = 163) chickens between April 2022 and March 2023, across 27 different farms in the Pirojpur district of Bangladesh. The farms were selected for sampling based on the presence of chickens having clinical signs such as diarrhea, decreased feed consumption, impaired weight gain, lameness, and increased mortality. After sacrificing the suspected chickens, the intestine was carefully inspected and examined for gross pathological lesions. Mucosal scrapings from different intestinal segments and fecal samples were analyzed microscopically for the presence of oocysts using standard parasitological methods. The identification of different Eimeria species was conducted based on the morphological and morphometric characteristics of the oocysts. The result revealed that the overall prevalence of coccidiosis was 13.78%. Among the chicken types, Sonali demonstrated the significantly highest prevalence (21.47%), followed by layers (13.66%) and broilers (8.37%). Five different Eimeria species were identified, with E. tenella (45.12%) being the most prevalent, followed by E. acervulina (18.29%), E. maxima (15.85%), E. brunetti (10.98%), and E. necatrix (9.76%). No significant influence of age or season on coccidiosis prevalence was observed in broiler and layer chickens. In Sonali chickens, the prevalence of coccidiosis increased significantly with age, while no significant effects of season were observed. It has been concluded that the total prevalence of coccidiosis was 13.78%, with Sonali chickens exhibiting the highest prevalence. Five distinct species of Eimeria were identified, with E. tenella being the most common species. Furthermore, no effects of season and age on prevalence of Eimeria species were observed, except for Sonali chickens, where the prevalence increased with age.
Keywords: Coccidiosis, Eimeria, Morphometry, Poultry, Prevalence, Sonali chicken
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
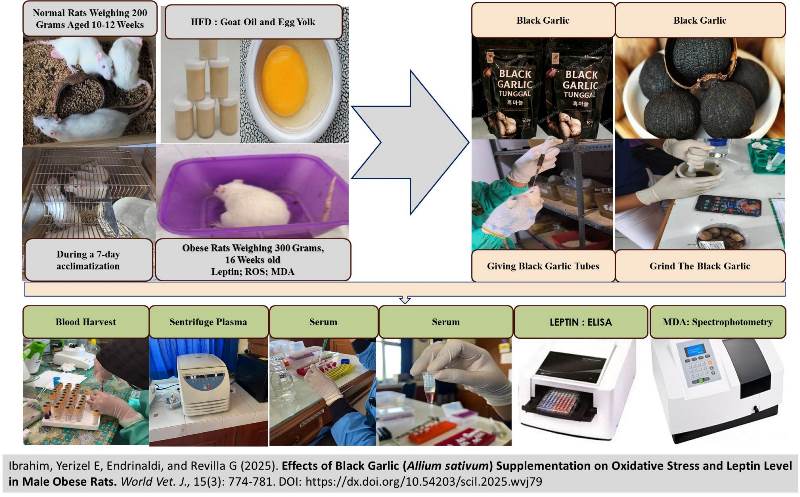
Effects of Black Garlic (Allium sativum) Supplementation on Oxidative Stress and Leptin Level in Male Obese Rats
|
|
Ibrahim, Yerizel E, Endrinaldi, and Revilla G.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 774-781, 2025; pii:S232245682500079-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj79
ABSTRACT: Obesity is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in tissues, leading to leptin resistance and chronic inflammation. Black garlic is a well-documented natural remedy capable of improving leptin resistance and oxidative stress through its antioxidant compounds, such as S-Allyl cysteine and polyphenol flavonoids. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of black garlic on oxidative stress and leptin levels in obese male rats. Twenty-five adult male Wistar rats, aged 10 to 12 weeks and weighing approximately 200 g, were divided into five experimental groups, each comprising five rats. These groups included a negative control group fed a standard diet (K1), a positive control group given a high-fat diet (K2), Treatment group 1 receiving a high-fat diet plus 200 mg of black garlic (P1), Treatment group 2 receiving a high-fat diet plus 400 mg of black garlic (P2), and Treatment group 3 receiving a high-fat diet plus 800 mg of black garlic (P3). The rats received black garlic orally for 28 days. The blood samples were analyzed for markers of oxidative stress, specifically malondialdehyde, as well as leptin levels. The present findings indicated that black garlic significantly decreased malondialdehyde and leptin concentrations in groups P1, P2, and P3 compared to the positive control group. Black garlic, administered at doses of 200, 400, and 800 mg, demonstrated the capacity to diminish oxidative stress and leptin levels in obese male rats.
Keywords: Antioxidant, Black garlic, Leptin, Malondialdehyde, Obesity, Oxidative stress, Rat
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Determinants Influencing Calving to Service Interval in Danish Holstein Cows
|
|
Dung BV, Thuong LTL, and Nam NH.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 782-789, 2025; pii:S232245682500080-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj80
ABSTRACT: The calving-to-first-service interval is crucial for dairy herd productivity. However, factors influencing this reproductive parameter remain understudied in modern dairy systems. The present study aimed to investigate the determinants of the calving-to-first-service interval in Danish Holstein cows, focusing on parity, age at first insemination, age at first calving, gestation length, gender of the born calf, and calving season. Data from 699 cows, managed on a single farm in Southwest Denmark, were collected and analyzed to identify risk factors associated with the calving-to-first-service interval. The mean calving-to-the-first-service interval was 87.6 ± 23.7 days. The present results indicated that parity, age at first calving, and calving season are key modifiable factors that affected the calving-to-first-service interval of the investigated Danish Holstein cows. The final multivariate linear regression model, which explained 13.7% of the variation in the calving-to-first-service interval, identified parity, age at first calving, and the gender of the born calf as significant risk factors for the interval. Parity and age at first calving were negatively related to the calving-to-first-service interval. Male calves were linked to an increased calving-to-first-service interval. Gestation length and age at the first artificial insemination indicated no association with the calving-to-first-service interval. Focusing on key factors such as parity, age at first calving, and gender of the born calf can improve reproductive success and profitability in dairy herds.
Keywords: Age, Calving, First calving, Gender, Parity, Service interval
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
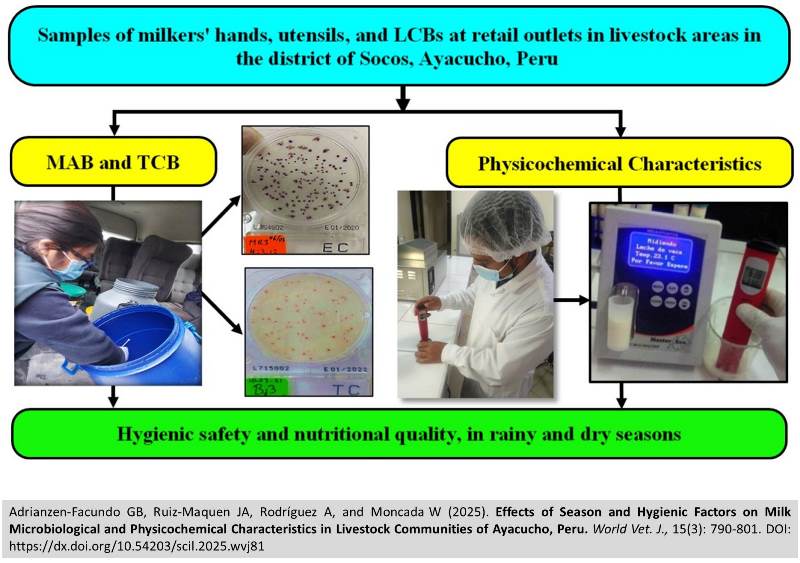
Effects of Season and Hygienic Factors on Milk Microbiological and Physicochemical Characteristics in Livestock Communities of Ayacucho, Peru
|
|
Adrianzen-Facundo GB, Ruiz-Maquen JA, Rodríguez A, and Moncada W.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 790-801, 2025; pii:S232245682500081-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj81
ABSTRACT: Climatic changes can influence milking practices and the dairy production chain, thereby influencing the microbiological safety and physicochemical quality of raw bovine milk (RBM), with potential implications for public health. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of seasonal variability on the hygienic factors and characteristics of RBM produced in livestock communities in the Socos district, Ayacucho, Peru. For mesophilic aerobic bacteria (MAB) and total coliform bacteria (TCB), the compact dry plate method was used. Sixty random samples were collected during the rainy season (RS) and the dry season (DS). Samples were taken from milkers' hands (six in the RS and six in the DS), rags (six in the RS and six in the DS), buckets (six in the RS and six in the DS), receiving tanks (eight in the RS and eight in the DS), and distribution centers (four in the RS and four in the DS). To evaluate physicochemical characteristics, including density, fat, protein, total solids, lactose, pH, and mineral salts, eight samples of Brown Swiss cattle RBM were collected directly from the tanks (four in the RS and four in the DS) of two distribution point centers. The present results indicated that the MAB count for hygienic factors was lower in the DS than in the RS, except in the milker's hands and distribution centers. For the TCB count related to hygienic factors, the values were lower in the DS than in the RS, except in receiving tanks and distribution centers. In the RS, the physicochemical qualities complied with the Peruvian Technical Standard (PTS), except for protein content and mineral salt levels. In the DS, the physicochemical quality did not comply with the PTS; however, these properties were within acceptable limits in the receiving tanks for MAB and on the milker's hands for TCB. As a result, the bacterial load on inert surfaces and the characteristics of RBM were lower in the DS compared to the RS. Still, contamination during milking and at distribution centers was greater.
Keywords: Coliform, Hygienic safety, Mesophilic, Milk, Physicochemical quality, Season
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
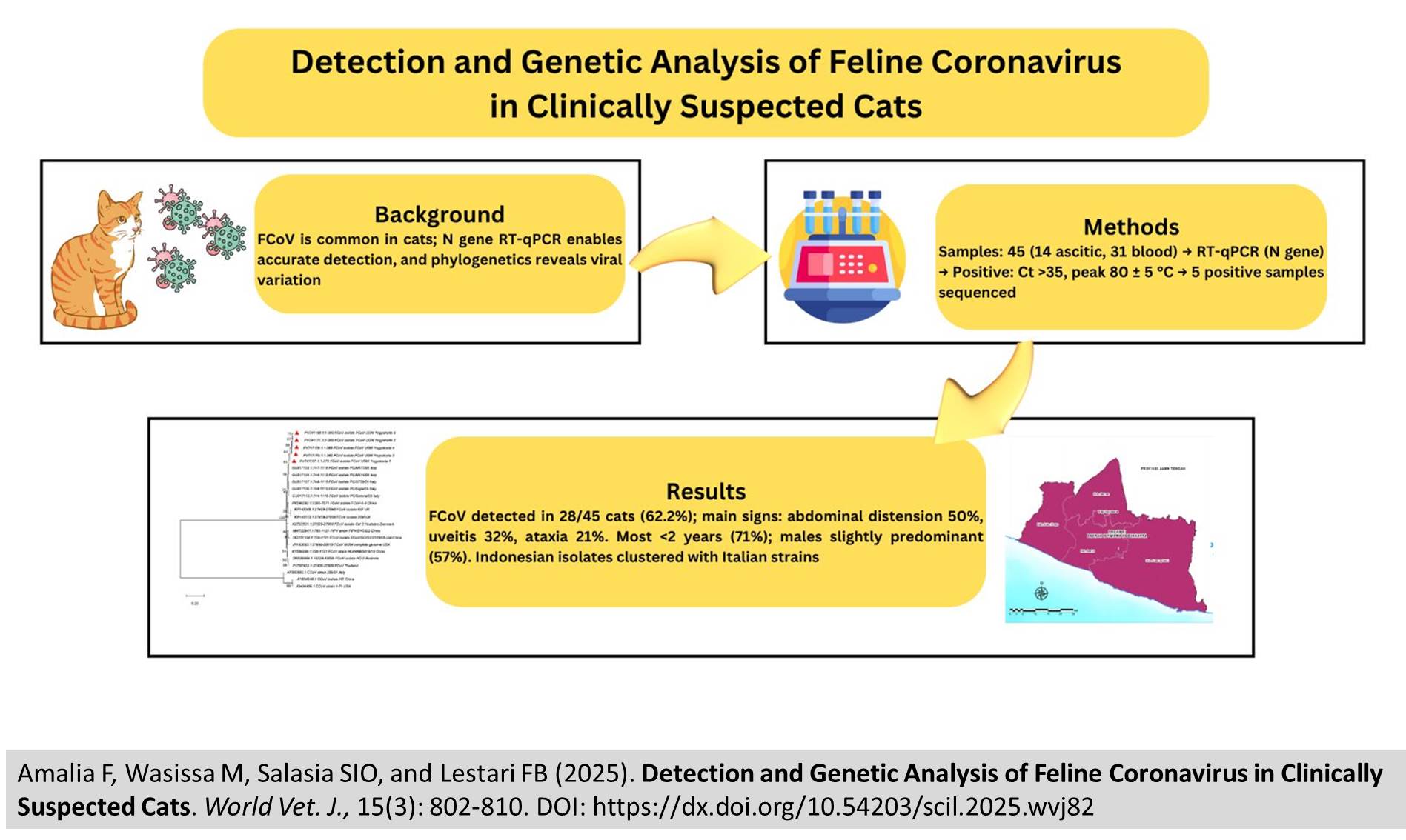
Detection and Genetic Analysis of Feline Coronavirus in Clinically Suspected Cats
|
|
Amalia F, Wasissa M, Salasia SIO, and Lestari FB.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 802-810, 2025; pii:S232245682500082-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj82
ABSTRACT: Feline coronavirus (FCoV) is a common infection in cats, producing outcomes that differ from mild intestinal disease to the fatal form known as feline infectious peritonitis (FIP). Accurate antemortem diagnosis is challenging, and reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) targeting the nucleocapsid (N) gene offers high sensitivity and specificity, while phylogenetic analysis reveals viral variation. The present study aimed to detect FCoV in clinically suspected cats using RT-qPCR and to analyze the phylogenetic relationships of local isolates from Yogyakarta, Indonesia. A total of 45 clinical samples, consisting of 14 ascitic fluid and 31 blood samples, were collected from cats of different breeds (mixed, domestic shorthair, and Persian), aged 0.5-4 years, including 22 males and 23 females, that were presented to seven veterinary clinics in Yogyakarta with clinical signs such as vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal effusion, uveitis, and ataxia. The RT-qPCR revealed 62.2% (28/45) positive cases, with detection rates of 100% (14/14) in ascitic fluid and 45.2% (14/31) in blood. The most frequent clinical findings among FCoV-positive cats were abdominal distension (50%), uveitis (32.1%), ataxia (21.4%), and rhinitis (17.9%). Most infected cats (71.4%) were under two years of age, with a slightly higher prevalence in males (57.1%). Phylogenetic analysis of three isolates from ascitic fluid demonstrated a close genetic relationship with strains from Italy, the United Kingdom, and China, clustering into two distinct clades. The present study highlighted the utility of RT-qPCR targeting the N gene as a reliable diagnostic tool for clinical cases, while providing new clinicopathological and molecular data on naturally occurring FCoV infection in Indonesia. These findings contribute to the global understanding of FCoV molecular epidemiology and support future surveillance and control strategies for coronavirus infections in domestic cats.
Keywords: Cat, Feline coronavirus, Feline infectious peritonitis, Phylogenetic analysis
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Antibacterial and Sensory Impact of β-carotene and Riboflavin on Pseudomonas Biofilm in Raw Milk
|
|
El-Shora HE, Sharaf DM, Fathalla EK, Lela RA, Aladl MM, and Elbanna AF.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 811-823, 2025; pii:S232245682500083-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj83
ABSTRACT: Milk is a highly nutritious yet perishable food that is susceptible to microbial contamination and spoilage, particularly by Pseudomonas species. The present study aimed to assess the antimicrobial and sensory effects of β-carotene and riboflavin as natural additives for preserving raw milk, with a specific emphasis on controlling biofilm-forming Pseudomonas strains. A total of 100 raw milk samples were collected from different markets in Gharbia, Egypt, and tested for Pseudomonas spp. Biofilm formation was assessed in isolates, followed by the detection of the quorum-sensing transcriptional regulator lasR, pellicle formation protein A (polysaccharide biosynthesis protein A) pelA, and polysaccharide synthesis locus protein A pslA genes. An in vitro trial was performed on eight groups of raw milk to evaluate the effects of β-carotene and riboflavin at concentrations of 1 µg/ml and 4 µg/ml, respectively, on Pseudomonas counts and sensory properties. The groups include positive control (G1), raw milk inoculated with Pseudomonas and fortified with β-carotene (G2), raw milk inoculated with Pseudomonas and fortified with riboflavin (G3), raw milk inoculated with Pseudomonas and fortified with a combination of β-carotene and riboflavin (G4), negative control (G5), milk fortified with β-carotene only (G6), milk fortified with riboflavin only (G7) and milk fortified with both β-carotene and riboflavin (G8). Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to assess the impact of these additives on Pseudomonas, specifically on 16S rRNA and pslA gene expression. Pseudomonas spp. were found in 20% of samples, with 75% forming biofilms. The pslA gene was detected in 83.33% of these samples. β-carotene and riboflavin indicated dose-dependent antibacterial effects, with minimum inhibitory concentration values, and minimum bactericidal concentration values. Milk fortified with these compounds, particularly in G4, demonstrated the most significant reduction in Pseudomonas during a 6-day storage period. Additionally, β-carotene maintained a preferable sensory quality compared to other groups. RT-PCR confirmed the highest pslA gene suppression with the combined treatment. The current findings indicated that β-carotene at a concentration of 1 µg/ml, whether used independently or in combination with riboflavin, can serve as an effective natural preservative in dairy products.
Keywords: Beta-Carotene, Biofilm, Pseudomonas, PslA Expression, Riboflavin
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Microbiological and Hematological Diagnostic Profiles of Strawberry Footrot in Sheep in Karawang, Indonesia
|
|
Yasyfa’ Sukmayani J, Bermani F, and Wicaksana DN.
World Vet. J. 15(3): 824-830, 2025; pii:S232245682500084-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj84
ABSTRACT: Dermatophilus congolensis (D. congolensis) is a gram-positive, coccus-shaped pathogenic bacterium that develops a filamentous structure during the infectious phase. The D. congolensis can cause scab lesions on sheep’s feet, which may eventually develop into bloody tissue resembling crushed strawberries. The present study aimed to provide diagnostic, microbiological, and hematological profiles of strawberry footrot in sheep in Karawang Regency, Indonesia. Six sheep (Ovis aries), with an average age of two years and exhibiting similar signs of strawberry footrot, were sampled from community farms in the region. Blood samples and exudate swabs from scab lesions on the feet and udder were collected in August 2024 for analysis. Hematological testing and bacterial isolation using blood agar, gram staining, fermentation, and biochemical tests were performed. The hematologic results indicated thrombocytosis, macrocytic normochromic anemia, and leukocytosis in the sheep. All samples exhibited beta hemolysis zones on blood agar and were gram-positive, coccus-shaped bacteria with a railroad appearance. Biochemical tests were positive for catalase, negative for indole, negative for Voges-Proskauer (VP), and showed the ability to ferment glucose and maltose. Based on clinical signs, hematological findings, and bacterial isolation, D. congolensis was confirmed as the causative agent of strawberry footrot in sheep in Karawang Regency, Indonesia.
Keywords: Dermatophilus congolensis, Hematological profile, Microbiology, Strawberry footrot
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).