Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 15 (4); December 2025 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 15 (4); December 2025 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
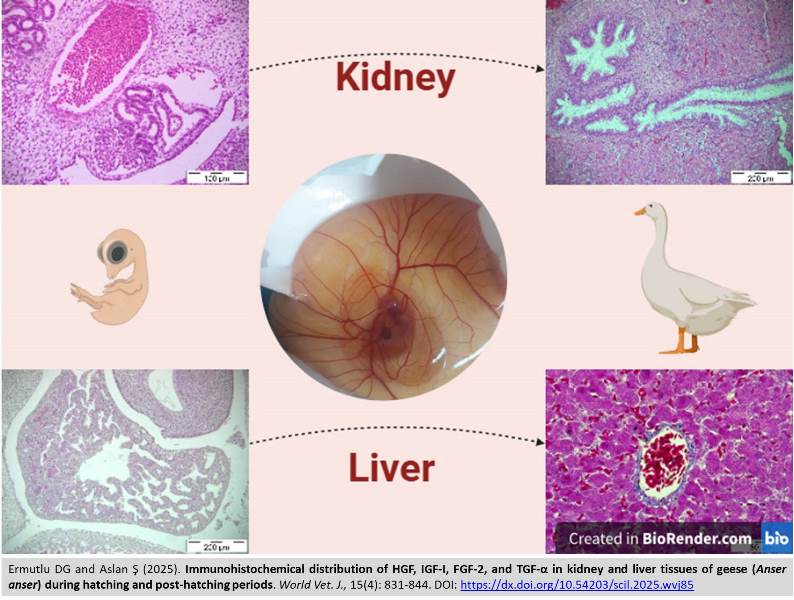
Immunohistochemical distribution of HGF, IGF-I, FGF-2, and TGF-α in kidney and liver tissues of geese (Anser anser) during hatching and post-hatching periods
|
|
Ermutlu DG and Aslan Ş.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 831-844, 2025; pii:S232245682500085-15
DOI:https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj85
ABSTRACT: Immunohistochemical studies during embryonic development of poultry are quite limited. The present study aimed to investigate the distribution of Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α) in the kidney and liver tissues of hatching and post-hatching geese via histologic and immunohistochemical methods. A total of 150 fertile goose eggs were used in the study. Throughout the incubation process (29 days), four eggs were used each day, starting from the sixth day, and the embryos were examined. The embryos were fixed in 10% formaldehyde solution. Geese at the 7, 15, 30, and 210 (adult) days after hatching were euthanized for a post-hatching evaluation. Routine histological procedures were performed on the kidney and liver tissues. For histological examinations were used Crossmonn’s triple staining, Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS), and Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining. HGF, IGF-I, FGF-2, and TGF-α immunoreactivities were investigated in the histological slides. An examination of kidney tissue development indicated that metanephric blastema formation started on day 10. The mesonephros was replaced by the metanephros, the permanent kidney, starting on the day 25. An examination of liver tissue development revealed that sinusoids began to narrow, hepatic plaques formed, and endothelial and Kupffer cells became distinguished as early as day 8. Upon general evaluation, FGF-2 was found to be the growth factor with the most intense immunoreactivity in the liver and kidney, while IGF-I had the least immunoreactivity. There is a paucity of studies on growth factors during the embryonic period in poultry. In the present study, all four growth factors were immunohistochemically investigated in the kidney and liver during the hatching and post-hatching periods. Because poultry have a shorter embryonic period than mammals, they need to utilize growth factors effectively and at high levels. The present study demonstrated that HGF, IGF-I, FGF-2, and TGF-α growth factors were effective in kidney and liver development during the incubation period in geese.
Keywords: Embryo, Goose, Growth factors, Kidney, Liver
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
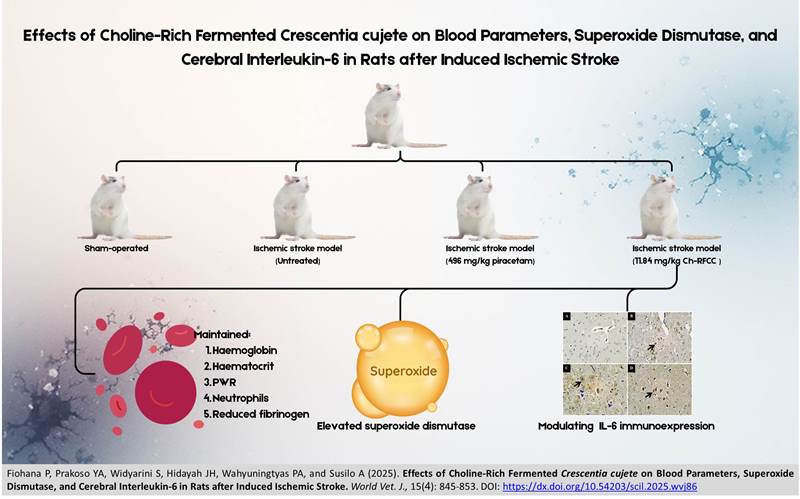
Effects of Choline-Rich Fermented Crescentia cujete on Blood Parameters, Superoxide Dismutase, and Cerebral Interleukin-6 in Rats after Induced Ischemic Stroke
|
|
Fiohana P, Prakoso YA, Widyarini S, Hidayah JH, Wahyuningtyas PA, and Susilo A.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 845-853, 2025; pii:S232245682500086-15
DOI:https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj86
ABSTRACT: Ischaemic stroke is a major vascular disorder that profoundly impacts human health. Choline-rich fermented Crescentia cujete (Ch-RFCC) has emerged as a promising adjunctive therapy for ischemic stroke; however, its effects on hematological parameters, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels remain unexplored. The present study aimed to assess the impacts of Ch-RFCC on hematological parameters, SOD activity, and brain IL-6 levels in the rats' ischemic stroke model (ISM). A total of 40 three-month-old male rats, weighing 247.31 ± 4.95 g, were randomly assigned into four groups, including healthy rats with a skin incision as the control group (sham-operated, T1), ISM without treatment (T2), ISM treated with 496 mg/kg body weight of piracetam (T3), and ISM treated with 11.84 mg/kg body weight of Ch-RFCC (T4). Treatments using piracetam (T3) and Ch-RFCC (T4) were administered orally via gavage twice daily for 14 consecutive days. The current results demonstrated that Group T4 maintained haemoglobin and haematocrit levels, normalised the platelet-to-leucocyte ratio and neutrophil counts, reduced fibrinogen levels, elevated SOD activity, and enhanced IL-6 immunoreactivity compared to the untreated ISM group (T2). Furthermore, rats in Group T4 exhibited the least body weight loss compared to those in groups T2 and T3. These findings indicated that Ch-RFCC may alleviate ischemic stroke in rats by enhancing antioxidant defenses, modulating IL-6 expression, and preserving hematological homeostasis.
Keywords: Choline-rich fermented Crescentia cujete, Hematology, Interleukin-6, Ischemic stroke, Superoxide dismutase
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
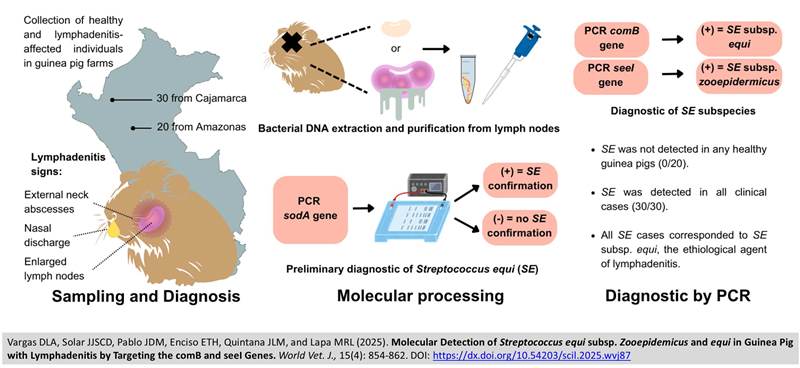
Molecular Detection of Streptococcus equi subsp. Zooepidemicus and equi in Guinea Pig with Lymphadenitis by Targeting the comB and seeI Genes
|
|
Vargas DLA, Solar JJSCD, Pablo JDM, Enciso ETH, Quintana JLM, and Lapa MRL.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 854-862, 2025; pii:S232245682500087-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj87
ABSTRACT: Despite the economic and sanitary relevance of cervical lymphadenitis in guinea pigs, little molecular information is available regarding the role of Streptococcus (S.) equi subspecies in cervical lymphadenitis in Peru. The present study aimed to identify the subspecies S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus (SEZ) and S. equi subsp. equi (SEE) in guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus), with and without cervical lymphadenitis, from the Amazonas and Cajamarca regions of Peru, using PCR amplification of the sodA, comB, and seeI genes. A total of 50 guinea pigs, aged 6-8 months, were evaluated, 30 from Cajamarca (mean weight 1210.1 grams; 22 Peruvian breed, 1 Inti, and 7 Brown) and 20 from Amazonas (mean weight 950 grams; 10 Peruvian breed and 10 Inti), comprising 30 animals with cervical lymphadenitis and 20 clinically healthy animals. The sodA gene was first employed as a preliminary diagnostic marker, which confirmed the presence of S. equi in all animals presenting lymphadenitis. Subsequent amplification of the comB gene confirmed the exclusive presence of SEZ in all clinical cases, with no detection in the 20 clinically healthy guinea pigs analyzed in both study regions. In contrast, the seeI gene, specific to SEE, indicated no amplification in any of the samples, indicating the absence of SEE in the study population. The prevalence of SEZ (positive comB) among guinea pigs with cervical lymphadenitis was 100% in Amazonas (10/10; 95% CI: 69.2-100%) and 100% in Cajamarca (20/20; 95% CI: 83.2-100%), with no significant difference between regions. The present findings established SEZ as the primary etiological agent of cervical lymphadenitis in guinea pigs from both regions, with no molecular evidence of SEE. The present study underscored the utility of comB and seeI as specific and reliable molecular markers for differentiating SEZ and SEE.
Keywords: comB gene, Guinea pig, seeI gene, Streptococcus equi subsp. equi, Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Essential and Toxic Element Profiles in Selected Spices from Greater Casablanca, Morocco
|
|
Safaa S, Sabri C, Salam MR, El Mellouli F, Lafram A, Khallouki H, Hassane YA, and Kabine M.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 863-881, 2025; pii:S232245682500088-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj88
ABSTRACT: In Morocco, spices are an integral part of daily cuisine and serve as a vector of both nutritional and toxicological exposure. Monitoring elemental composition is essential to ensure consumer safety, animal health when used as feed additives, and compliance with international standards. The present study aimed to determine the concentrations of essential (potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and iron) and toxic (lead, cadmium, arsenic, chromium, and nickel) elements in commonly consumed spices in Morocco, including cinnamon, cumin, ginger, black pepper, and turmeric. A total of 162 spice samples were obtained from markets in the Greater Casablanca, Morocco. Five essential elements, including potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and iron, and five toxic trace metals, including lead, cadmium, arsenic, chromium, and nickel, were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) after microwave-assisted digestion. Cumin indicated the highest levels of magnesium (6.86 ± 1.61 g/kg), sodium (3.98 ± 1.59 g/kg), calcium (11.13 ± 4.53 g/kg), and iron (753.71 ± 446.07 mg/kg). Turmeric had the highest levels of potassium (25.96 ± 13.51 g/kg). Cinnamon had elevated levels of lead (2.05 mg/kg) and cadmium (0.29 mg/kg), exceeding Moroccan and European regulatory limits. Additionally, cumin indicated the highest levels of arsenic (0.45 ± 0.30 mg/kg) and nickel (4.18 ± 2.85 mg/kg) compared to other spices. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed distinct elemental patterns. The first component (PC1), driven by magnesium and sodium, clearly separated cumin due to its high macronutrient content. The second component (PC2), influenced by cadmium and lead, isolated cinnamon because of its toxic metal burden. The PC1 and PC2 accounted for 64.6% of the total variance. Turmeric and ginger formed a close cluster in the PCA plot, associated with higher levels of potassium, calcium, and nickel. Black pepper was positioned between these groups, reflecting intermediate composition. Pearson correlation analysis supported these findings, with a strong correlation between lead and cadmium, suggesting a shared contamination source. These results emphasized the nutritional and toxicological roles of spices in Moroccan diets. Regular monitoring is essential to protect public health in both animals and humans.
Keywords: Food safety, Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Spices, Toxic metal
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
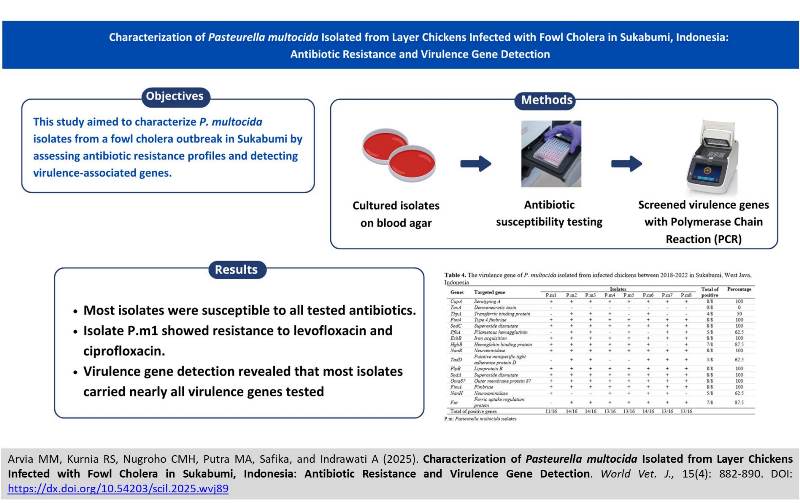
Characterization of Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Layer Chickens Infected with Fowl Cholera in Sukabumi, Indonesia: Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Gene Detection
|
|
Arvia MM, Kurnia RS, Nugroho CMH, Putra MA, Safika, and Indrawati A.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 882-890, 2025; pii:S232245682500089-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj89
ABSTRACT: Fowl cholera is a contagious bacterial disease in poultry caused by Pasteurella multocida (P. multocida), which presents a significant threat to layer chicken farming due to its economic impact and potential antibiotic resistance. This study aimed to characterize P. multocida isolates from a fowl cholera outbreak in Sukabumi by assessing antibiotic resistance profiles and detecting virulence-associated genes. Eight P. multocida bacterial isolates from organ sample were cultured on blood agar and subjected to antibiotic susceptibility testing using the Sensititre™ GN4F system. Genomic DNA was extracted and analyzed for 16 virulence genes through conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Results showed that all isolates were generally susceptible to the tested antibiotics, except for isolate P.m1, which was confirmed resistant to levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin. Virulence gene detection revealed that most isolates carried nearly all virulence genes tested, particularly those encoding capsule (capA), iron acquisition proteins (exbB, hgbB, fur), fimbriae and adhesins (fim4, fimA, pfhA, tadD), outer membrane proteins (oma87, plpB), sialidases (nanB, nanH), and superoxide dismutases (sodA, sodC). Notably, no isolates harbored the toxA gene. The presence of extensive virulence factors despite general antibiotic susceptibility underscored the pathogen’s potential to persist and cause disease, and highlighted the need for targeted surveillance and comprehensive control strategies in Indonesia. Keywords: Antibiotic resistance, Characterization, Fowl cholera, Pasteurella multocida, Virulence gene
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Rapid Simultaneous Detection of Salmonella and Campylobacter Bacteria Directly from Chicken Faeces
|
|
Ghafar SNA, Ahmad NI, Aziz SA, and Zakaria Z.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 891-900, 2025; pii:S232245682500090-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj90
ABSTRACT: Campylobacter and Salmonella are widely recognized as significant causes of foodborne diseases, with poultry and poultry products being the most frequent sources of infection in humans. Rapid, simultaneous detection of both pathogens can prevent contaminated food from entering the human food chain. The present study aimed to simultaneously detect Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. directly from faeces of broiler chickens aged 4 to 5 weeks by multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR). The suitability of the PCR protocol using pairs of primers targeting the invA and cadF genes was evaluated to detect Salmonella and Campylobacter spp., respectively, from 15 samples. The specificity of the PCR assay was 100% for both pathogens, as no positive cross-reactions were detected with non-targeted bacteria. The limit of detection for pure culture of Salmonella was 1 CFU/mL, whereas for Campylobacter it was 101 CFU/mL. Incubation of spiked faeces in brain heart infusion broth for 24 to 48 hours maintained a detection limit of 1 CFU/mL for Salmonella; however, the sensitivity decreased, resulting in a detection limit of 10² CFU/mL for Campylobacter. Simultaneous detection from 15 chicken faecal samples revealed two samples co-carrying both Salmonella and Campylobacter spp., four samples positive for Salmonella, six samples positive for Campylobacter, and three samples were negative for both pathogens. The developed mPCR protocol in the present study was highly specific and sensitive for detecting Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. directly from chicken faeces, achieving results in under 36 hours compared to the conventional culture method. The mPCR protocol can benefit veterinary and public health authorities during epidemiological investigations and rapid diagnostic purposes, which require timely confirmation of the disease status in chickens during the grow period.
Keywords: Campylobacter, Faeces, Multiplex PCR, Salmonella, Simultaneous detection
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
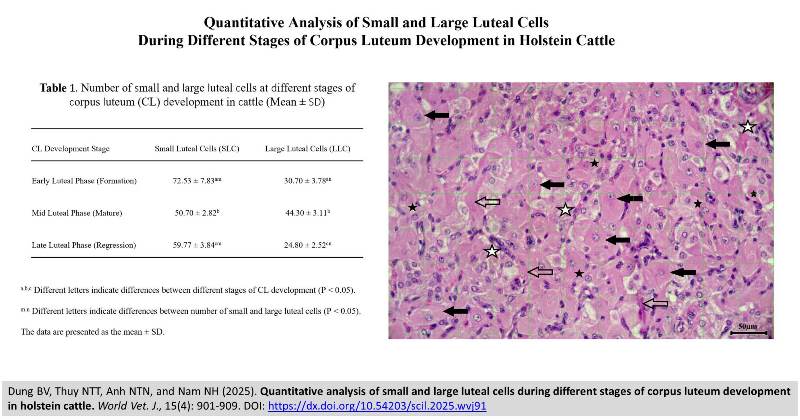
Quantitative analysis of small and large luteal cells during different stages of corpus luteum development in holstein cattle
|
|
Dung BV, Thuy NTT, Anh NTN, and Nam NH.
World Vet. J. 15(2): 901-909, 2025; pii:S232245682500091-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj91
ABSTRACT: The bovine corpus luteum (CL) undergoes dynamic structural and functional changes throughout its lifespan, driven by distinct populations of steroidogenic cells, including small luteal cells (SLCs) and large luteal cells (LLCs). Although these cell types have been morphologically characterized, quantitative evaluations of their numerical abundance and relative distribution across different developmental phases of the CL in cows remain limited. This study sought to quantify the populations of small and large luteal cells across the early, mid, and late stages of corpus luteum development in Holstein cows. Histomorphometric analysis of hematoxylin and eosin–stained ovarian sections was performed to provide insights into their temporal roles in luteal function. Ovarian samples were obtained from 30 Holstein cows (30 pairs), immediately after slaughter, and categorized into early, mid, or late luteal phases according to ovarian morphology and the appearance of corpora lutea. A total of 30 CL samples (10 per stage) were selected for evaluation. Each CL was fixed, paraffin-embedded, and sectioned longitudinally (5 µm thick) for histological examination. Small (<20 µm) and large (> 35 µm) luteal cells were quantified in standardized microscopic fields at × 40 magnification using ImageJ software. The results revealed that SLC counts were highest during the early luteal phase (72.53 ± 7.83) and significantly exceeded LLC counts (30.70 ± 3.78). In the mid-luteal phase, SLCs decreased (50.70 ± 2.82) while LLCs increased (44.30 ± 3.11), with no significant difference between them. During the late luteal phase, SLCs increased slightly (59.77 ± 3.84), whereas LLCs declined markedly (24.80 ± 2.52). Overall, SLCs counted were highest during the early luteal phase and declined toward the mid phase, while LLCs increased markedly at the mid luteal phase and decreased again at the late phase.
Keywords: Corpus luteum, Histology, Large luteal cell, Small luteal cell
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effect of Glutathione Supplementation in Liquid Semen Diluent During Cold Storage on Sperm Membrane Structure in Ongole Crossbred Bull
|
|
X Ervandi M and Dangkua T.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 910-920, 2025; pii:S232245682500092-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj92
ABSTRACT: Damage to bovine spermatozoa membranes results from factors such as oxidative stress, high temperatures, extreme pH levels, and exposure to chemicals or infections. The present study aimed to explore the potential use of glutathione in liquid semen extenders during cold storage to protect the membrane structure of Peranakan Ongole (PO) crossbred bull semen. Semen samples were collected twice weekly from two PO crossbred bulls aged 2-3 years. Semen that met the quality standards was diluted with a red fruit (Pandanus conoideus Lamk) extract extender, supplemented with glutathione at various concentrations per 100 mL of the total volume extender. Sperm membrane evaluation included membrane integrity assessed by the hypoosmotic swelling test (HOST), sperm capacitation, and acrosome reaction assessed by chlortetracycline fluorescence staining. The treatments consisted of red fruit extract extender with 15% egg yolk (P0, control), red fruit extract extender with 15% egg yolk and 0.75 mM glutathione (P1), red fruit extract extender with 15% egg yolk and 1 mM glutathione (P2), and red fruit extract extender with 15% egg yolk plus 1.25 mM glutathione (P3). The present results indicated that Group P1 performed superior than other treatment groups. This was evidenced by higher spermatozoa membrane integrity and a higher proportion of non-capacitated spermatozoa, while the proportions of capacitated spermatozoa and acrosome reaction remained low. The extender formulation containing red fruit extract, 15% egg yolk, and 0.75 mM glutathione-maintained acrosome status above 50% after six days of cold storage. Therefore, the combination of red fruit extract, 15% egg yolk, and 0.75 mM glutathione was identified as the optimal formulation for liquid semen preservation, meeting the necessary conditions for practical use in artificial insemination programs in the field.
Keywords: Acrosome reaction, Glutathione, Membrane integrity, Red fruit extract
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
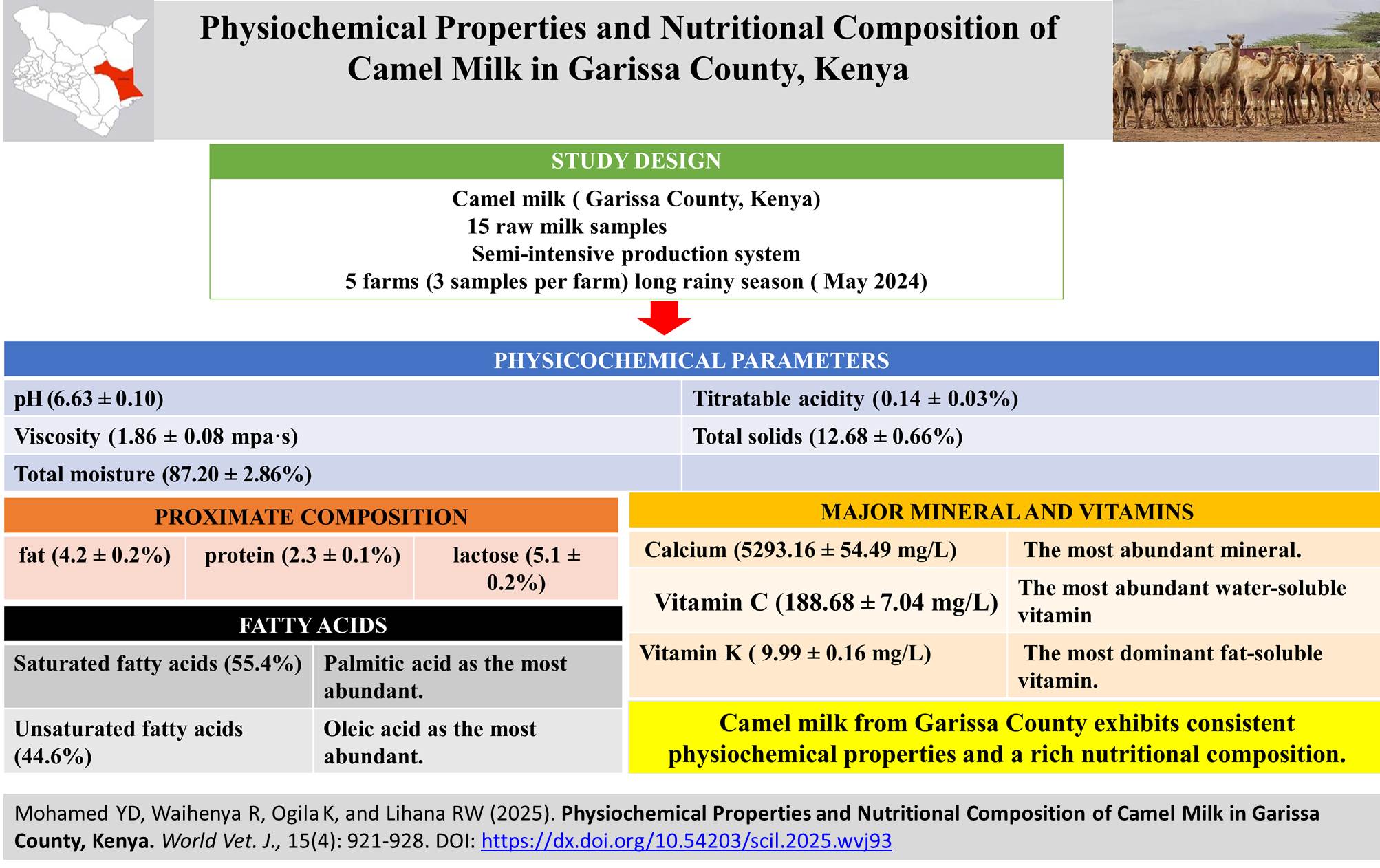
Physiochemical Properties and Nutritional Composition of Camel Milk in Garissa County, Kenya
|
|
Mohamed YD, Waihenya R, Ogila K, and Lihana RW.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 921-928, 2025; pii:S232245682500093-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj93
ABSTRACT: Camel milk is an important source of food, income, and livelihood for communities in arid and semi-arid regions. It contains essential macronutrients, minerals, vitamins, and bioactive compounds that contribute to human health. Despite Kenya's status as a prominent producer of camel milk, especially in Garissa County, comprehensive data regarding its physicochemical and nutritional composition remain scarce. The present study aimed to determine the physicochemical attributes and nutritional profile of camel milk sourced from Garissa County. Fifteen raw milk samples were collected in May 2024 during the long rainy season from randomly selected, clinically healthy lactating Somali dromedary camels reared under semi-intensive systems on five dairy farms in Garissa County, Kenya, under hygienic conditions (three samples per farm). Physicochemical parameters measured included pH, color, titratable acidity, viscosity, total solids, and moisture. Nutritional components analyzed were fat, protein, lactose, minerals, vitamins, and fatty acids using AOAC methods and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The camel milk samples exhibited a mean pH of 6.63 ± 0.10, 0.14 ± 0.03% titratable acidity, 1.86 ± 0.08 mPa·s viscosity, 12.68 ± 0.66% total solids, and 87.20 ± 2.86% moisture. Proximate composition indicated 4.2 ± 0.2% fat, 2.3 ± 0.1% protein, and 5.1 ± 0.2% lactose. Calcium (5293.16 ± 54.49mg/l) was the most abundant mineral. Among vitamins, vitamin C was the most abundant water-soluble vitamin, while vitamin K was the most dominant fat-soluble vitamin. Fatty acid analysis indicated that (55.4%) of the fatty acids were saturated and (44.6%) were unsaturated. Palmitic acid and oleic acid were the most abundant. The results indicated relatively uniform physicochemical and nutritional characteristics of camel milk produced under semi-intensive systems from selected farms in Garissa County, Kenya. The results of this study provided descriptive insight for future studies with larger sample sizes within this county, as well as comparative study across counties and different seasonal conditions.
Keywords: Camel milk, Fatty acid, Nutritional composition, Physicochemical characteristic
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Birth Characteristics of Lambs Resulting from Crossbreeding Dorper and Awassi Rams with Texel Cross Ewes
|
|
As A, Pratama MJG., Susilorini TE, Kuswati K, Septian WA, Nugraha CD, Putri RF, Ardiantoro A, and Suyadi S.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 929-939, 2025; pii:S232245682500094-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj94
ABSTRACT: Crossbreeding is an effective strategy to enhance sheep productivity under tropical conditions. This study evaluated the birth characteristics of lambs resulting from crossbreeding Dorper and Awassi rams with Texel cross ewes in Indonesia’s tropical environment. The experiment was conducted from April to November 2023 at CV Kambing Burja, Malang Regency, East Java, Indonesia. A total of 125 Texel cross ewes aged 1.5 to over 3 years were naturally mated with 71 Dorper and 54 Awassi rams using a controlled colony mating system at a ram-to-ewe ratio of 1:25. The study employed complete enumeration, including all ewes that successfully lambed during the observation period. Sire groups comprising two to three rams per breed were rotated every 45 days to ensure equal mating opportunities and prevent exhaustion. Estrus synchronization followed a two-step hormonal protocol, including the administration of Conceptase (PGF₂α, 2.5 mL/ewe) intramuscularly to induce luteolysis, followed 48 hours later by PG600 (1.5 mL/ewe) containing eCG and hCG to stimulate follicular development and ovulation. Mating behavior was observed daily, with successful copulation indicated by restlessness, vocalization, and receptivity. Measured parameters included birth weight, litter size, and sex ratio. Results showed no significant differences in mean litter size or birth weight between Dorper × Texel cross and Awassi × Texel cross lambs, although Awassi crosses exhibited more uniform birth weights. Birth weight decreased as litter size increased, and sex ratios remained balanced in both groups. These findings suggest that both Dorper and Awassi rams are suitable for enhancing the reproductive performance of Texel cross ewes under tropical management systems, highlighting the importance of integrating hormonal synchronization and controlled breeding for sustainable sheep production in Indonesia.
Keywords: Awassi sheep, Birth weight, Dorper sheep, Litter size, Sex ratio, Texel cross sheep
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
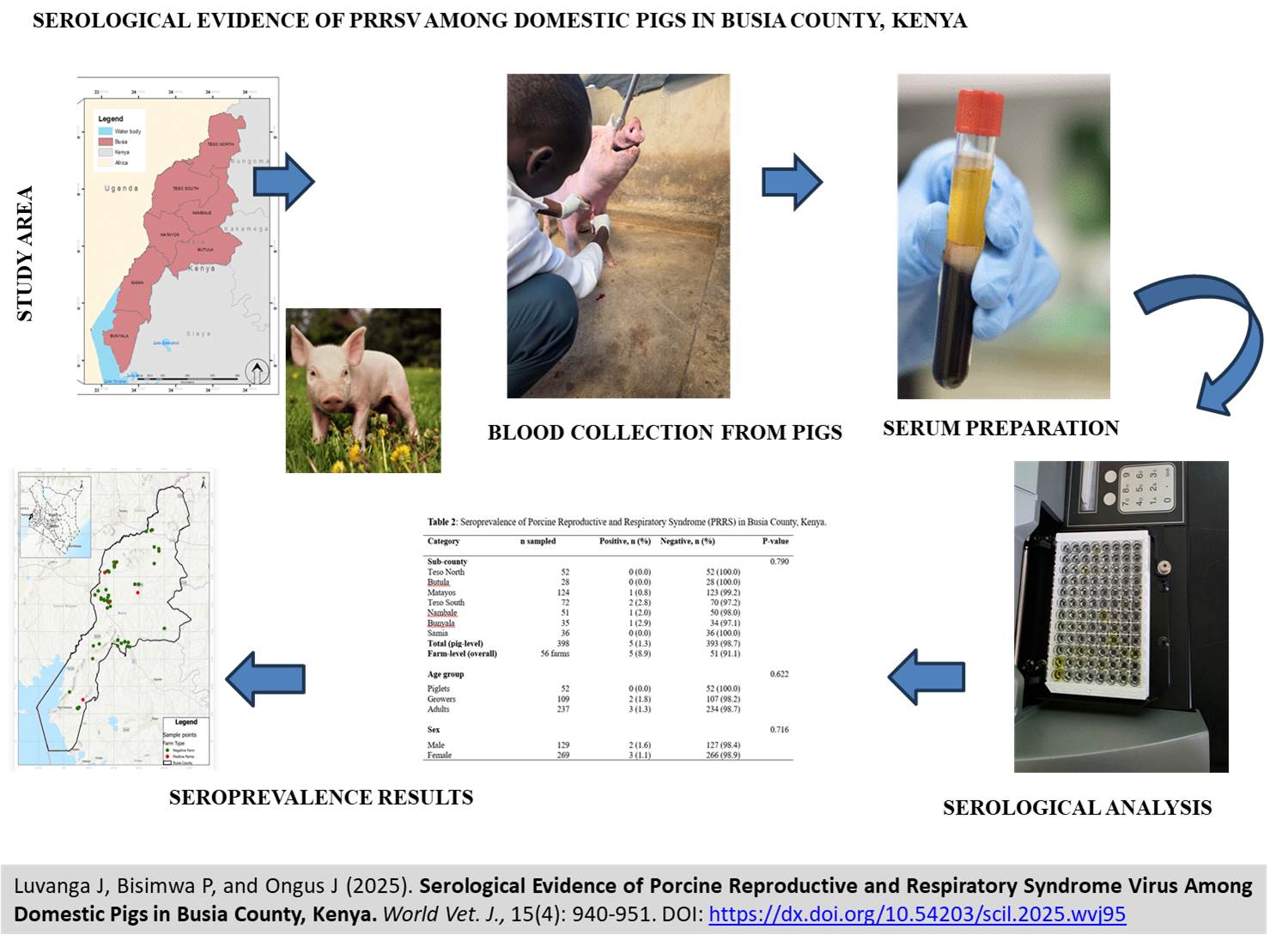
Serological Evidence of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Among Domestic Pigs in Busia County, Kenya
|
|
Luvanga J, Bisimwa P, and Ongus J.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 940-951, 2025; pii:S232245682500095-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj95
ABSTRACT: Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) is a significant swine pathogen and one of the most damaging viruses affecting the global pig industry. Although clinical signs compatible with PRRS have been observed within Kenyan pig production systems, the virus has not yet been officially reported in the country. The present study sought to estimate the seroprevalence of PRRSV, describe farm characteristics, and identify risk factors associated with PRRSV infection among domestic pigs in Busia County, Kenya. Serum samples were collected from 398 pigs (52 piglets, 109 growers, and 237 adults) originating from 56 pig keeping farms/households and analyzed using a commercial indirect Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Farm characteristics, pig farming practices, pig husbandry, and biosecurity data were recorded via structured questionnaires. Pig-level seroprevalence was 1.3% (5/398), with positives detected in Matayos 0.8% (1/124), Nambale 2.0% (1/51), Teso South 2.8% (2/72), and Bunyala 2.9% (1/35) sub-counties, respectively. The farm-level seroprevalence was 8.9% (5/56). Seropositivity did not differ significantly by location, sex, or age category. Biosecurity uptake was generally low, with the use of dedicated clothing/aprons (14%), wearing of boots (32%), presence of footbaths (12.5%), quarantine of new pigs (11%), and handwashing after pig handling (16%). Not using separate clothing/aprons was the only risk factor significantly associated with farm seropositivity. The present findings provided evidence of PRRSV exposure in Kenyan pigs and reveal important gaps in farm-level biosecurity practices at the human-pig interface, underscoring the epidemiological relevance of these observations for pig industry in the region, although the small number of seropositive farms means that some degree of false positivity or false negativity may not be excluded.
Keywords: Biosecurity, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, Seroprevalence
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
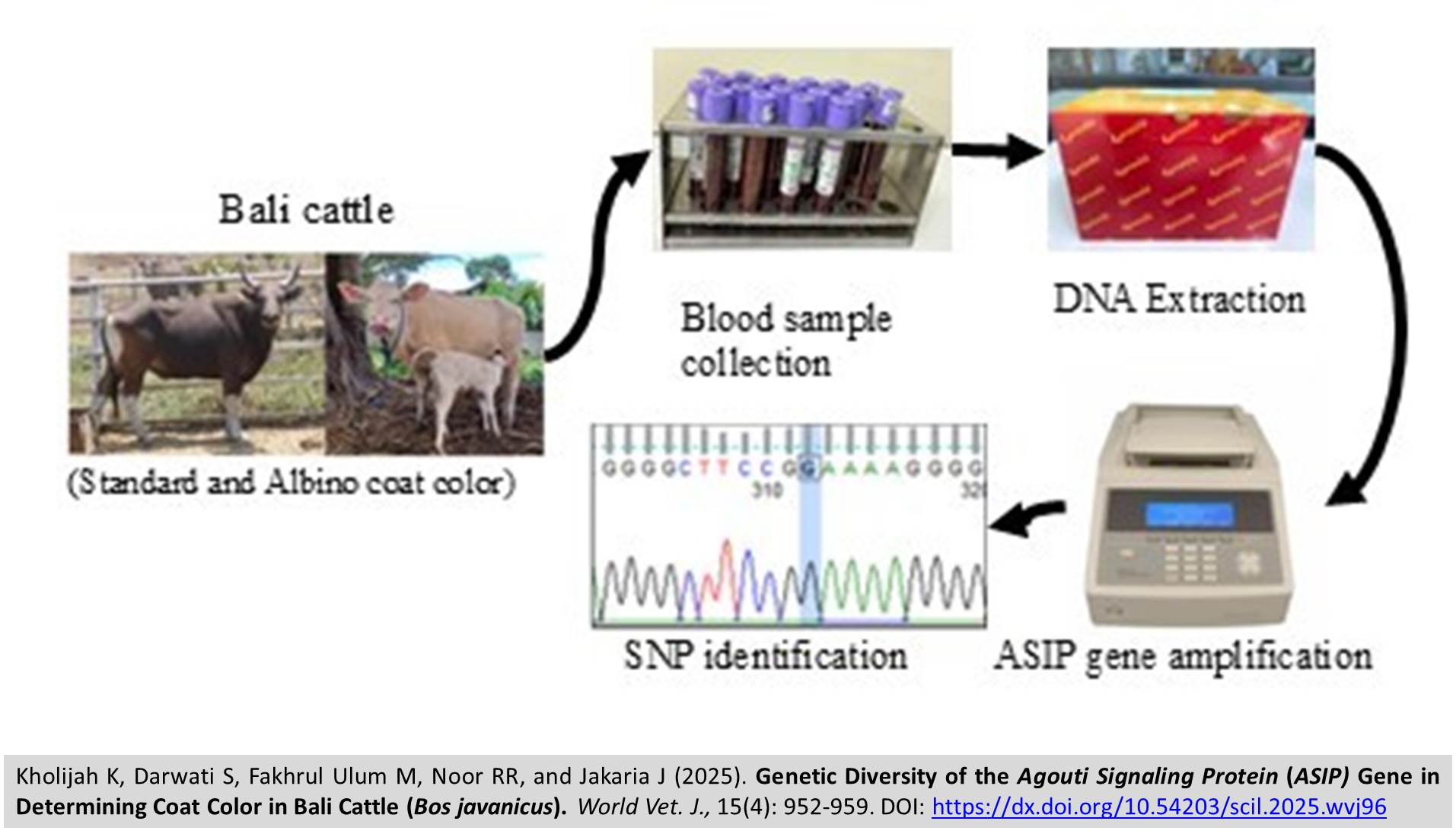
Genetic Diversity of the Agouti Signaling Protein (ASIP) Gene in Determining Coat Color in Bali Cattle (Bos javanicus)
|
|
Kholijah K, Darwati S, Fakhrul Ulum M, Noor RR, and Jakaria J.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 952-959, 2025; pii:S232245682500096-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj96
ABSTRACT: Bali cattle, which are indigenous to Indonesia, display distinctive and unique coat color characteristics. The appearance of albinos has been observed as an abnormality. The present study aimed to explore the agouti signaling protein (ASIP) gene in Bali cattle and analyze its association with the occurrence of albinism and white-spotted coat colors in Bali cattle. A total of 68 blood samples from cattle were used, including standard Bali cattle (N = 39), Bali cattle with spotting (N = 9), and albino Bali cattle (N = 20). Standard and white-spotted Bali cattle samples were collected from the Bali Cattle Breeding Centre in Jembrana, Bali Province, and the Breeding Center Unit in Serading, West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Albino cattle samples were obtained from Taro Village, Gianyar Regency, Bali. The DNA amplification was performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were determined through direct sequencing, and genotyping was performed using the PCR-RFLP method. The exon 1 and exon 2 regions of the ASIP gene were monomorphic or uniform. The coding region of exon 3 of the ASIP gene in Bali cattle exhibited polymorphisms, specifically regarding coat color. A novel SNP (g.498 A > G) was detected exclusively in Bali cattle; however, it has not yet been validated as a potential genetic marker for coat color in this breed. The findings of this study further revealed that the ASIP gene sequence does not distinguish between standard and albino coat colors in Bali cattle, despite the identification of this specific SNP.
Keywords: Agouti signaling protein gene, Bali cattle, Coat color, Polymerase chain reaction, Single nucleotide polymorphism
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
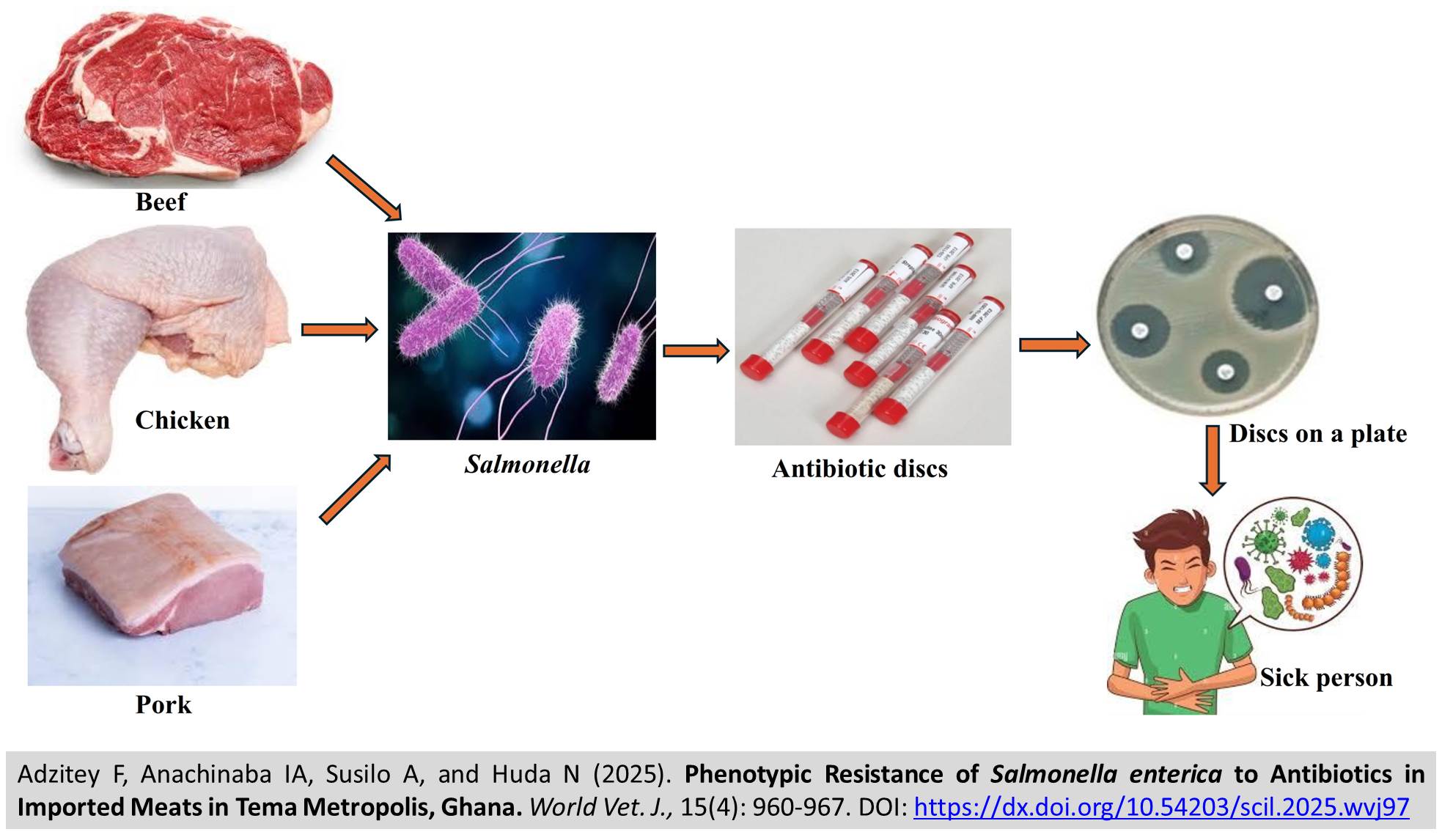
Phenotypic Resistance of Salmonella enterica to Antibiotics in Imported Meats in Tema Metropolis, Ghana
|
|
Adzitey F, Anachinaba IA, Susilo A, and Huda N.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 960-967, 2025; pii:S232245682500097-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj97
ABSTRACT: Salmonella enterica (S. enterica) causes certain foodborne diseases and poses public health concerns when it becomes antibiotic-resistant. The present study aimed to determine the resistance of S. enterica to antibiotics from imported meats sold in the Tema Metropolis, Ghana. A total of 300 beef, chicken, and pork samples randomly selected from markets of the Metropolis were tested for S. eneterica. The disc diffusion method was used to determine the antibiotic resistance in 60 S. enterica isolates. The current results revealed that 40% of imported chicken, 38% of imported pork, and 29% of imported beef were positive for S. enterica. The S. enterica isolated from imported meat sources was 36.7% resistant to tetracycline but susceptible (≥ 68%) to imipenem, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim, gentamicin, and ceftriaxone. The multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index fell within the range of 0.1 to 0.6, and 12 different patterns were observed. The present study revealed the contamination of S. enterica in some imported meat sold in Tema Metropolis, Ghana. Avoidance of cross-contamination and adequate thermal treatment of meats before eating is essential.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance, Meat, Prevalence, Salmonella enterica
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Prevalence and Parasite Load of Helminths in Reintroduced Vicuñas (Vicugna vicugna) in High-Andean Communities, Huancavelica, Peru
|
|
Rojas E, Machuca ANG, and Bezada S.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 968-977, 2025; pii:S232245682500098-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj98
ABSTRACT: Gastrointestinal helminth infections represent a major threat to the health and conservation of vicuñas (Vicugna vicugna) in the Peruvian Andes, while epidemiological information on repopulated populations under community-based management remains limited. The present study aimed to determine the prevalence and parasite load of gastrointestinal helminths in reintroduced vicuñas from the high-Andean communities of Huancavelica, Peru. In the present study, 102 vicuñas from the communities of Atuna and Allarpo (Huancavelica), Peru, were evaluated during the 2023 chaccu, a traditional Andean practice in which wild vicuñas are collectively herded, captured, and shorn for fiber under community supervision. The sample consisted of 66 females and 36 males, of which 80 were classified as adults (>3 years old) and 22 as juveniles (1-3 years old). Rectal fecal samples were collected and analyzed to detect and quantify gastrointestinal helminth eggs, including strongyle-type eggs, Nematodirus, Trichuris, and Fasciola hepatica (F. hepatica). Samples were analyzed using flotation, modified McMaster, and sedimentation techniques to detect and quantify helminth eggs. Overall prevalence, including by community, sex, age, and parasite load (eggs per gram, EFG) as a geometric mean, was determined. The overall prevalence was 75.5%, with F. hepatica as the most frequent parasite, 79.2% in Allarpo and 60.9% in Atuna, followed by Trichuris spp. (11.6%) and Nematodirus spp. (10.2%), and Strongyle-type eggs 42.0% in Allarpo and 17.45% in Atuna. Juveniles had a higher prevalence of F. hepatica infection (90.9%) compared to adults (71.3%). The mean F. hepatica egg count was higher in Allarpo (34.4 EPG) than in Atuna (11.7 EPG), and this difference was statistically significant. When analyzed by sex, females indicated a higher mean egg count (24.6 EPG; 95% CI: 16.9-35.7) than males (17.4 EPG; 95% CI: 9.8-30.7). Regarding age, adults presented a higher mean EPG (23.6; 95% CI: 16.0-34.8) compared to juveniles (16.5; 95% CI: 8.8-31.1), although mentioned differences were not statistically significant. The findings of the present study indicated that helminth infections, particularly fascioliasis, are widespread, with higher risk in juveniles and environmentally favorable areas, highlighting the need for locally adapted monitoring and control strategies in reintroduced vicuña populations.
Keywords: Fasciola hepatica, Gastrointestinal helminth, Prevalence, Vicugna vicugna
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
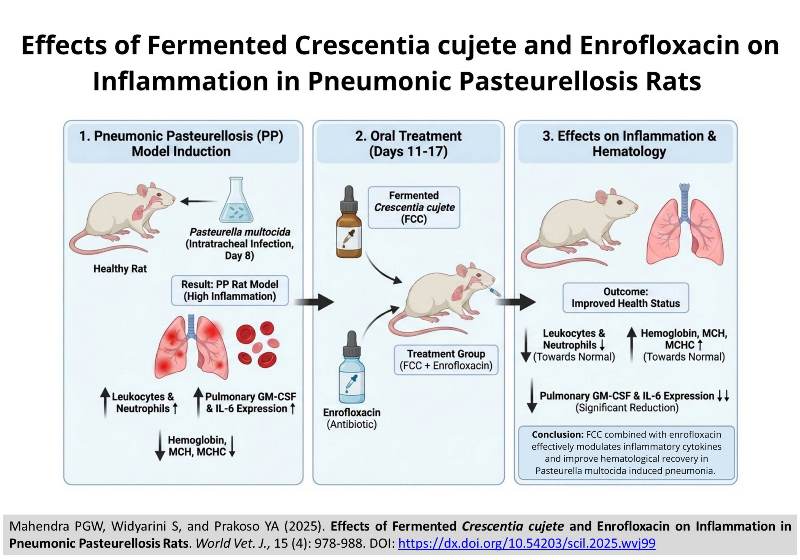
Effects of Fermented Crescentia cujete and Enrofloxacin on Inflammation in Pneumonic Pasteurellosis Rats
|
|
Mahendra PGW, Widyarini S, and Prakoso YA.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 978-988, 2025; pii:S232245682500099-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj99
ABSTRACT: Pneumonic pasteurellosis (PP) is a respiratory disease caused by Pasteurella multocida (P. multocida) with broad host susceptibility and zoonotic potential. Pasteurellosis is classified as a strategic infectious animal disease and a neglected tropical disease in Indonesia, highlighting the need for effective supportive therapies. Fermented Crescentia cujete L. (FCC) contains bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. The present study aimed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effects of FCC combined with enrofloxacin on hematological parameters and the immune expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in an induced PP rat model. Twenty male Sprague-Dawley rats, three months old and weighing 250-300 g, were divided into five groups, including healthy control (P1), untreated infected rats (P2), rats treated with 20 mg/kg body weight (BW) of enrofloxacin (P3), rats given 20 and 30 mg/kg BW of enrofloxacin and ibuprofen, respectively (P4), and rats administered 20 and 5.92 mg/kg BW of enrofloxacin and FCC (P5), respectively. After a 7-day acclimatization, rats were infected intratracheally with P. multocida on day 8, and treatments were administered orally for seven days starting on day 11. Hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) decreased significantly in P2 compared to P1, with no difference between P2 and P3. Although hemoglobin, MCH, and MCHC improved in P4 and P5 toward control levels, most variables remained significantly different from P1. Leukocyte and neutrophil counts were significantly elevated in P2 compared to P1; however, P5 demonstrated a declining trend toward normal values and did not differ significantly from P1. Pulmonary GM-CSF and IL-6 immune expression increased markedly in P2 compared to P1. Groups P3 and P4 exhibited elevated cytokine expression compared to P1, without significant differences from P2. In contrast, P5 indicated a significant reduction in GM-CSF and IL-6 expression compared to P2, reaching levels comparable to those of P1. The FCC combined with enrofloxacin improved hematological status and modulated inflammatory cytokines in PP. The present findings indicated that FCC could be a potential supplementary treatment for managing inflammation and aiding hematological recovery in bacterial infection pneumonia.
Keywords: Crescentia cujete, Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor, Hematology, Interleukin-6, Pasteurella multocida
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
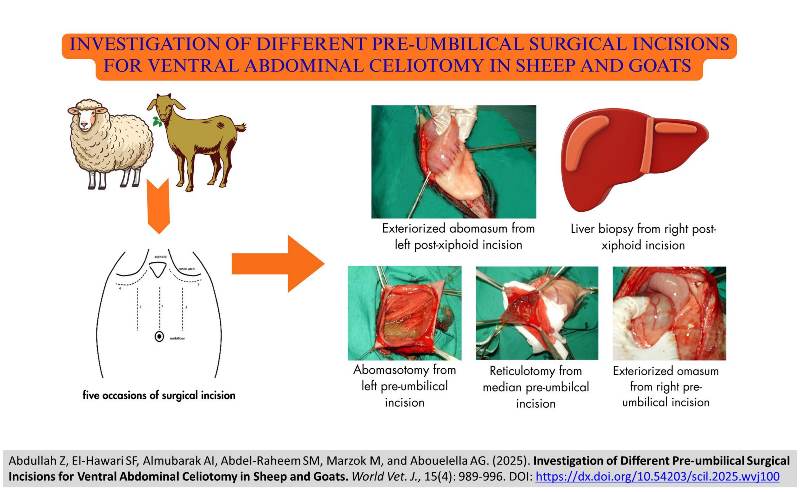
Investigation of Different Pre-umbilical Surgical Incisions for Ventral Abdominal Celiotomy in Sheep and Goats
|
|
Abdullah Z, El-Hawari SF, Almubarak AI, Abdel-Raheem SM, Marzok M, and Abouelella AG.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 989-996, 2025; pii:S232245682500100-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj100
ABSTRACT: Identifying the correct site for surgical incision and reducing unnecessary handling are crucial in veterinary surgical procedures. The current study aimed to evaluate surgical incisions in the pre-umbilical region in small ruminants with correlation to possible surgical operations in the abdominal organs. A randomized experimental study was conducted on 15 sheep (12 females and three males) and 15 goats (12 females and three males), with body weights of 44.9 ± 3.7 kilograms in sheep and 26.3 ± 4.6 kilograms in goats. Five different surgical exposures, including median, left paramedian, right paramedian, left post-xiphoid, and right post-xiphoid, were applied. The accessibility of abdominal viscera was evaluated for each incision site by documenting directly visible organs, organs that could be readily moved to the site of incision, and organs that could only be palpated. Access to the ventral ruminal sac and omentum was achieved through median, left, and right pre-umbilical celiotomy incisions. Furthermore, these surgical approaches allowed for reaching the abomasum and performing of abomasotomy. Abomasotomy and reticulutomy operations were performed through a median pre-umbilical incision. Omasum was palpable and easily examined via the right pre-umbilical celiotomy. The liver and gall bladder were exposed via a right post-xiphoid curved incision. In contrast, the reticulum was accessed for surgical intervention through a left post-xiphoid curved incision. The only recorded postoperative complication was tympany after gastrointestinal surgery. The present study indicated that choosing the appropriate pre-umbilical or post-xiphoid incision greatly improves access to targeted abdominal organs in small ruminants. Right and left pre-umbilical incisions were identified as the most effective approaches for abomasal procedures, whereas post-xiphoid incisions provided the optimal exposure to the reticulum, liver, and gall bladder. Furthermore, access to abdominal organs may vary between sheep and goats when employing the same surgical approach.
Keywords: Abomasotomy, Incision, Laparotomy, Paramedian, Small ruminant
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Evaluation of the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of Dried Orange Pulp
|
|
Chaib Eddour AR, Litim M, and Bouderoua K.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 997-1006, 2025; pii:S232245682500101-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj101
ABSTRACT: The disposal of orange juice by-products presents an environmental challenge due to their high volume and accumulation in landfills. Valorizing these residues supports the development of a circular economy within the agro-industrial sector, offering both environmental and economic benefits. This study aimed to valorize orange juice processing residues by producing a dried orange pulp (DOP) flour and characterizing its physicochemical and phytochemical properties to assess its potential suitability as a sustainable feed ingredient for broiler chickens. The physicochemical properties of the sun-dried and finely milled orange by-products (<1 mm) were analyzed using standard methods, including proximate composition analysis (moisture, ash, crude protein, crude cellulose), and spectrophotometric assays for phytochemicals (total phenolics, flavonoids, condensed tannins) and antioxidant activity [2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)]. The DOP demonstrated high levels of dietary cellulose (89.19% Dry Matter), ash (3.81% Dry Matter), total phenolics (202.59 ± 15.93 mg Gallic Acids Equivalent/100 g DM), total flavonoids (430.70 ± 2.78 mg Quercetin Equivalent/100 g), and strong antioxidant activity (FRAP: 1158.8 ± 19.22 mg/g). Phenolic profiling via High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) revealed flavanones as the dominant subclass, with hesperidin (61.29 mg/g) and ferulic acid (27.1 mg/g) as major constituents. These results highlight the nutritional and functional potential of DOP as a feed additive. The remarkable antioxidant capacity and high concentration of bioactive compounds like hesperidin position DOP not just as a filler, but as a functional feed additive that could enhance animal health.
Keywords: Ferulic acid, Hesperidin, Hydrocinnamic acid, Orange waste
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Association of Sex and Age with Histomorphometric Features of Agranulocytic Leukocytes and Erythrocyte Indices in Sumbawa Horses
|
|
Pratama KFAD, Suwiti NK, Ardana IBK, Setiasih NLE, Dharmawan NS, Sulabda IN, and Besung INK.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1007-1014, 2025; pii:S232245682500102-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj102
ABSTRACT: The Sumbawa horse, an indigenous Indonesian breed, plays important ecological and cultural roles in the region, such as participation in traditional ceremonies, local transportation, and horse-racing competitions; however, scientific data on its hematological and cellular characteristics remain limited, hindering accurate clinical evaluation and breed-specific health management. This study aimed to provide baseline histomorphometric and hematological data by examining 80 clinically healthy Sumbawa horses, grouped by sex (male and female) and age (young and adult). Peripheral blood smears were prepared immediately after venipuncture and stained using the modified Diff Quick method. Morphometric parameters of lymphocytes and monocytes, including cell diameter, perimeter, cell area, and nucleus to cytoplasm ratio, were measured using calibrated digital image analysis. Complete blood count parameters, including mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), red cell distribution width coefficient of variation (RDW-CV), and red cell distribution width standard deviation (RDW-SD), were obtained using an automated hematology analyzer. Females exhibited larger lymphocyte dimensions (17.79 ± 5.89 μm² versus 16.57 ± 6.29 μm², whereas males showed larger monocyte size (18.44 ± 7.60 μm² versus 14.88 ± 5.46 μm²). Lymphocyte counts and percentages were higher in females, while monocyte values and RDW-CV were higher in males. Age significantly influenced lymphocyte morphometry and leukocyte profiles, whereas its effects on monocytes were limited, with only monocyte area showing a significant difference between age groups. These findings indicated significant age-related increases in lymphocyte perimeter, area, and diameter, whereas most monocyte and erythrocyte indices remained relatively stable between age groups. Sex related differences were also evident, with females exhibiting significantly higher lymphocyte counts and percentages, and males showing significantly higher monocyte counts and greater erythrocyte variability. These reference values provide clear morphometric distinctions between groups of Sumbawa horses, with adults exhibiting larger lymphocyte dimensions and males showing higher monocyte counts and greater erythrocyte variability, thus offering a biologically calibrated basis for further physiological interpretation.
Keywords: Age, Agranulocytic leukocyte, Erythrocyte indice, Histomorphometry, Horse, Sex
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Risk Factors Associated with Conception Rate in Holstein and Lai Sind Crossbred Cows in Small Holding Farms in Vietnam
|
|
Thanh NV, Lanh DTK, Nam NH, and Dung BV.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1015-1023, 2025; pii:S232245682500103-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj103
ABSTRACT: Reproductive efficiency is a critical factor in smallholder dairy systems, where management limitations often reduce fertility. Identifying factors influencing conception is essential to improving breeding performance in crossbred dairy cows raised in smallholder farms. The present study aimed to identify reproductive and management-related risk factors influencing conception rates in Holstein × Lai Sind crossbred cows at smallholder farms in Northern Vietnam. A retrospective analysis was conducted to evaluate the effects of ovarian disorders, estrus detection timing, age, parity, body condition score (BCS), calving-to-service interval, artificial insemination (AI) order, month of service, and age at first AI on conception rates in 433 cows. Farms were selected based on their willingness to participate, including a total of 40 smallholder farms in Northern Vietnam. Cows were included only if they had complete records on estrus detection, insemination, and pregnancy diagnosis; cows with missing or inconsistent data were excluded. Data was collected from the farm database and direct observation by trained personnel. Univariate analysis identified parity, age, age at first AI, month of AI, and BCS as significant factors influencing conception rates. The overall conception rate was 45.6%. Cows inseminated during December-January had a higher conception rate (52.9%) compared with those inseminated in September-October (37.7%). Heifers exhibited the highest conception rate (55.7%), while cows in parity 2 and parity 4-8 had significantly reduced fertility (37.6% and 42.0%, respectively). In the multivariate logistic regression model, parity and age at first AI were the most influential predictors of reproductive performance in Holstein crossbred cows. Cows first inseminated at 13-15 months, 16-17 months, and older than 17 months had significantly higher conception rates than those inseminated at 8-12 months. The present study demonstrated that both physiological factors (age, parity, and BCS) and seasonal management conditions (month of service) influence conception in Holstein × Lai Sind crossbred cows under smallholder conditions.
Keywords: Artificial insemination, Body condition, Month of service, Smallholder
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Fresh Celery as a Natural Curing Agent on Physicochemical Characteristics and Sensory Quality of Beef Jerky
|
|
Mallu N, Hatta W, and Maruddin F.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1024-1033, 2025; pii:S232245682500104-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj104
ABSTRACT: Beef jerky is a processed meat product. Nitrite or nitrate salts are usually used as curing agents for beef jerky processing. However, excessive nitrite intake can pose health risks and raise public concern, so natural alternatives such as celery can be used. This study evaluated fresh celery as a natural curing agent for beef jerky based on its physicochemical and sensory qualities. The study was conducted in two stages. In the first stage, beef was treated with celery at three levels (2%, 4%, and 6%) and saltpeter as a control, combined with three incubation periods (1, 2, and 3 hours) to identify the optimal treatment for the subsequent stage based on color characteristics and nitrite residue. In the second stage, the selected curing treatments (saltpeter, 4% celery, and 6% celery) were applied to beef jerky and evaluated over different storage periods (0, 2, and 4 weeks). The parameters analyzed included color values, lightness (L*), redness (a*), yellowness (b*), nitrite content, and lipid oxidation, as well as sensory attributes. The results of the first stage showed that the use of saltpeter produced the highest nitrite content (0.54 mg/kg), while the highest b* value was obtained in the treatment of 4% and 6% celery. The incubation length had no significant effect on all parameters, but there was a significant interaction between the type of curing material and the length of incubation on the value of a*. In the second stage, neither curing material treatment nor storage time had a significant impact on organoleptic characteristics, and Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances values were relatively low (< 0.5 mg MDA/kg) up to 4 weeks of storage. A 6% celery treatment yielded the highest L* value, while the highest a* value was indicated by saltpeter, followed by 6% and 4% celery. Overall, the 6% celery treatment showed comparable performance to saltpeter, especially in retaining redness, suppressing lipid oxidation, and maintaining the sensory qualities of ground beef jerky.
Keywords: Beef jerky, Celery leaf, Meat quality, Natural curing, Residual nitrite
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Substitution of Corn with Dried Orange Pulp on Health and Growth Performance of Broiler Chickens
|
|
Chaib Eddour AR, Litim M, and Bouderoua K.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1034-1041, 2025; pii:S232245682500105-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj105
ABSTRACT: The rising cost of cereal-based ingredients and restrictions on the use of antibiotic growth promoters in poultry have increased demand for sustainable alternatives. Agro-industrial by-products, particularly dried orange pulp (DOP), offer an economical, nutrient-rich solution with bioactive compounds that may improve broiler health and growth. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of incorporating different levels of dried orange pulp (Citrus sinensis) on growth performance and blood serum biochemical parameters in broiler chickens. A total of 200 one-day-old Arbor Acres chickens (45 ± 1.7 g) were randomly divided into four dietary groups. Each group consisted of 50 chickens, with five replicates of 10 chickens, and was reared for 49 days. The dietary groups included a control diet without DOP and three experimental diets in which DOP was partially replaced by corn at inclusion levels of 5% (50 g/kg of dry matter [DM]), 10% (100 g/kg of DM), and 15% (150 g/kg of DM). Growth performance was monitored throughout the entire rearing period. Blood samples were collected at 37 and 49 days of age to assess glucose, triglycerides, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Broiler chickens fed DOP-substituted diets generally exhibited lower serum lipid levels, especially triglycerides and total cholesterol, compared to the control group at both sampling times. However, there was a slight increase in triglycerides in the 5% DOP group at 49 days compared to the control group. Glucose concentrations generally increased with higher levels of DOP inclusion, especially at 15%. Regarding growth performance, chickens fed the 5% DOP diet had the highest live weight, whereas those fed the 10% DOP diet demonstrated an improvement in feed conversion ratio compared to the control group. The dietary incorporation of DOP enhanced growth performance and positively influenced serum biochemical profiles in broiler chickens, with the 5% DOP level demonstrating the most significant improvements in performance and productivity parameters, while 10% DOP exerted the most beneficial effects on blood biochemical parameters.
Keywords: Cholesterol, HDL, LDL, Lipid fraction, Triglyceride
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Liver Anatomy of Long-Eared Hedgehog (Hemiechinus auritus) Using Multimodal Imaging
|
|
Pisheh MG, Masouleh MN, Gilanpour H, Bokaie S, and Mashhadirafiee S.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1042-1052, 2025; pii:S232245682500106-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj106
ABSTRACT: The long-eared hedgehog (Hemiechinus auritus), a small insectivorous species commonly encountered in exotic animal practice, lacks established imaging references for liver anatomy. The present study aimed to characterize the liver of clinically healthy adult animals using radiography, ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Seven clinically healthy adult one-year-old male hedgehogs with body weights of 320-410 grams were examined at the Diagnostic Imaging Unit of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran. Radiography identified hepatic position and overall shape, while ultrasonography provided real-time assessment of parenchymal echotexture, gallbladder morphology, and major vascular landmarks. The CT and MRI provided detailed cross-sectional visualization, including morphometric measurements and evaluation of parenchymal and vascular architecture. Across all imaging techniques, the right and left hepatic lobes exhibited comparable dimensions and tissue characteristics, with no statistically significant morphometric differences between lobes. The present study established a preliminary reference for liver anatomy in Hemiechinus auritus using multimodal imaging, thereby facilitating clinical diagnosis in this species.
Keywords: Hedgehog, Liver, MRI, Radiography, Ultrasonography
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Impacts of Tenebrio molitor Larval Meal on Zootechnical Performance, Biochemical Indices, and Intestinal Morphometry in Broiler Chickens
|
|
Nassi Guidi HI, Komi A, Komi A, Gnatepe MK, Vinakpon G, and Kokou T.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1053-1062, 2025; pii:S232245682500107-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj107
ABSTRACT: Protein resources availability is a major challenge for poultry farming in Sub-Saharan Africa. Insects such as Tenebrio molitor (T. molitor), known as yellow mealworm, which are rich in high-quality protein, offer a promising solution. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of T. molitor larvae meal as an alternative protein source in broiler chicken diets. A total of 375 day-old hybrid broiler chickens (Crossbreeding of Sasso and Faso) were randomly assigned to five dietary treatments. Each treatment included five replicates with 15 chickens. During the 12-week study period, from hatching to the finishing phase, five dietary treatments were administered, including T. molitor larvae meal at 4% (TM4%), 6% (TM6%), 8% (TM8), black soldier fly larvae meal at 8% (BSF8), and as the control diet, fish meal at 8% (FM8). Biochemical parameters, including total protein, albumin, triglycerides, and cholesterol, as well as the small intestinal weight and length, and zootechnic performance such as feed intake, body weight gain, and feed conversion ratio (FCR), were measured. The current results indicated that feed consumption did not differ significantly among the treatments. However, the live weight of broiler chickens in TM8 was significantly higher in the finisher phase compared to other treatments, and their weight gain was higher in the grower and finisher phases. The FCR was significantly lower in the TM8 during the finisher phase than in other treatments. Carcass yield and gut length were significantly higher in the TM8. Total protein and albumin did not differ significantly among all groups. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels in TM6 were significantly higher than other groups. The incorporation of T. molitor meal at 8% inclusion level is recommended for broiler chicken feed.
Keywords: Biochemical parameter, Black soldier fly, Broiler chicken, Carcass yield, Tenebrio molitor, Weight gain
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Serodetection of Contagious Caprine Pleuropneumonia in Mosul City, Iraq
|
|
Al-lahibi MT and Al-Farwachi MI.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1063-1069, 2025; pii:S232245682500108-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj108
ABSTRACT: Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia (CCPP) is a severe, highly transmissible respiratory disease in goats, resulting in significant economic losses. The precise antibody detection is critical for disease surveillance and control in suspected locations. The present study aimed to detect CCPP antibodies in goat sera using indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and latex agglutination tests (LAT) and to compare the diagnostic performance of these two serological methods. A cross-sectional study was conducted at the University of Mosul, Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Iraq. A total of 90 serum samples were collected from unvaccinated local goats (aged 1-7 years; 30 males, 60 females) exhibiting respiratory signs, including cough, nasal discharge, and dyspnea. The serum samples were analyzed for CCPP antibodies using both an indirect ELISA and LAT. The overall seropositivity rate was 21.1% for indirect ELISA and 46.6% for LAT. Among the latex-positive samples, 16.7% were weakly positive (+), 50% moderately positive (++), and 33.3% strongly positive (+++). The seroprevalence of CCPP was significantly higher in female goats than in males, as confirmed by both ELISA and LAT. Indirect ELISA revealed seroprevalence rates of 30.0% in females compared to 3.3% in males, while LAT results indicated a seroprevalence rate of 66.7% in females compared to 6.7% in males. The highest CCPP seroprevalence was found in the 2-3-year-old age group, with rates of 89.5% by ELISA and 92.9% by LAT. The LAT results demonstrated a sensitivity of 84.21%, a specificity of 63.38%, and an overall accuracy of 67.78%. Cohen's kappa coefficient (0.33) indicated fair agreement, while McNamara's test demonstrated a significant difference between the two tests. Based on receiver operating curve analysis, the indirect ELISA demonstrated an area under the curve of 0.83, with a suitable optical density limit of 0.15, resulting in 85% sensitivity and 70% specificity. Indirect ELISA offers greater reliability in detecting CCPP antibodies compared to LAT. The variability in LAT results highlighted the need for ELISA, revealing higher seropositivity in older females, a distinct epidemiological feature of the population.
Keywords: Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia, Goat, Mycoplasma infection, Serodiagnosis
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Impacts of Cilnidipine and Glibenclamide Combination on Lipid Profile and Glycemic Control in Male Diabetic Rats
|
|
Abdel Rasool AM, Mahmood NS, and Mohammad SH.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1070-1084, 2025; pii:S232245682500109-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj109
ABSTRACT: Current diabetes therapies frequently do not succeed in achieving target levels for hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in a considerable number of patients. Glibenclamide is an oral hypoglycemic agent, whereas cilnidipine is a calcium channel blocker, which has been utilized for its additional metabolic benefits beyond its primary effect on blood pressure control. The presented study aimed to evaluate the synergistic effects of cilnidipine and glibenclamide on glycemic response, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profile in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Forty-eight male rats were allocated into eight groups, each with six rats, including a normal control, a diabetic control, and six diabetic groups. Three groups were treated with oral cilnidipine alone at 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg, respectively, while the other three groups were treated with a combination of cilnidipine and glibenclamide at 2.5 mg/kg, orally. Diabetes was induced through the use of alloxan at a dosage of 100 mg/kg, intraperitoneally. Successful induction of diabetes was confirmed by an increase in blood glucose level over 200 mg/dl. Serum insulin, HOMA-IR, C-peptide, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and the lipid markers were measured at the end of the treatment on day 28. In assessing the medicines' interactions, the combination index (CI) method was used. The present results indicated that a significant effect was observed with 10 mg/kg of cilnidipine combined with glibenclamide, which lowered glucose levels to 80.10 ± 5.80 mg/dL, increased insulin levels to 13 ± 0.64 mU/L, and raised C-peptide levels to 1.40 ± 0.09 ng/mL, while normalizing HOMA-IR to 2.56 ± 0.45, compared to the diabetic control group. The value of CI indicating a significant synergy was below 1 for FPG, insulin, and C-peptide. However, the combined medication therapy had an opposing effect (CI > 1) on all lipid parameters, including total, low- and high-density cholesterol, and triglycerides. Although it may be beneficial in enhancing glucose metabolism, it is insufficient to resolve the issues associated with diabetic dyslipidemia and should be considered as a part of a mixed treatment regime.
Keywords: Cilnidipine, Insulin sensitivity, Glibenclamide, HOMA-IR, Lipid profile
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Bromelain Loaded with Gold Nanoparticles on Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Parameters in Albino Mice with Testicular Damage
|
|
Faraj SS, Al-Rubaye RHKh, Mutlak BH, and Mnati EM.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1085-1094, 2025; pii:S232245682500110-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj110
ABSTRACT: Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) has been demonstrated to induce testicular damage via oxidative stress. Bromelain (Br), a proteolytic enzyme known for its biological activities and pharmacological properties, exhibits limited absorption owing to its low solubility and bioavailability. The present study aimed to investigate the histological and immunohistochemical effects of bromelain conjugated with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) on the testis histology of albino mice treated with CCl4. Thirty-five male albino mice (Mus musculus), with an average age of 9 weeks, were randomly divided into five groups, each containing seven mice. The experiment was prolonged for four weeks. The first group (G1) was the control group, the second group (G2) received weekly sub-peritoneal injections of CCl4 until the end of the experiment, and the third group (G3) received an oral dose of Au-NPs solution. The fourth group (G4) received injections of CCl4; one hour later, the mice were given an oral dose of 300 mg/kg bromelain. The fifth group (G5) received an injection of CCl4; subsequently, the mice received the same oral dosage of 300 mg/kg Au-NPs-bromelain after 60 minutes. The mice's testes were sampled to evaluate histopathological alterations and immunohistochemical markers, particularly Ki-67 and caspase-9. The present results indicated that mice treated with CCl4 displayed a range of histological alterations, including testicular damage, degeneration in seminiferous tubules, vacuolation, and loss of germ cells. Furthermore, the immunohistochemistry study demonstrated that Ki-67 intensity decreased while caspase-9 intensity increased in groups G2 and G4 compared to the control group. Bromelain loaded with gold nanoparticles at a dosage of 300 mg/kg exhibited a notable reduction in the harmful effects of CCl4 on the testicular tissue of mice by restoring the histological structure, enhancing the Ki-67 proliferation protein, and suppressing the apoptotic cascade protein indicated by caspase 9.
Keywords: Bromelain, Carbon tetrachloride, Caspase, Gold nanoparticle
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia) Extract on Glucose Transporters 2 and 4 Levels in Streptozotocin-induced Hyperglycaemic Rats
|
|
Putri D, Utama IH, Suatha IK, Suartini IGAA, Suharsono H, Astawa INM, Kendran AAS, and Suarsana IN.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1095-1100, 2025; pii:S232245682500111-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj111
ABSTRACT: Glucose transporters (GLUTs) are essential for regulating glucose metabolism, with GLUT2 and GLUT4 serving as the primary transporters in muscle cells. In diabetic conditions, oxidative stress caused by free radicals damages glucose uptake into cells. Bioactive compounds in bitter melon, including triterpenoids, charantin, and conjugated linoleic acid, have been shown to have hypoglycaemic effects. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the effect of bitter melon extract (Momordica charantia) on blood glucose, GLUT2, and GLUT4 in streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic rats. The present study involved 15 male Wistar rats (white strain), 2 months old, with an average body weight of 130 grams. Diabetes was induced by administering streptozotocin at a dose of 60 mg/kg body weight. The animals were divided into three treatment groups, including the diabetic control group (P0), the diabetic group treated with 50% weight/volume (w/v) bitter melon extract (P1), and the diabetic group treated with 100% (w/v) bitter melon extract (P2). The extract was given orally at a dosage of 1 ml per rat for 14 days. Blood glucose concentrations were determined using a glucometer, whereas serum GLUT2 and GLUT4 levels were quantified with an ELISA kit. The results indicated that treatment P2 significantly lowered blood glucose levels compared to the diabetic control group, decreasing from 414.60 mg/dL (P0) to 223.60 mg/dL (P2). Serum GLUT2 concentrations declined from 21.51 (P0) to 16.50 (P2), and GLUT4 levels decreased from 19.94 (P0) to 17.60 (P2). These changes suggested an adaptive response intended to restore glucose homeostasis. Based on the present results, 100% w/v bitter melon extract concentration demonstrated a significant reduction in blood glucose, GLUT2, and GLUT4 levels in the serum of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Keywords: Bitter melon, Diabetes mellitus, Hyperglycemia, Glucose transporter
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Multidrug-Resistant Profile of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Dogs with Pyoderma in Lima, Peru
|
|
Tomas J, Rivas B, Palomino-Farfán J, and Siuce J.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1101-1106, 2025; pii:S232245682500112-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj112
ABSTRACT: Methicillin resistance is a major global health concern, and recently, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP) has emerged as a significant issue in veterinary medicine, with the potential to spread to humans. The present study aimed to analyze Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (S. pseudintermedius) strains isolated from 585 canine pyoderma samples from 2016 to 2024 at the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, National University of San Marcos, Peru. The mecA gene was detected by conventional polymerase chain reaction, and antimicrobial susceptibility test included seven antibiotic families, including tetracyclines, sulfonamides, aminoglycosides, second-generation cephalosporins, penicillins, fluoroquinolones, and lincosamides. Out of 585 samples, 143 (24.4%) were positive for the mecA gene, confirming the presence of MRSP. Among these strains, 107 (74.8%) were multidrug resistant (MDR), and 119 (83.2%) exhibited phenotypic oxacillin resistance. The highest resistance rates of the S. pseudintermedius carrying the mecA gene were observed for lincosamides (86.0%), cephalosporins (78.3%), and sulfonamides (76.9%), whereas resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate was the lowest (6.3%). In addition, two isolates were resistant to all the antibiotic families evaluated. These findings underscored the increasing prevalence of MRSP and MDR S. pseudintermedius, highlighting the need for improved antibiotic protocols in veterinary medicine to mitigate resistance and ensure effective treatment strategies for canine pyoderma.
Keywords: Dog, Methicillin, Resistance, Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Ducks Suspected of Colibacillosis in Vietnam
|
|
Huong CTT, Oanh TL, Tra VTT, and Thai TH.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1107-1112, 2025; pii:S232245682500113-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj113
ABSTRACT: The extensive application of antibiotics within the livestock sector has led to a rise in bacterial resistance, especially against Escherichia coli (E. coli), complicating the treatment of bacterial infections in poultry. The present study aimed to determine the antibiotic resistance of the E. coli isolated from Cherry Valley ducks exhibiting signs of colibacillosis in northern Vietnam. From March to May 2025, 21 Cherry Valley duck flocks raised on 15 duck farms in Ha Nam Province, Vietnam, experienced disease outbreaks characterized by clinical signs such as anorexia, reduced mobility, abnormal movement, and respiratory distress, including sneezing, gasping, and nasal discharge, which were suspected of being caused by E. coli infection. A total of 63 ducks suspected of colibacillosis were necropsied for sampling and pathological observation. Heart, liver, and lung samples were collected simultaneously from all ducks for E. coli isolation. The isolated E. coli strains were examined for antibiotic susceptibility by the agar diffusion method. The E. coli strains demonstrated the highest susceptibility to levofloxacin (82.9%), followed by norfloxacin (78.0%), gentamicin (73.2%), and colistin (70.7%). The highest resistance rates were observed for ampicillin (75.6%) and tetracycline (73.2%), whereas resistance to ciprofloxacin, streptomycin, and doxycycline ranged from 31.7% to 48.8%. Of the 41 E. coli strains, 82.9% were resistant to at least one antibiotic; these strains exhibited 17 distinct antibiotic resistance patterns. Additionally, 63.4% isolated strains were identified as multi-drug resistant (MDR). The current results emphasized the high resistance of E. coli strains isolated from ducks to multiple antibiotics.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance, Duck, Colibacillosis, Diffusion method
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Detection in Bali Cattle (Bos sondaicus) by RT-PCR in Lombok Island
|
|
Kholik K, Sukri A, Ayu IW, Nidom RV, and Indrasari S.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1113-1119, 2025; pii:S232245682500114-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj114
ABSTRACT: Aphthovirus is responsible for foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in cloven-hoofed animals, a highly infectious disease that has significant economic repercussions in various countries, including Indonesia. The present study aimed to use reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to detect FMD in suspected Bali cattle in West Lombok, Indonesia. The current study was an observational, descriptive investigation conducted from July to August 2025, collecting 15 swab samples from male Bali cattle with an average weight of 210 kilograms and an average age of 2 years old. The samples were collected via purposive sampling from cattle demonstrating clinical signs of FMD, specifically from oral vesicular fluid. The samples were sourced from two smallholder farms in West Lombok; farm one, with 12 samples, and farm two, with three samples. The FMD was identified with a prevalence rate of 20% (3 out of 15), and a 328 bp DNA fragment was detected during gel electrophoresis. The current result indicated that the virus pathogen was detected in 20% of samples, and RT-PCR can be used as a high-sensitivity diagnostic method for this disease.
Keywords: Bali cattle, Foot-and-Mouth disease, PCR, Reverse transcription
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
In Silico Study on Structure Prediction of Apical Membrane Antigen 1 in Eimeria tenella
|
|
Hung PHS, Dung HT, Hai DT, and Thao TN.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1120-1129, 2025; pii:S232245682500115-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj115
ABSTRACT: The micronemal apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1) has been demonstrated to be critical for host cell invasion by apicomplexan parasites. The present study predicted the structure of Eimeria tenella AMA1 (EtAMA1) using AlphaFold3. The structural model ranked first by AlphaFold3 was selected for analysis after removing unreliable regions. Comparative structural analyses were performed between the resulting EtAMA1 model and the well-characterized Plasmodium falciparum AMA1 (PfAMA1) using PyMOL. The results indicated that domains I and II of EtAMA1 may adopt the PAN motif (a conserved structural fold consisting of a five-stranded β-sheet and an α-helix) stabilized by five disulfide bonds, similar to PfAMA1. In addition, aromatic residues within the ligand binding pocket of PfAMA1 are conserved in EtAMA1, except for the critical Y251. The Proline-rich DII loop at the corner of the conserved hydrophobic pocket in EtAMA1 is shorter than that of PfAMA1, which possibly makes the hydrophobic pocket wider. Notably, domain III of EtAMA1 is predicted to form a three-stranded β-sheet with no disordered loop and α-helix, which is different from Plasmodium AMA1 structures. The present study provided preliminary information on structural divergences of EtAMA1, based on AlphaFold3 prediction, underscoring the need for experimental validation and investigation of possible implications for the parasite invasion mechanism.
Keywords: Apical membrane antigen 1, Domain, Hydrophobic pocket, Eimeria tenella
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Effects of Heat Stress on Growth Performance, Egg Production, Egg Quality, and Potential Controlling Strategies in Layer Chicken: A Review
|
|
Gobezie E, Timotiwos A, and Simeneh G.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1130-1137, 2025; pii:S232245682500116-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj116
ABSTRACT: Egg production is a key indicator of laying hens' reproductive efficiency. High ambient temperatures cause heat stress in laying hens, which negatively impacts their health, behavior, blood chemistry, feed intake, egg production, and egg quality. The present study aimed to focus on the effects of heat stress on growth performance, egg production, egg quality, and potential controlling strategies for heat stress in layer chickens. Heat stress reduces body weight, feed efficiency, egg yield, and egg quality. Reduced feed intake is the main reason contributing to its negative impacts on production. The reduced feed intake and decreased nutrient digestibility have adverse effects on egg quality and production performance. Heat stress reduces egg production and impairs the behavior, welfare, and immunity of layer chickens, resulting in significant financial losses. Higher ambient temperatures (above 25°C) can lead to lower egg quality (soft shells or shell-less eggs), weakened skeletal integrity in hens, and fewer eggs. Poor hatchability results from reduced feed intake due to high temperatures, which adversely affects semen fertility and quality. Eggs produced under extreme heat stress had lower Haugh units, egg yolk color, and eggshell thickness and strength. Overcrowding, also known as high stocking density, adversely affects animal health by degrading their habitat and increasing competition for resources such as feed, which can ultimately lead to feather pecking and cannibalism. Due to a quicker metabolic rate, chickens produce more body heat and are more susceptible to heat stress. High stocking density and high ambient temperature increase the risk of heat stress. Reducing stocking density to prevent heat stress may limit the number of hens that can be raised in a given space. Heat stress significantly reduces egg production, egg quality, and egg weight in laying hens under hot conditions. The current findings highlighted the need for improved environmental management and methods to mitigate the harmful effects of heat stress in laying hens.
Keywords: Egg production, Egg quality, Egg weight, Heat stress, Laying chicken
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus ID: ] [Export from ePrint]
The Role of Chronic Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Gizzard Erosion in Pipped Poultry Embryos: A Review
|
|
Dutta D and Roy R.
World Vet. J. 15(4): 1139-1148, 2025; pii:S232245682500117-15
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/scil.2025.wvj117
ABSTRACT: Gizzard erosion remains a recurrent issue in commercial broiler and layer embryos, leading to poor hatchability and early chick mortality, yet the mechanisms linking infectious, nutritional, and toxic factors remain poorly understood. The present review synthesized published pathological, immunological, and toxicological evidence to explore how these diverse factors may contribute to the development of gizzard erosion. A structured evaluation of experimental and field studies was performed to integrate the available findings. On the basis of this synthesis, the review proposed a two-hit inflammatory hypothesis to explain disease onset. In this hypothesis, the first hit involved chronic, low-grade inflammatory priming during embryogenesis driven by maternal mycotoxins, breeder immune stress, or vertically transmitted infections, whereas the second hit consisted of acute oxidative and metabolic stress during pipping and hatching that may precipitate visible epithelial injury in predisposed gizzards. The hypothesis is presented as a conceptual framework derived from existing literature rather than as an established mechanism, emphasizing that current evidence supports a plausible sequential inflammatory process. Understanding gizzard erosion through this exploratory framework underscores the need for preventive control of prenatal inflammatory triggers and identifies clear directions for future experimental validation at the embryonic level.
Keywords: Broiler, Chronic inflammation, Gizzard erosion, Immunology, Layer, Toxicology
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Scopus] [Export from ePrint]
Previous issue| Next issue | Archive
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).